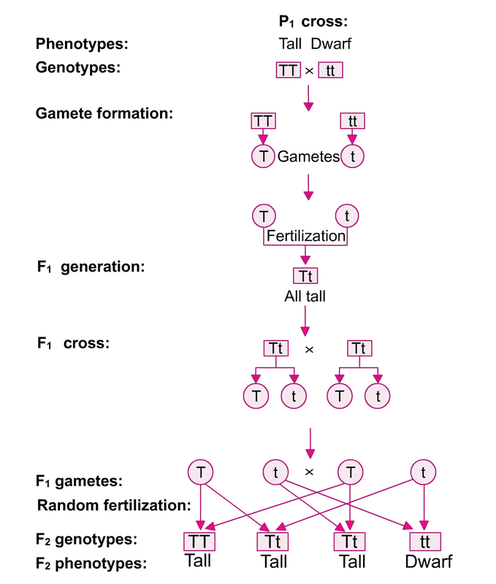
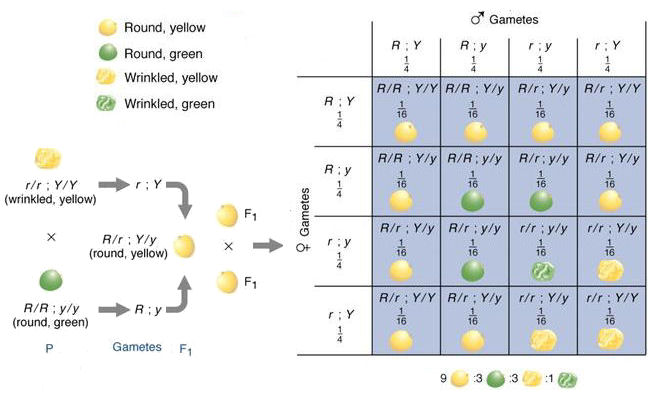
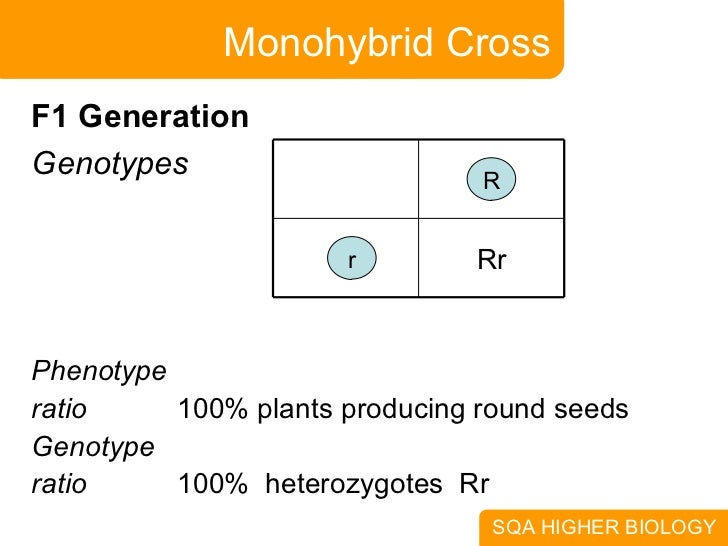
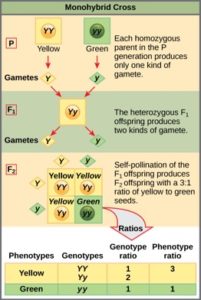
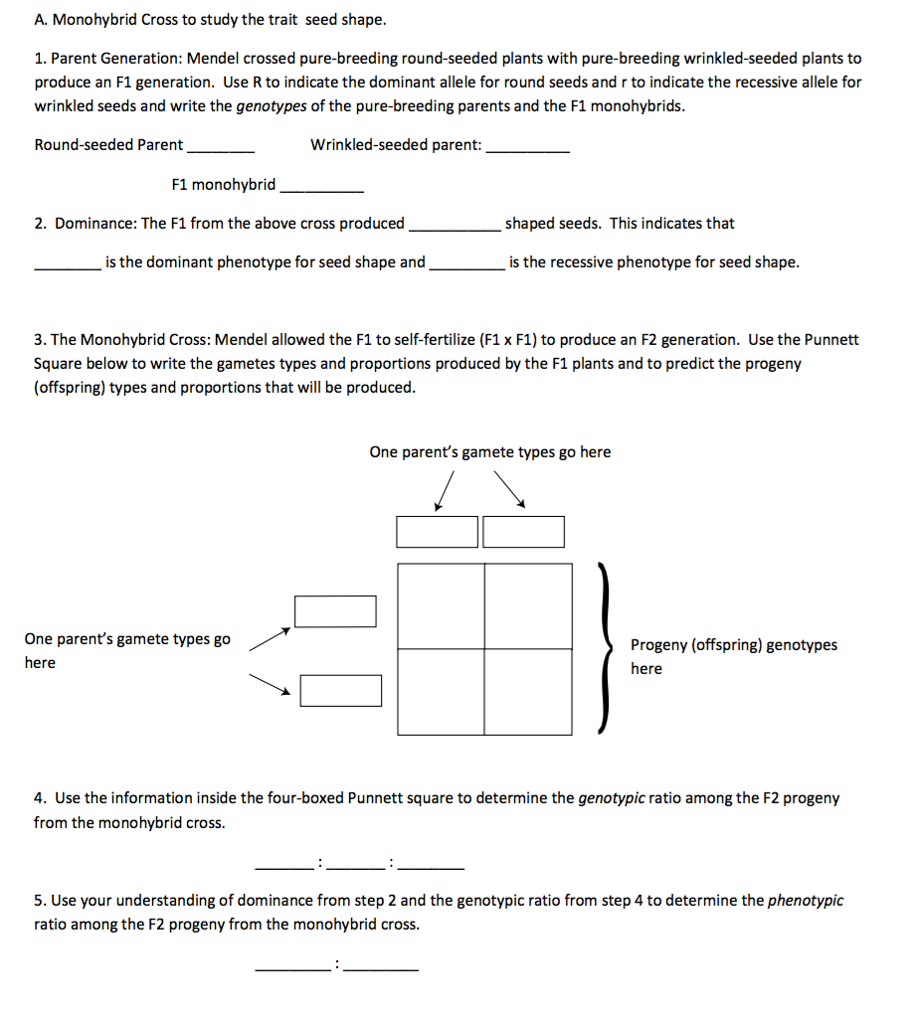
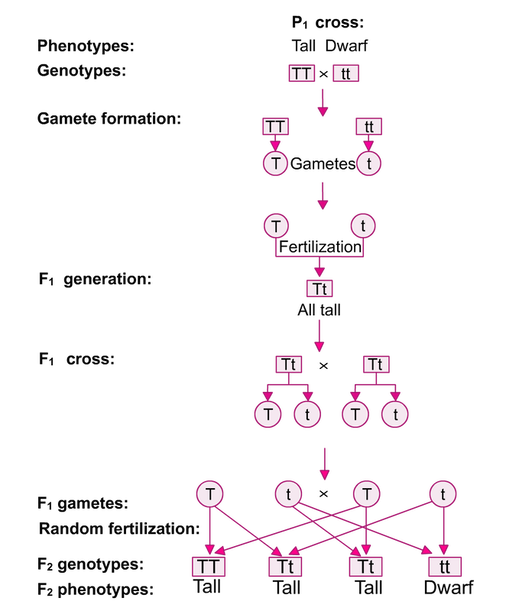
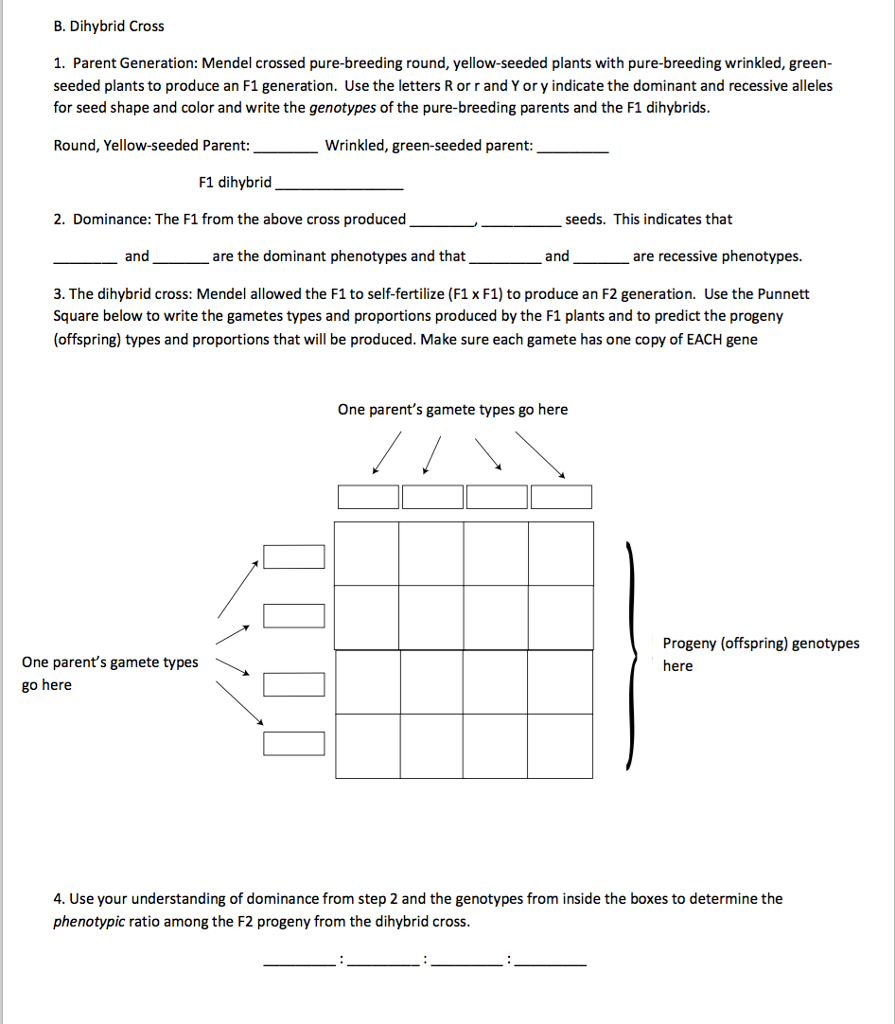
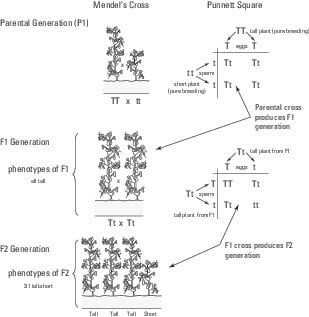
Monohybrid Cross F1 Genotype Ratio
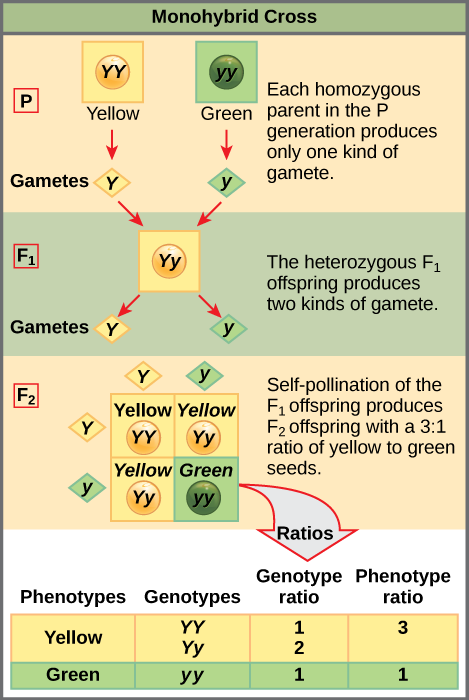
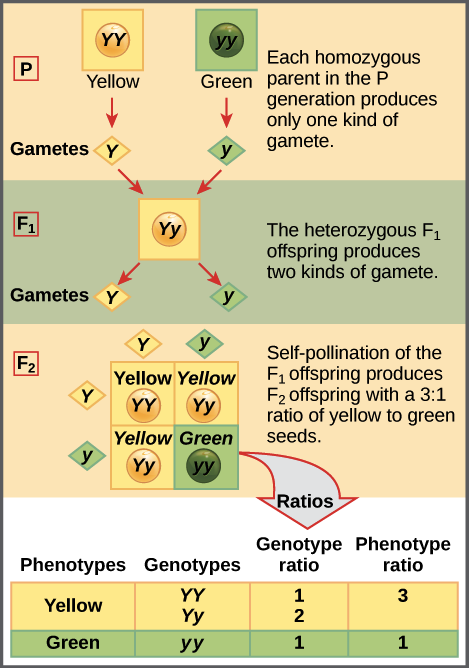
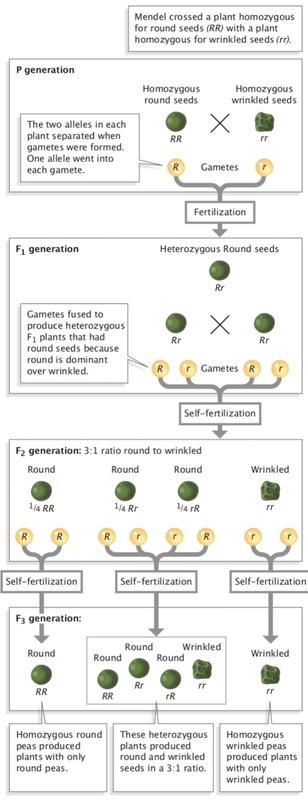
Should the f 1 generation be allowed to self pollinate the potential allele combinations will be different in the next generation f 2 generation.

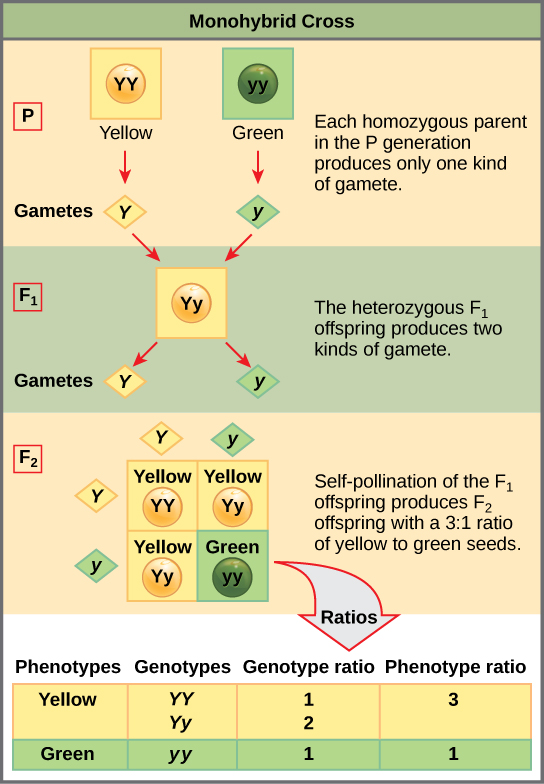
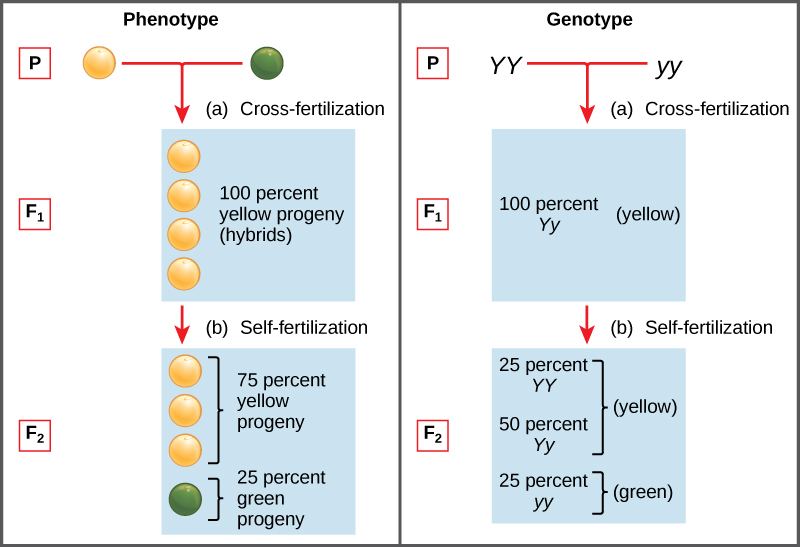
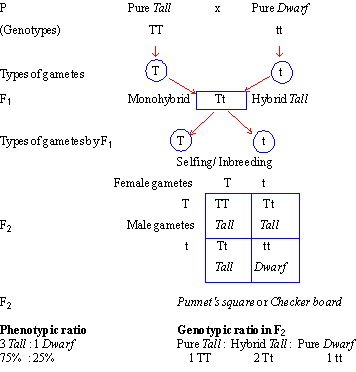
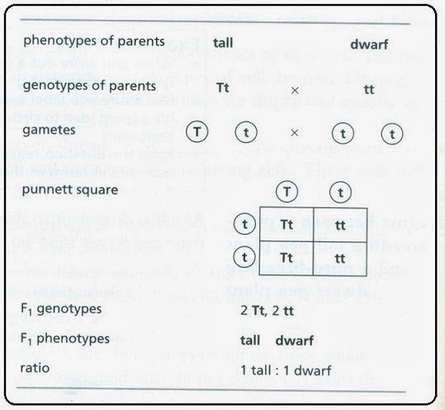
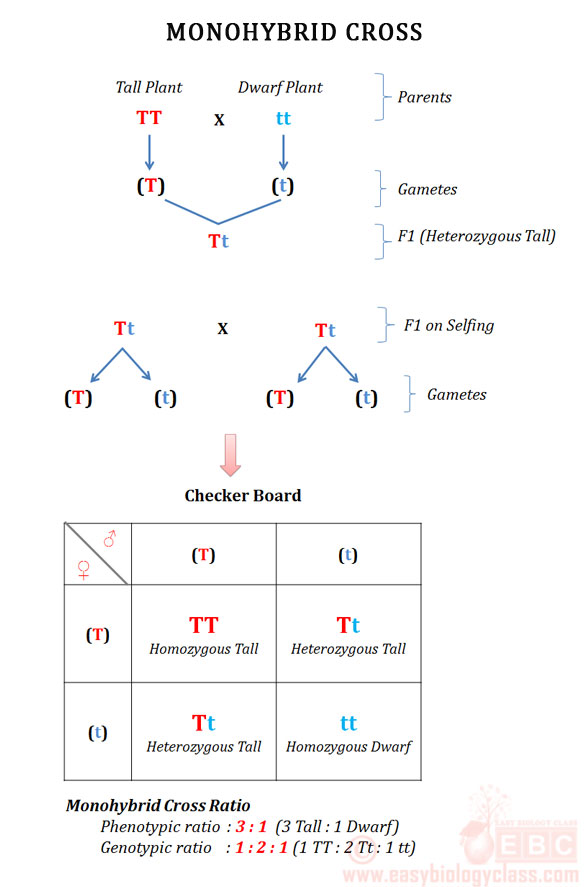
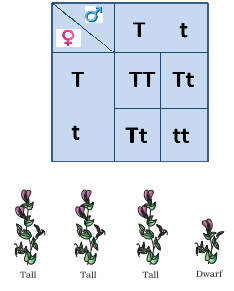
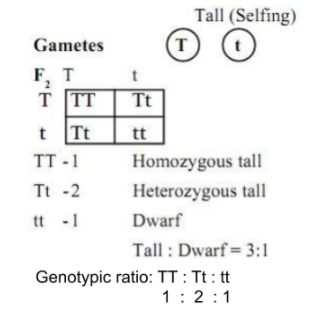
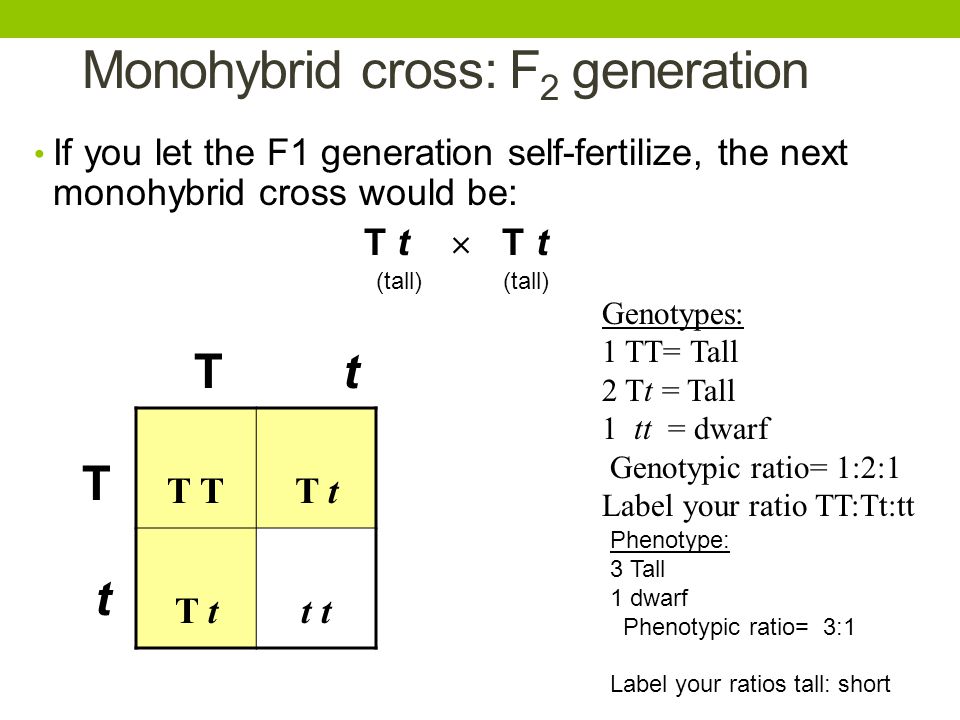
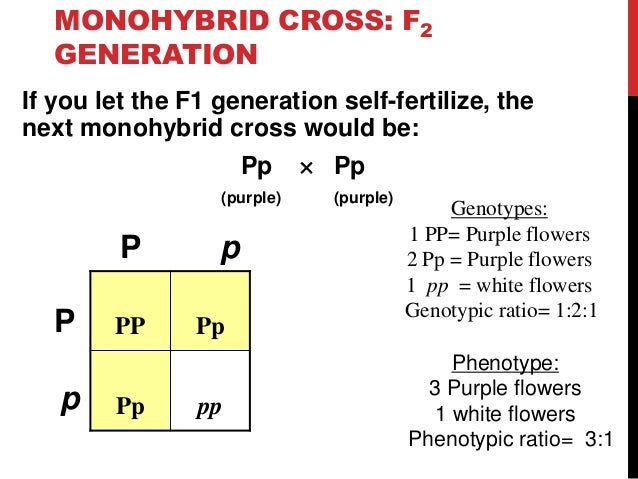
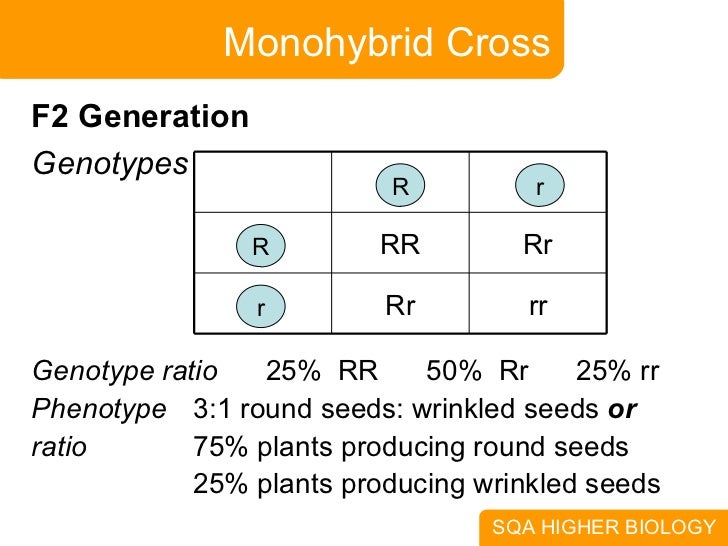
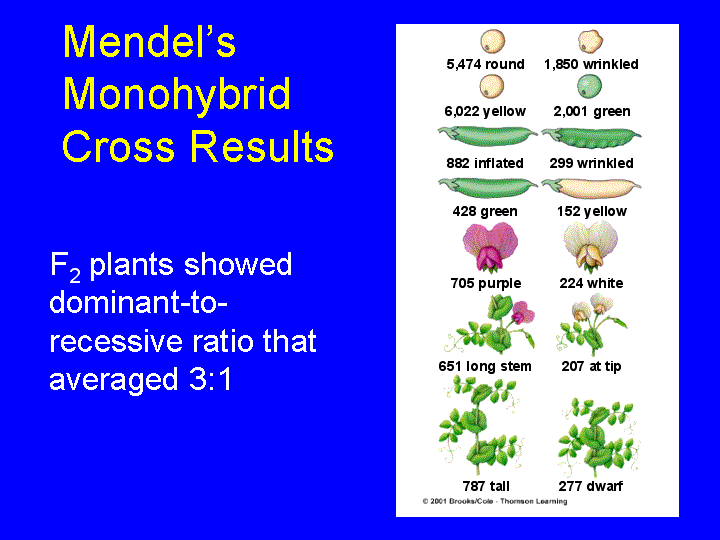
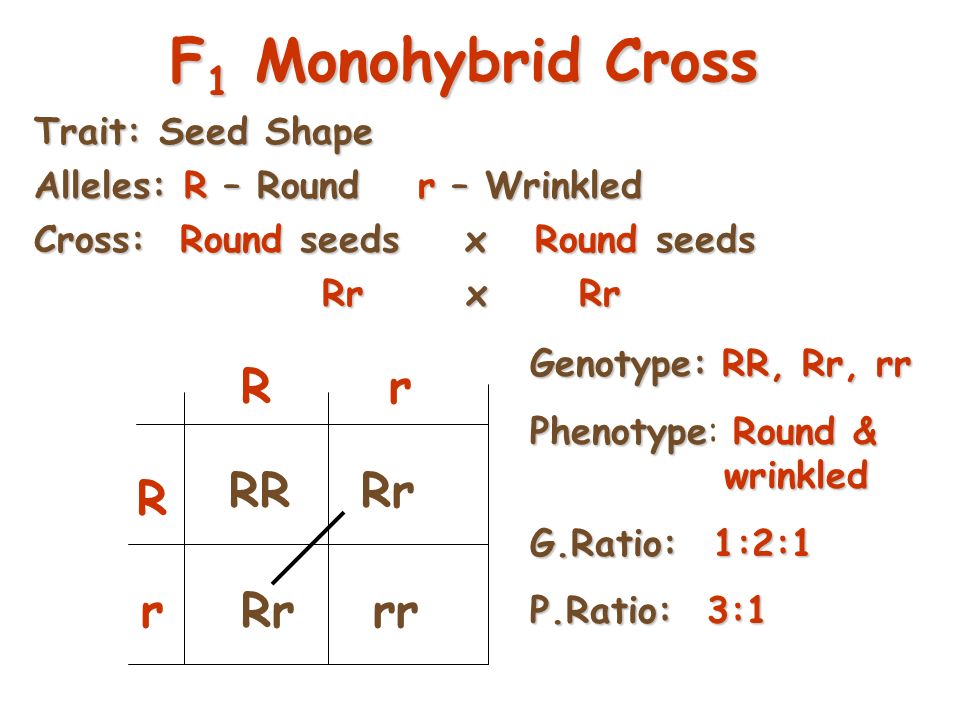
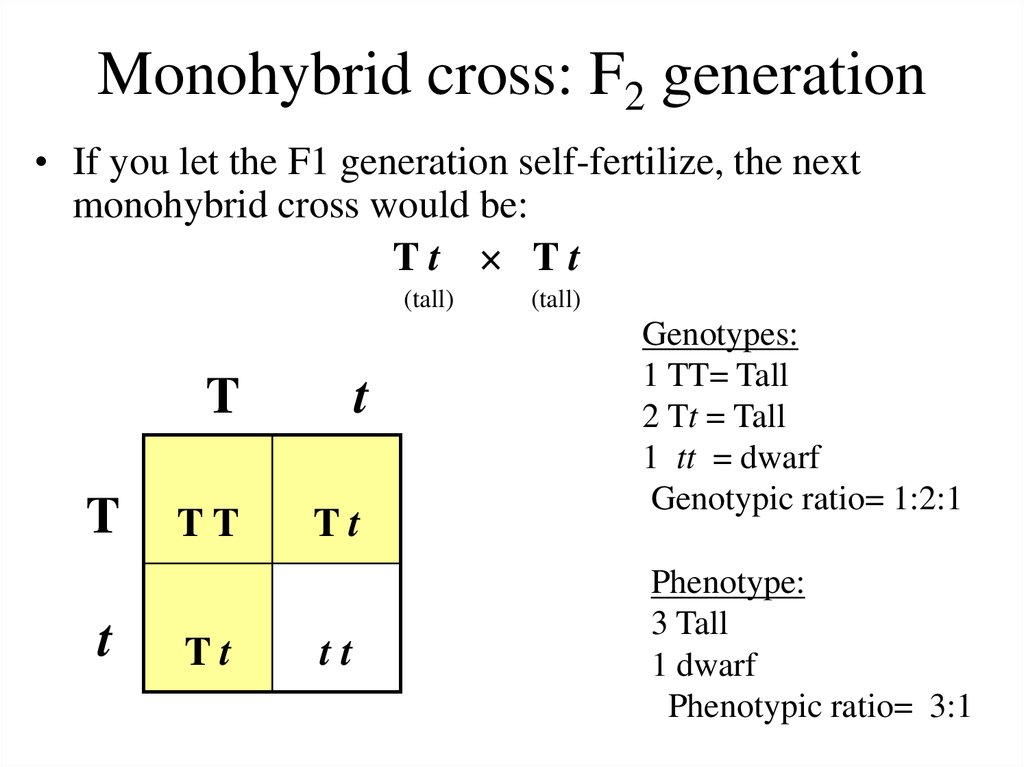
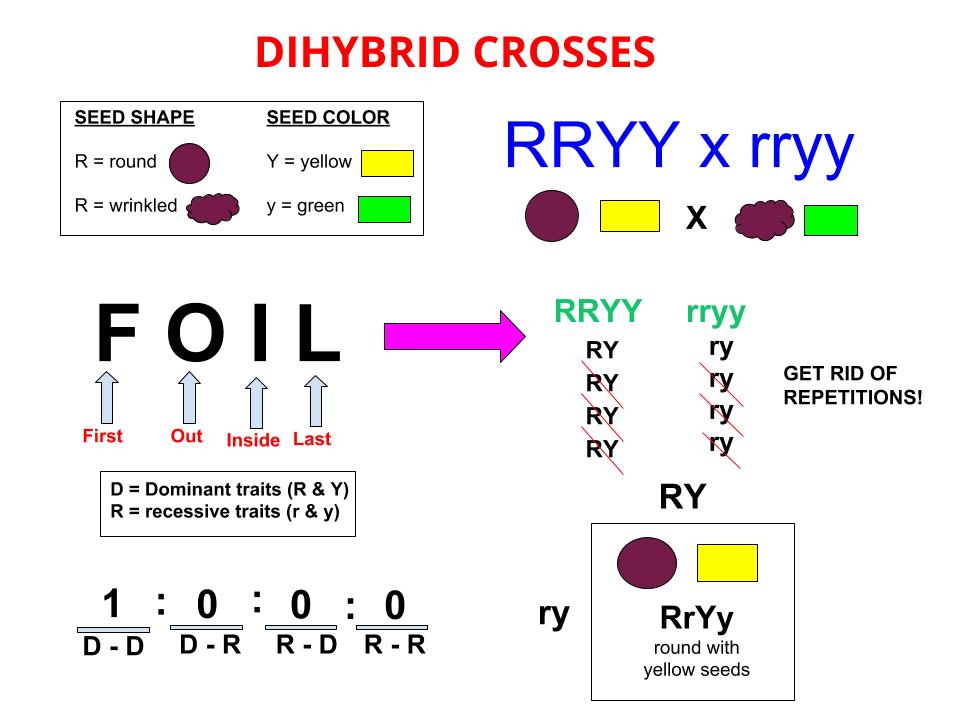
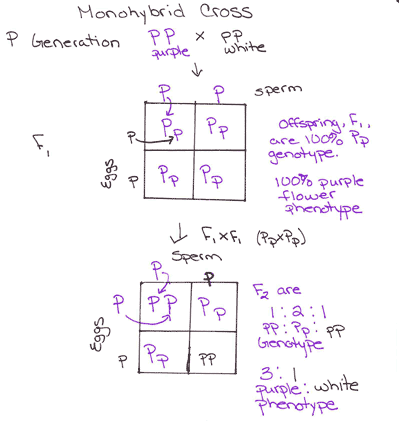
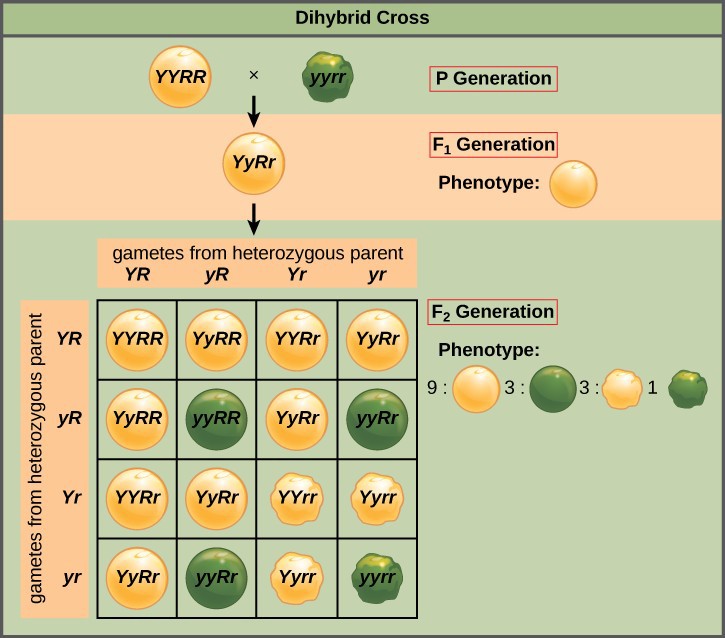
Monohybrid cross f1 genotype ratio. It can be easily shown through a punnett square. For a monohybrid cross suppose two true breeding parents are crossed and their offspring f1 are self crossed. The f 2 generation would have genotypes of gg gg and gg and a genotypic ratio of 121. The f1 dihybrid phenotypic ration is 1 to 3 to 3 to 1.
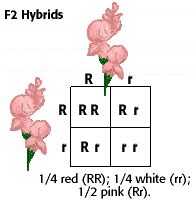
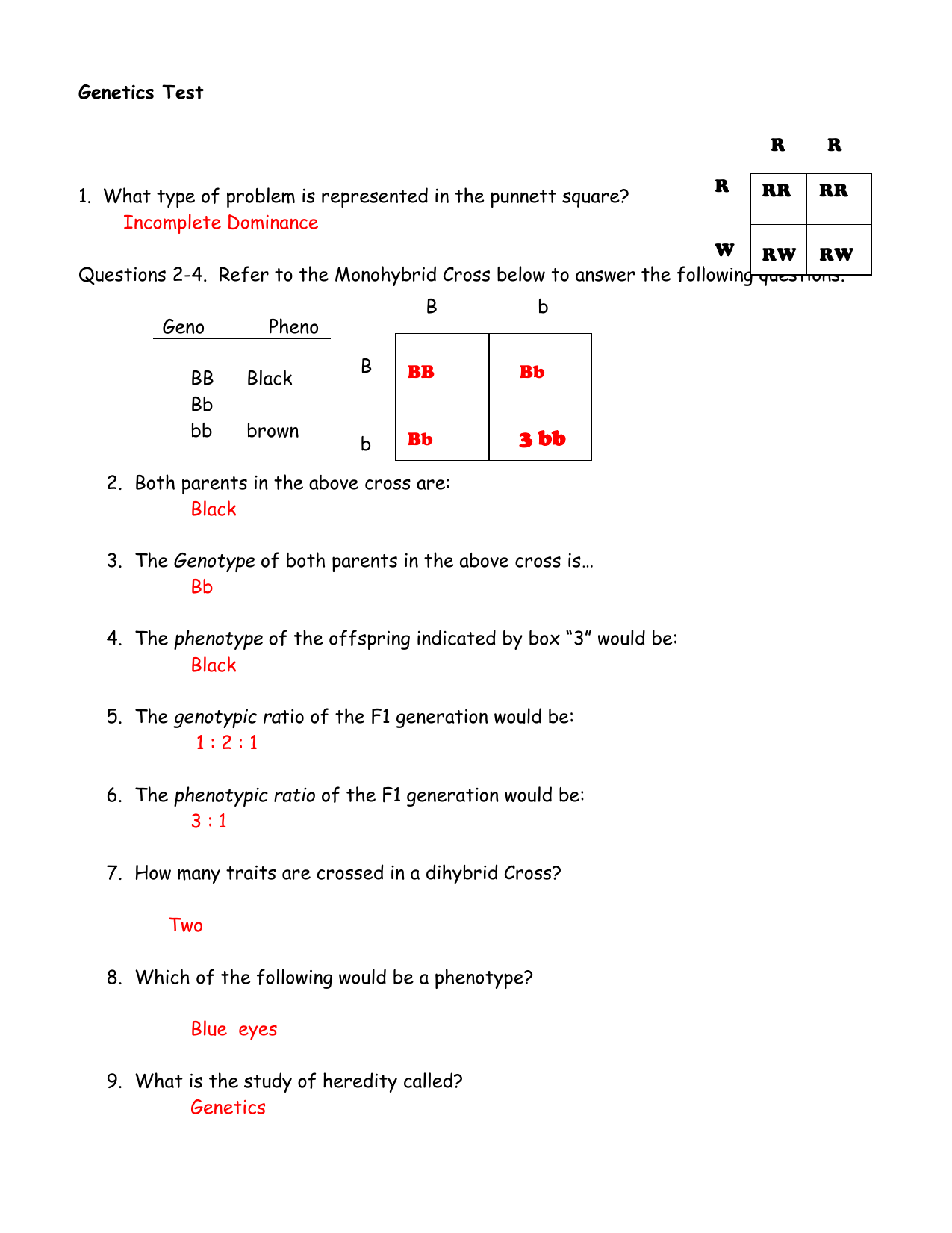
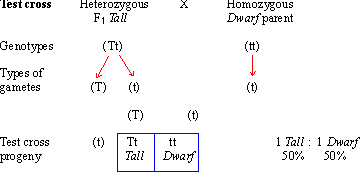
The probability of a cross producing a genotype in any box is 1 in 16. Monohybrid cross problem set problem 3. How to carry out a monohybrid cross. The ratios of the phenotype and the genotype that are estimated are only probabilities.
What genotypic and phenotypic ratios do you expect to observe in the f2 generation. Mendels experiment 1 tutorial to help answer the question. There is a 50 chance of the child being heterozygous a 25 chance of the child being homozygous dominant and a 25 chance of being homozygous recessive. If the same genotype is present in two boxes its probability of occurring doubles to 18 116 116.
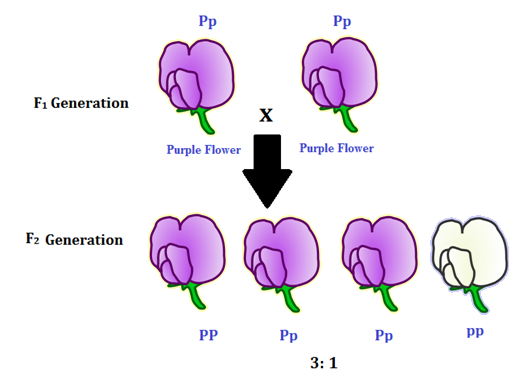
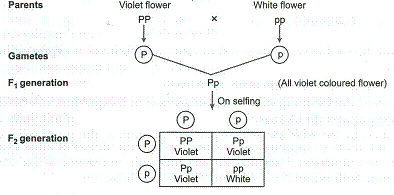
When a cross satisfies the conditions for a. Modern scientists now describe the cross of mendels f1 generation as a monohybrid cross. Monohybrid cross is used by geneticists to observe how homozygous offspring express heterozygous genotypes inherited from their parents. Why does the genotypic ratio often differ from the expected photypic ratio resulting from a.
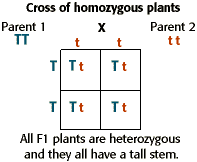
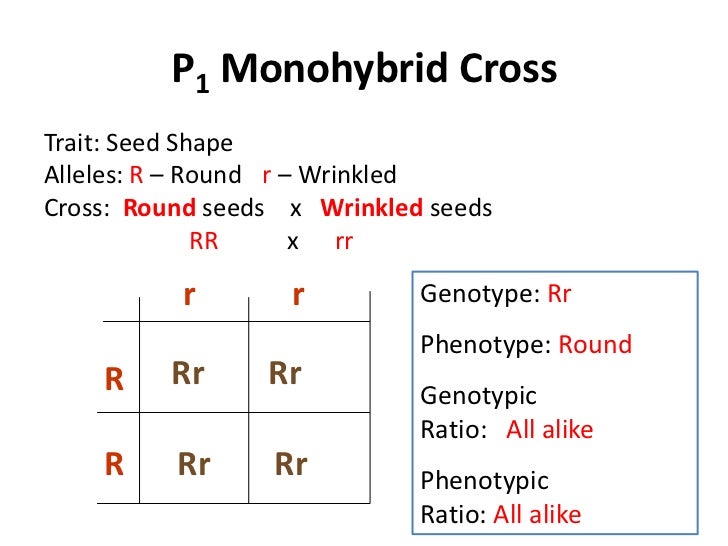
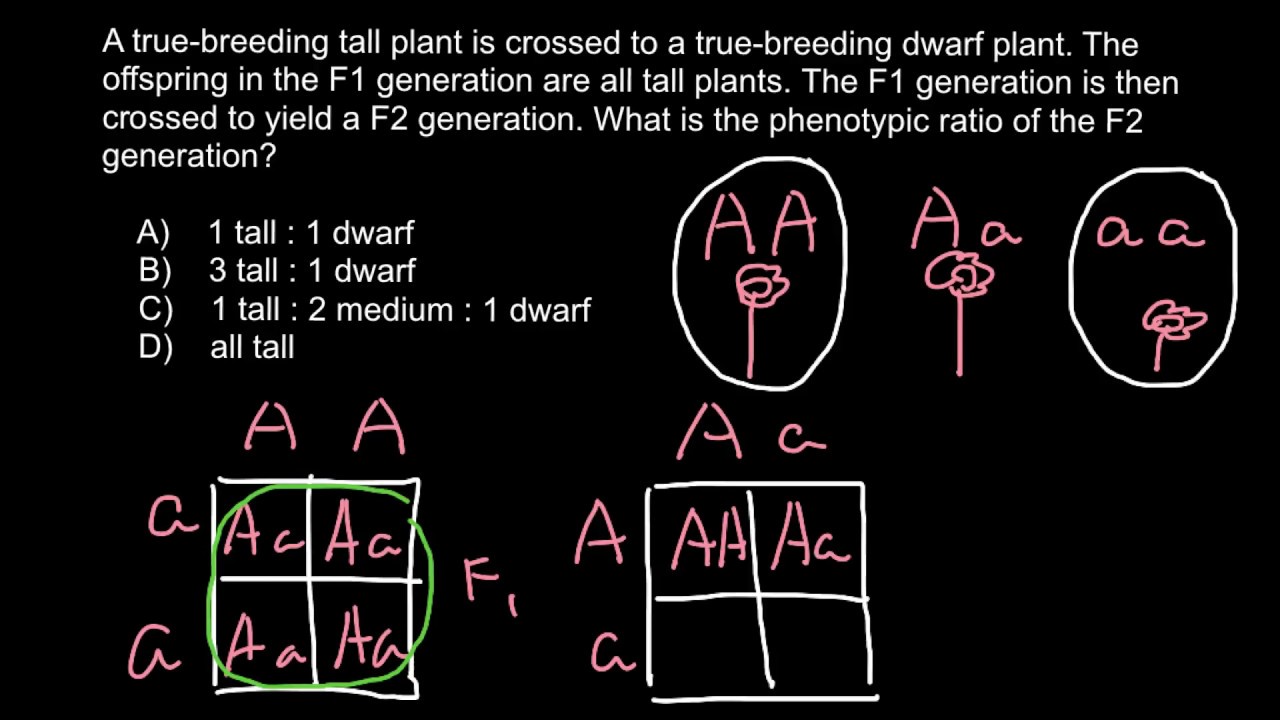
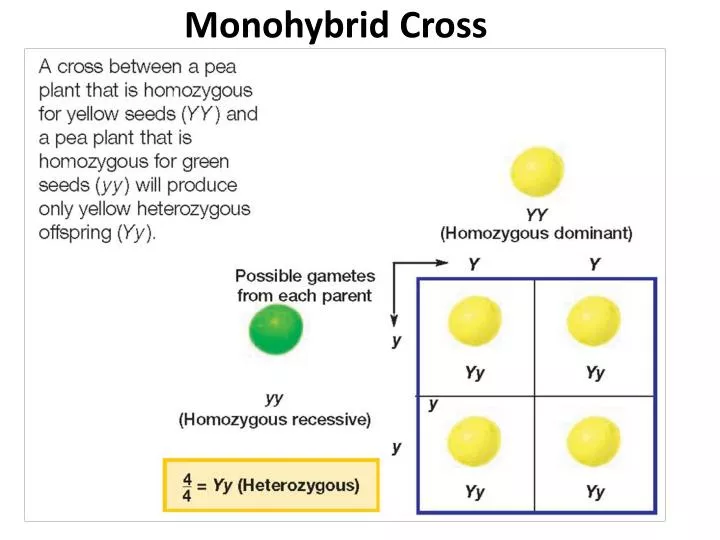
Listed below are steps that can be used to calculate a monohybrid cross. The characters being studied in a monohybrid cross are governed by two or multiple variations for a single locus. F1 generation f2 generation plants. All of the f1 generation plants will have the genotype of ss heterozygous and all will be spherical seeded.
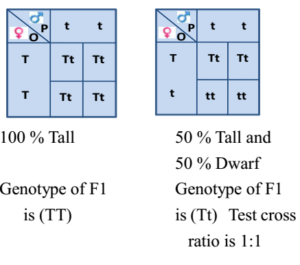
Monohybrid cross is responsible for the inheritance of one gene. Each person with the trait must have at least one parent who also has the trait. Mendel showed that the 31 ratio of yellow pod to green pod plants could only be obtainable if both parents carried a copy of both the yellow and green alleles and that the yellow allele had to be dominant over green. You can use the punnet square to show this monohybrid cross and conclude that the ratio is 211.
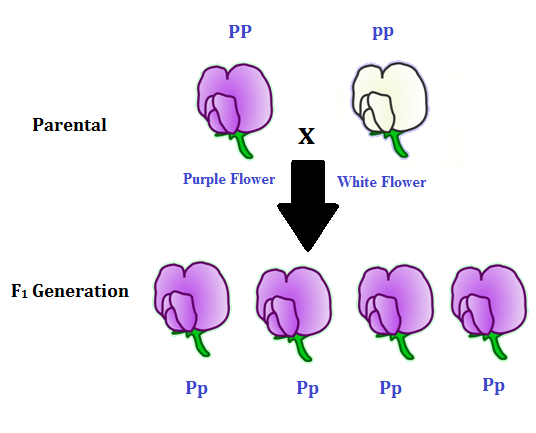
To carry out such a cross each parent is chosen to be homozygous or true breeding for a given trait locus.










/genetic-crosses-56e97ae13df78c5ba057ca68.jpg)















/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg)





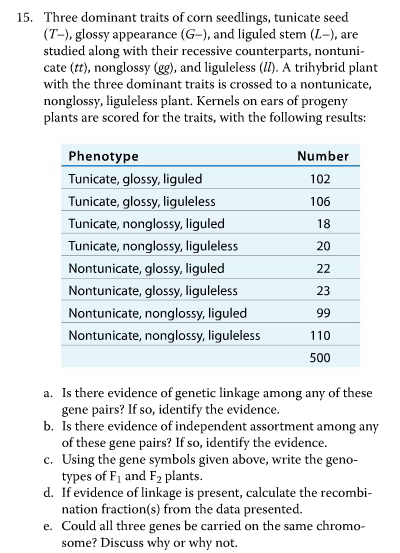
.PNG)