F1 Vs F2 Biology
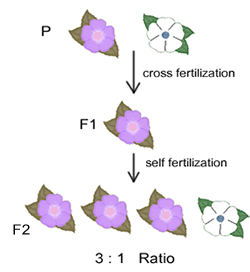
The first set of offspring from these parents is then known as the f1 generation.

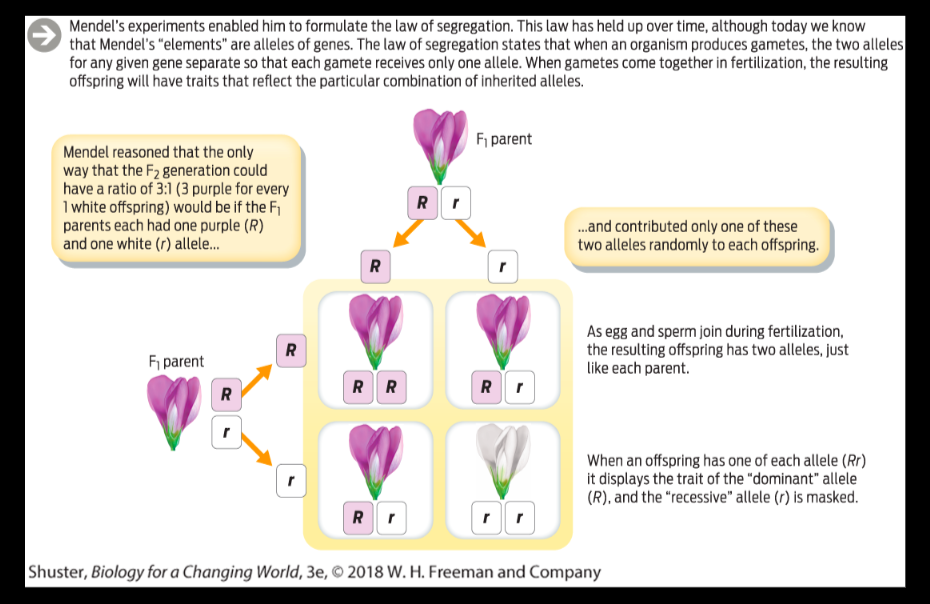
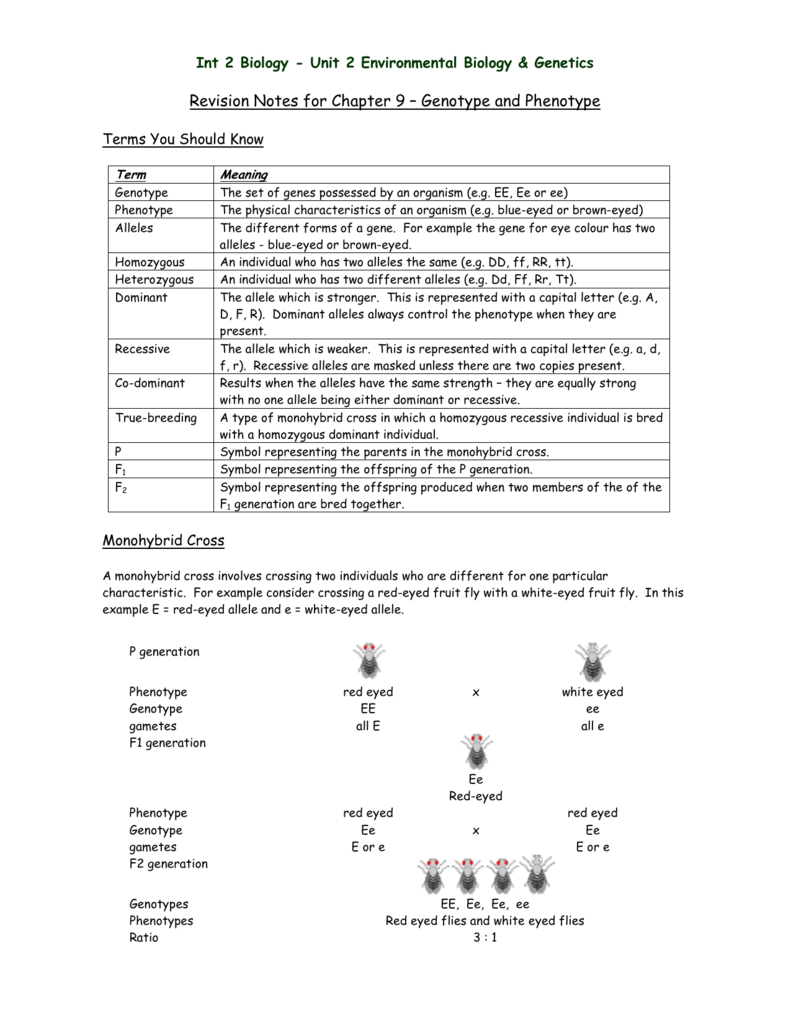
F1 vs f2 biology. Answered by lifeeasy authors. The characters being studied in a monohybrid cross are governed by two or multiple variations for a single locus. The first crossing is always called p for parentes. F1 generation tend to increase hybridization while f2 generation maintain stable traits for a generation f1 generation exhibit different phenotypes while f2 generation exhibit similar phenotypes the genotype of f1 generation parents can be homozygous dominant for both or the second be homozygous recessive while f2 generation parents have heterozygous traits for both.
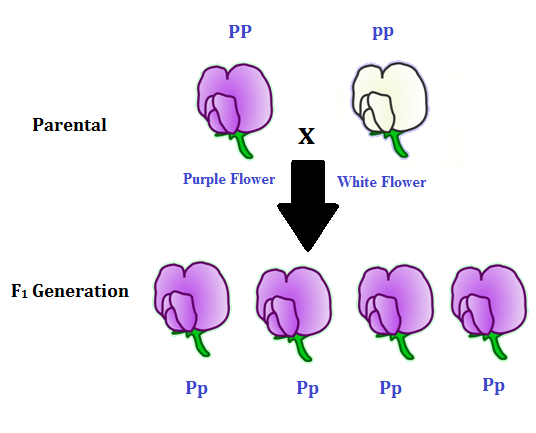
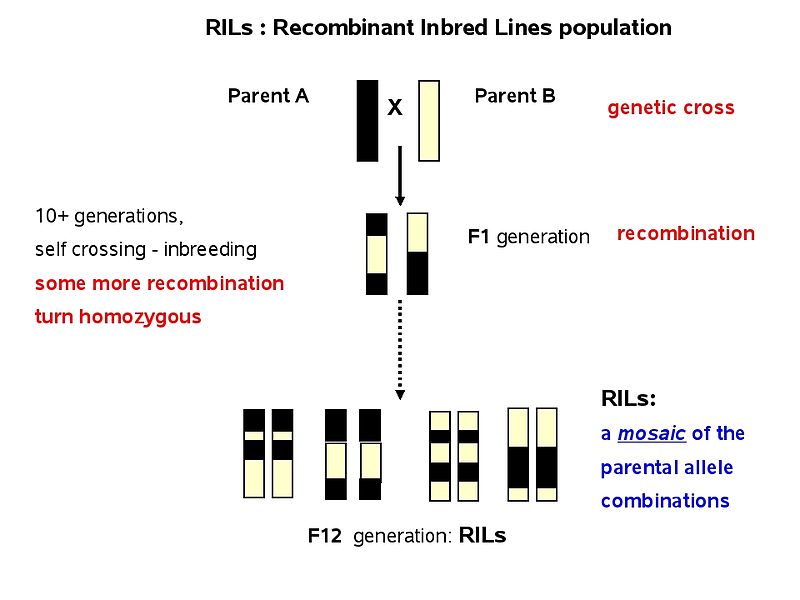
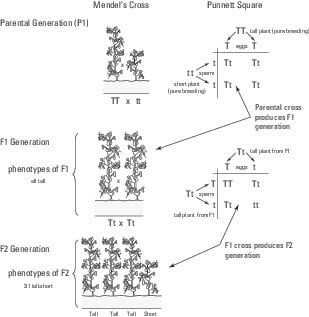
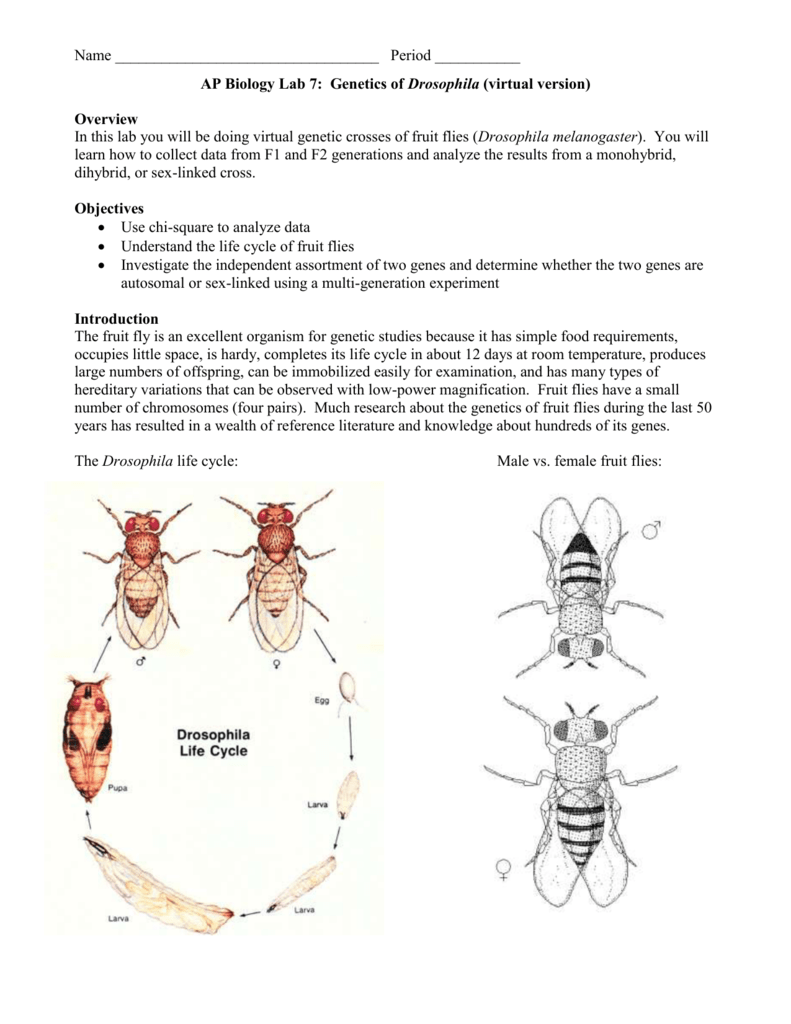
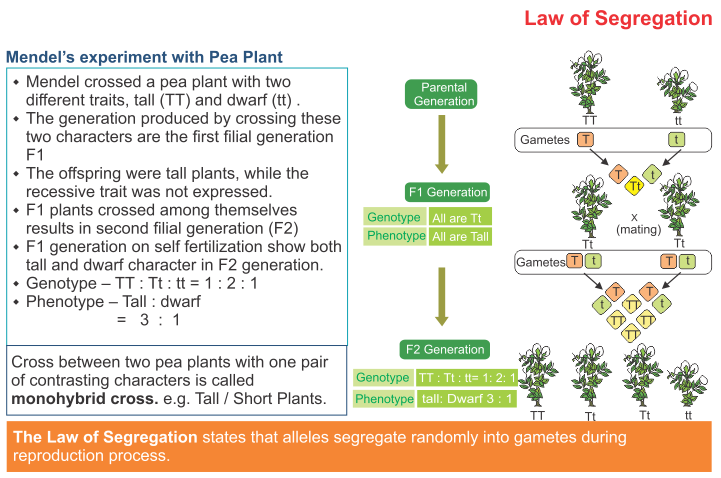
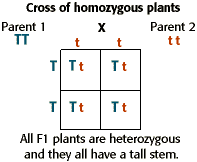
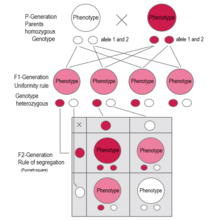
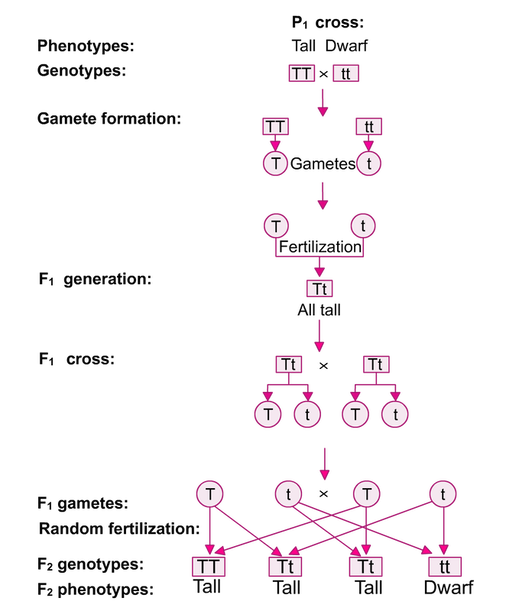
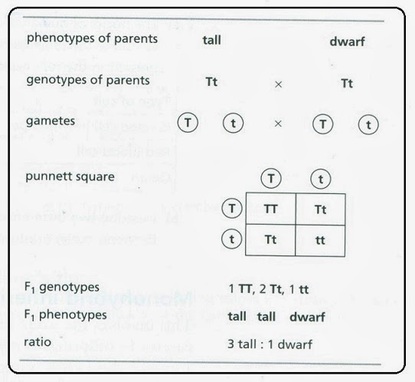
F1 generation is the first filial generation and the offspring of p generation. To carry out such a cross each parent is chosen to be homozygous or true breeding for a given trait locus. The f1 generation can reproduce to create the f2 generation and so forth. When displaying crossings between two parental organisms the resulting offspring are referred to as f1.
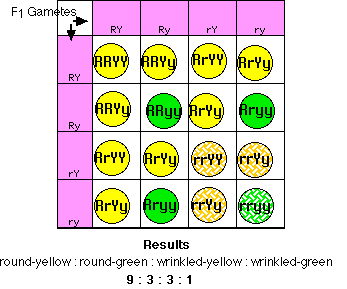
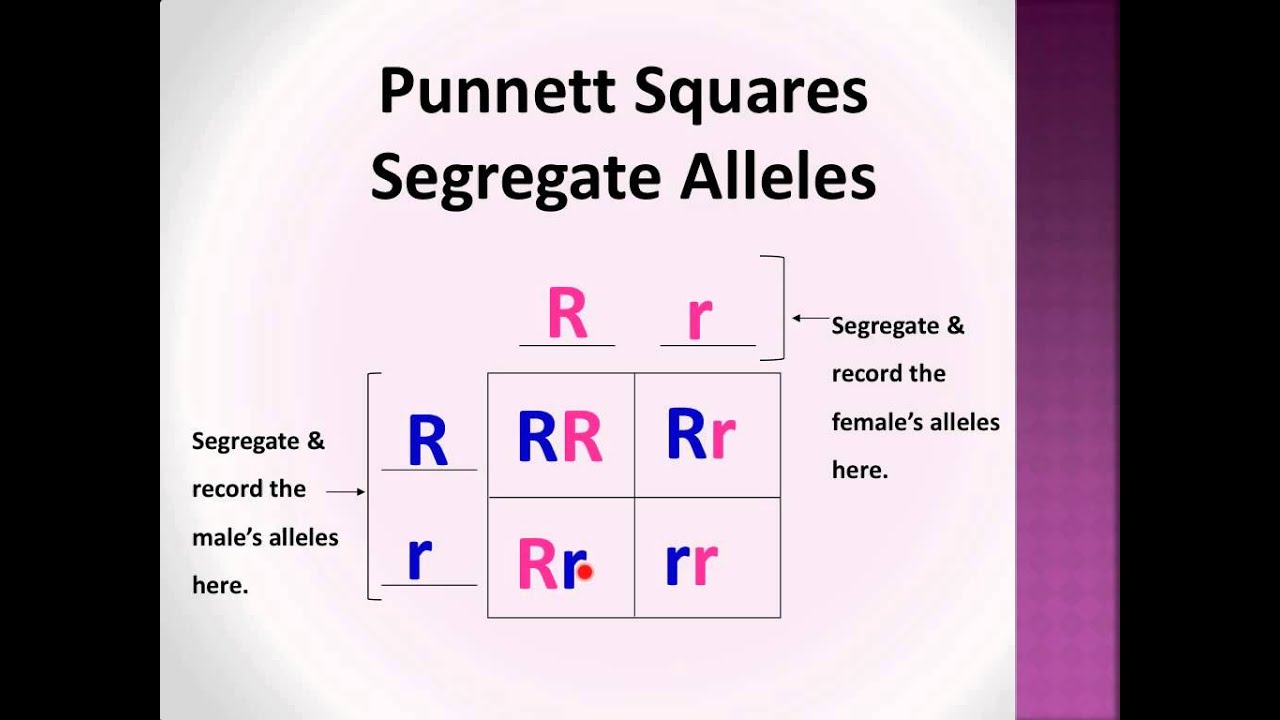
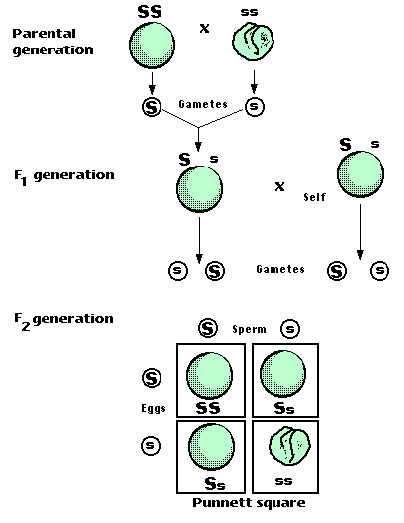
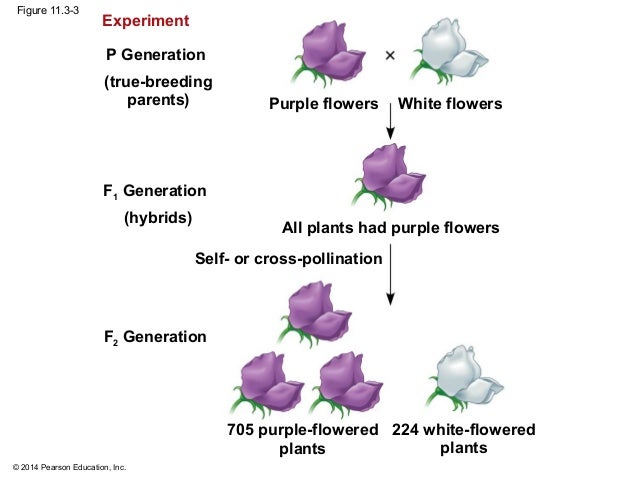
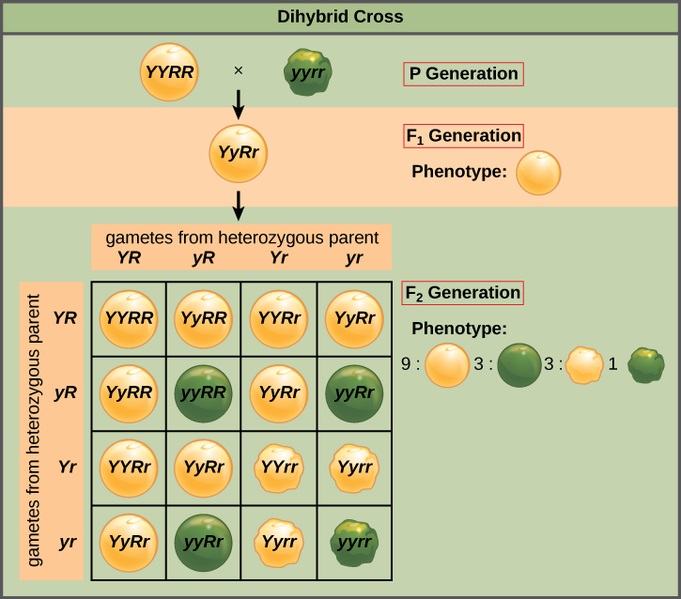
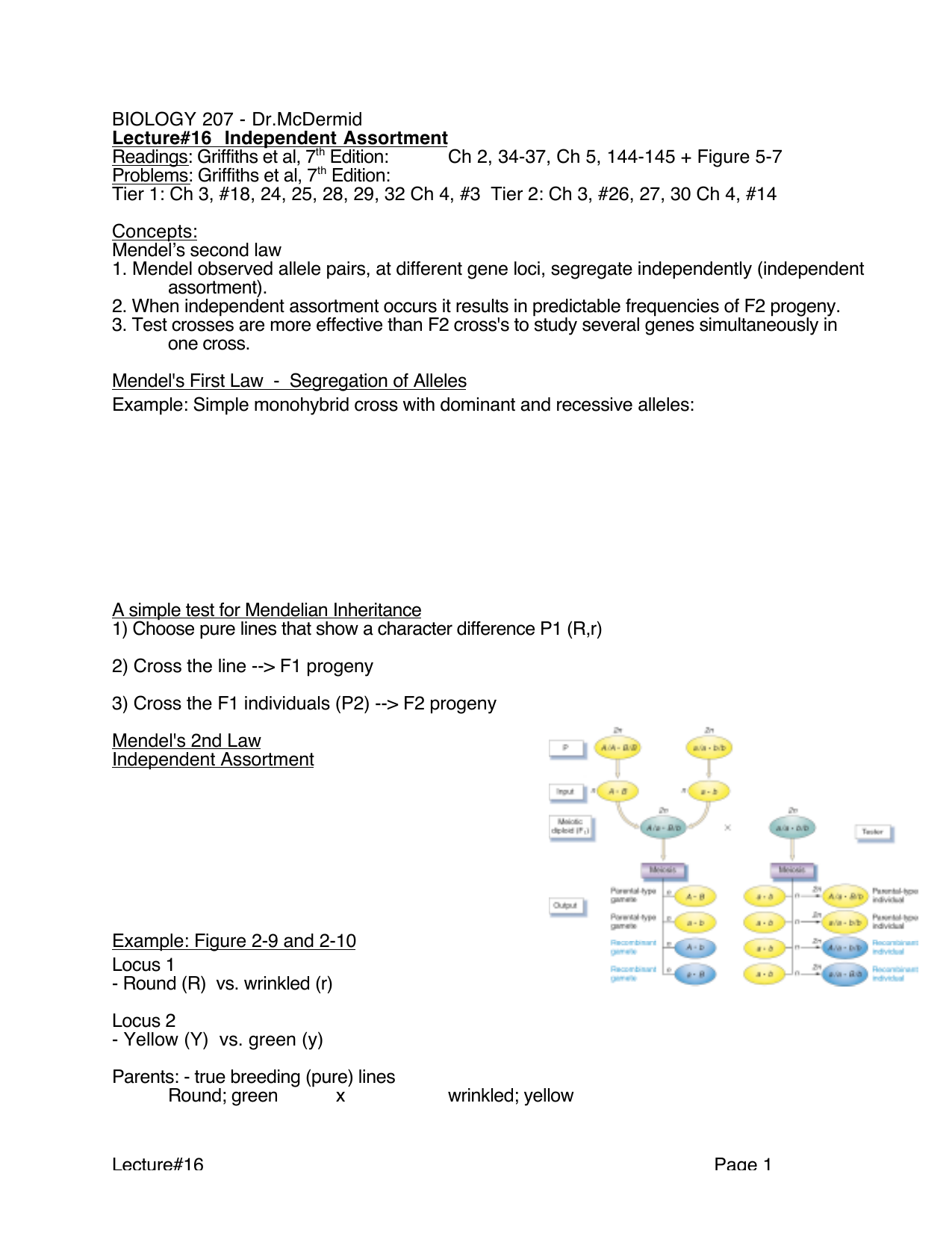
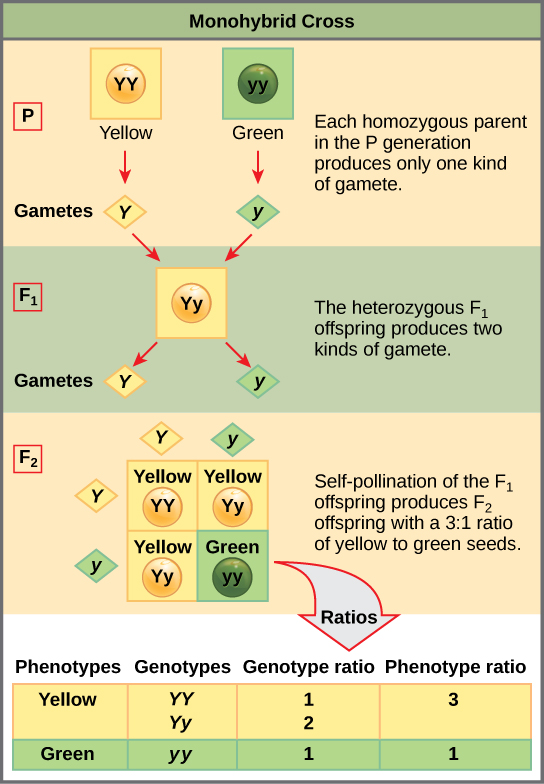
A monohybrid cross is a cross between two organisms with different variations at one genetic chromosome of interest. When a cross satisfies the conditions for a. F1 and f2 are two offspring generations and each of the generations of offspring provided new evidence in respect to inheritance and natural variation that occurs within different organisms. This screencast explains punnett squares p f1 f2 generations.
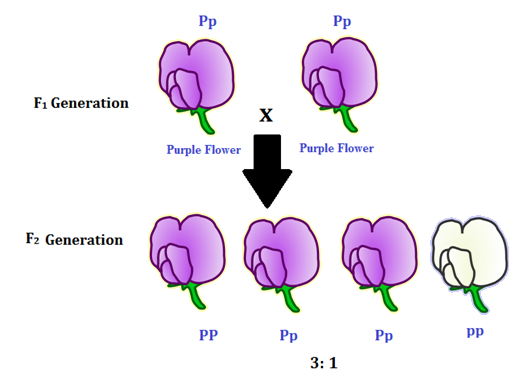
F2 generation is the second filial generation obtained by crossing of f1 individualsie. Summary f1 vs f2 generation f1 generation is also known as the first filial generation of offspring is resulted in the. Scientists use this designation to track groups of offspring as they observe the genetics of various generations. If those offspring are crossed between themselves the resulting generation is called f2.
F1 vs f2 generation f1 generation is the generation of offspring resulted from the parental p generation when they interbreed. Offspring of f1 generation. It is the first set or first generation in the study of inheritance.

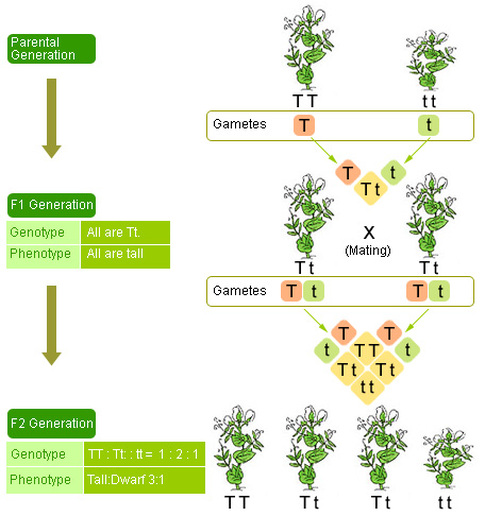






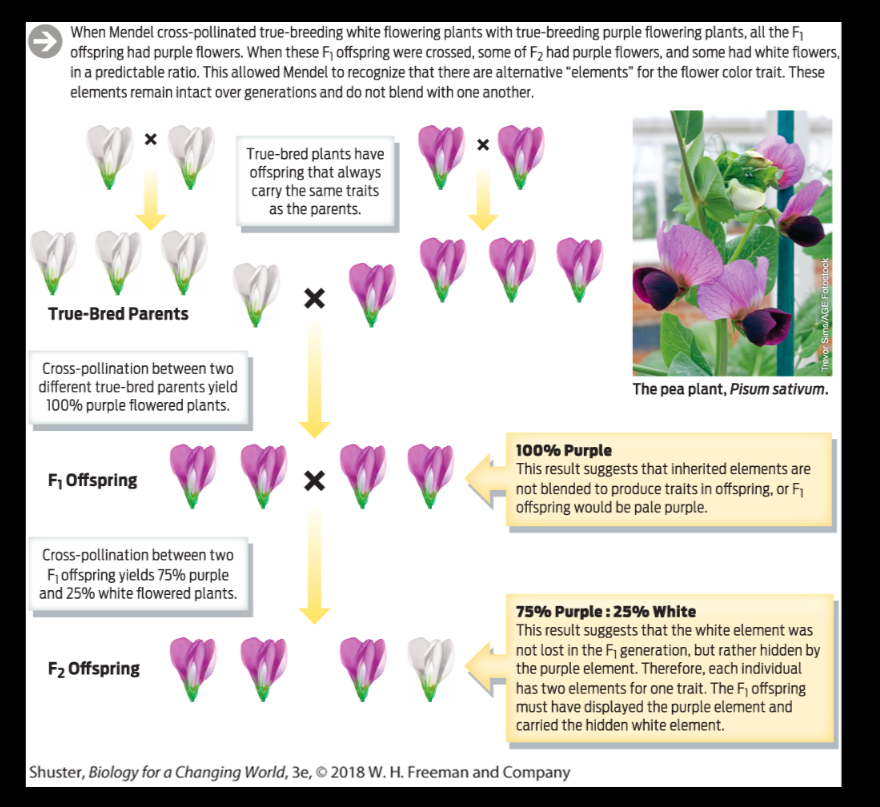
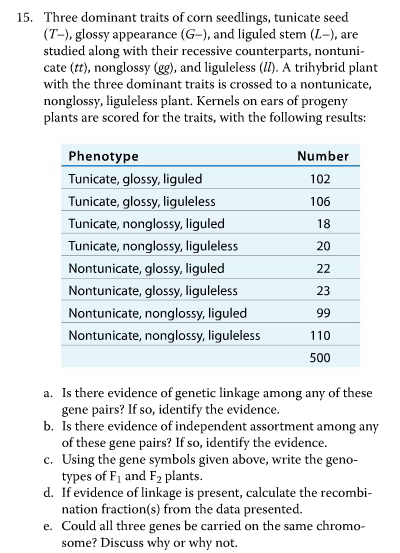
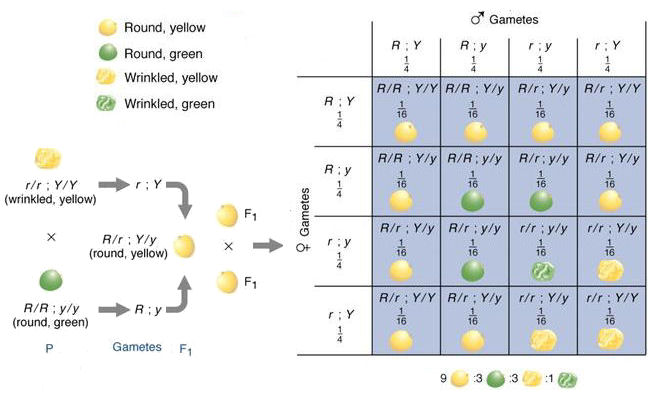


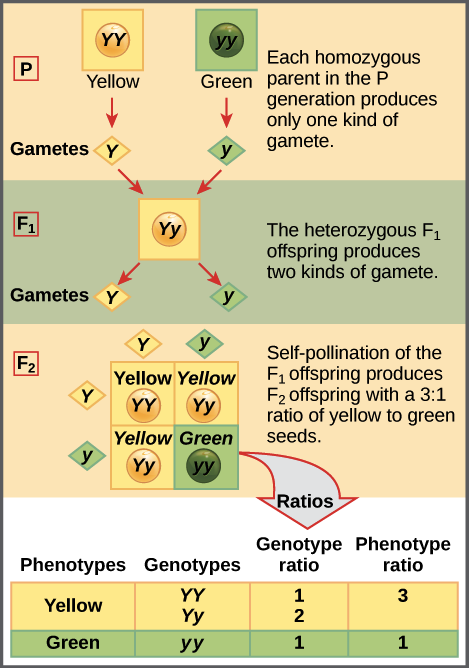
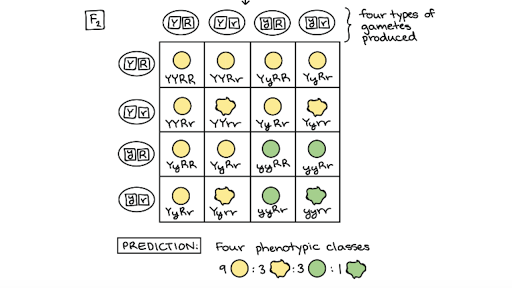




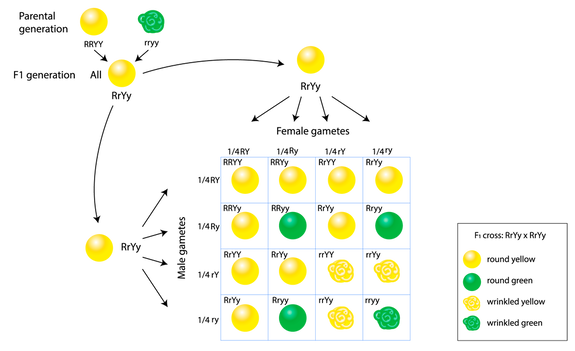
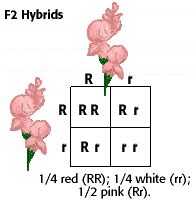





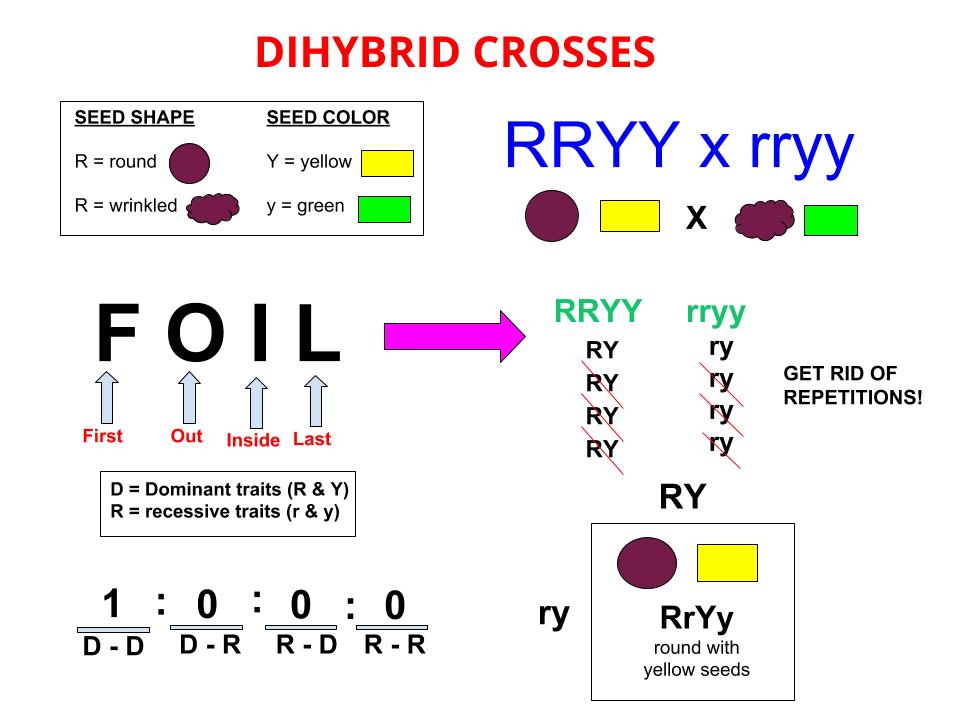
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dihybrid_cross_ratios-58ef9ddd5f9b582c4d02ceb2.jpg)
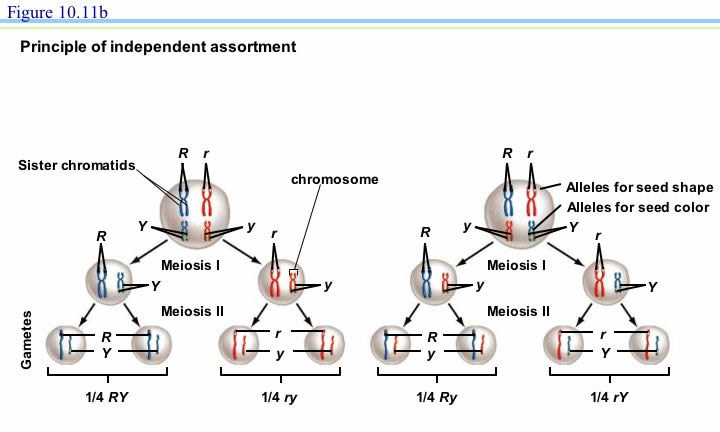



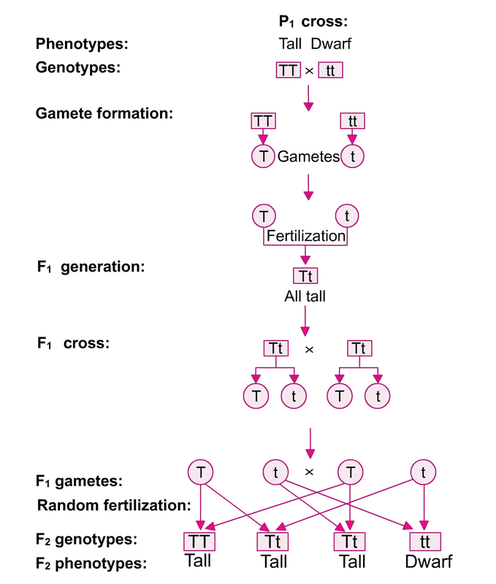



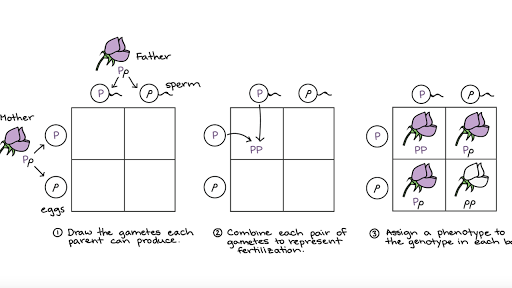














/dihybrid_cross_2-58ef84973df78cd3fc70a061.jpg)



/genetic-crosses-56e97ae13df78c5ba057ca68.jpg)