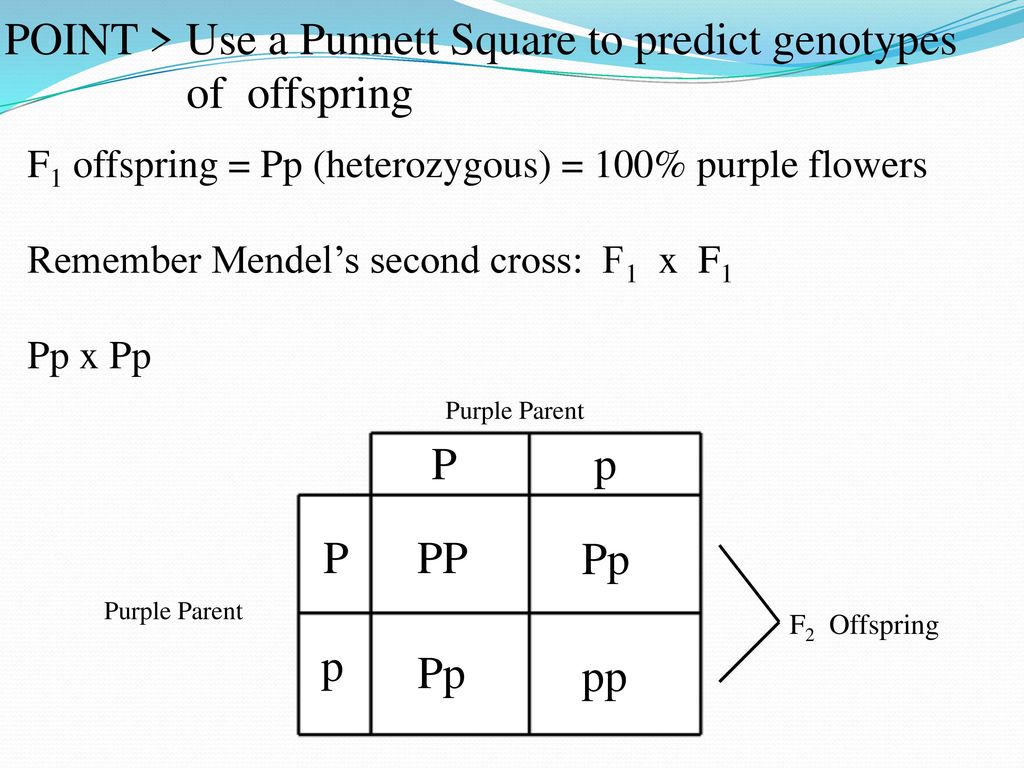
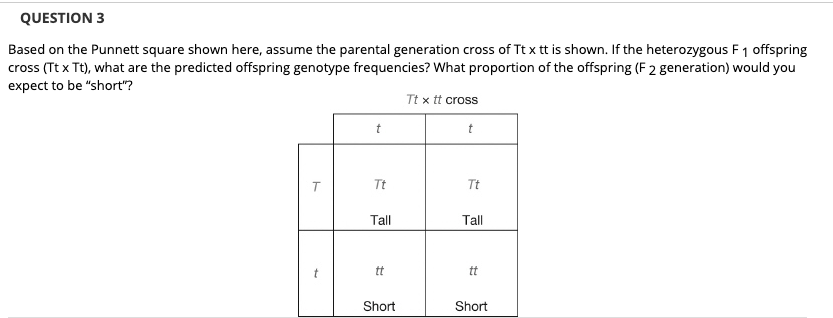
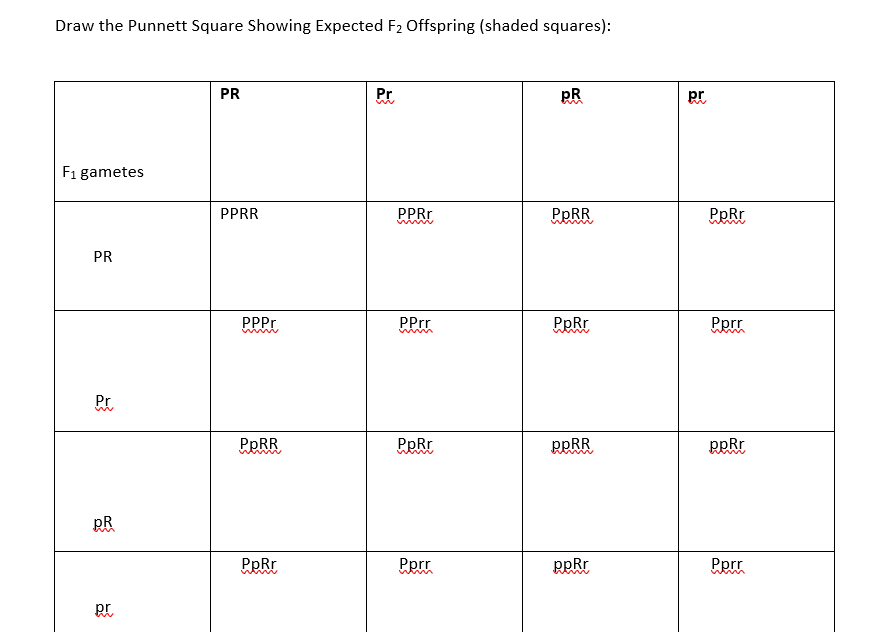
F1 Offspring Punnett Square
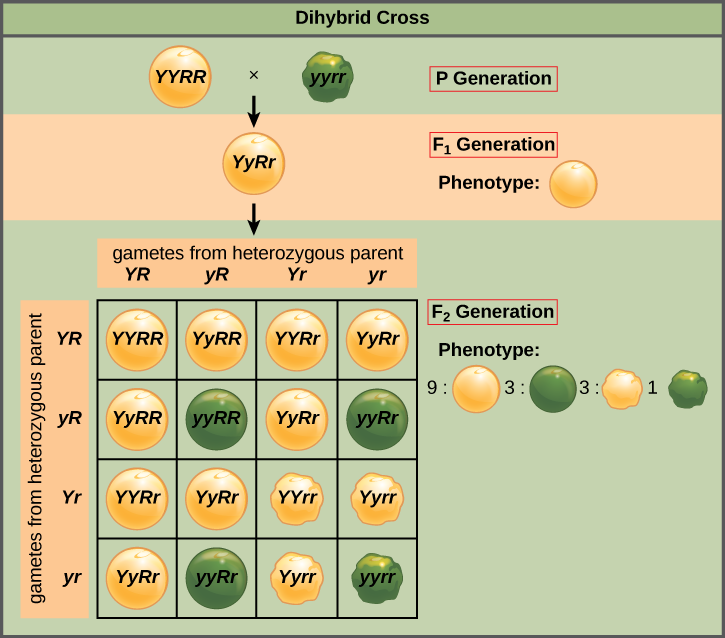
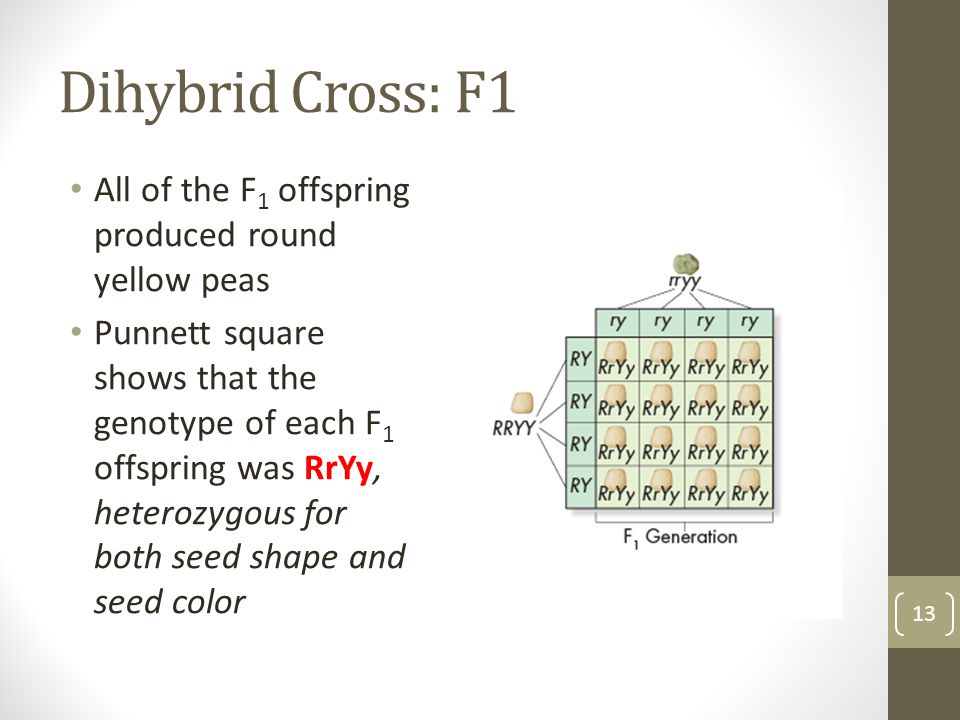
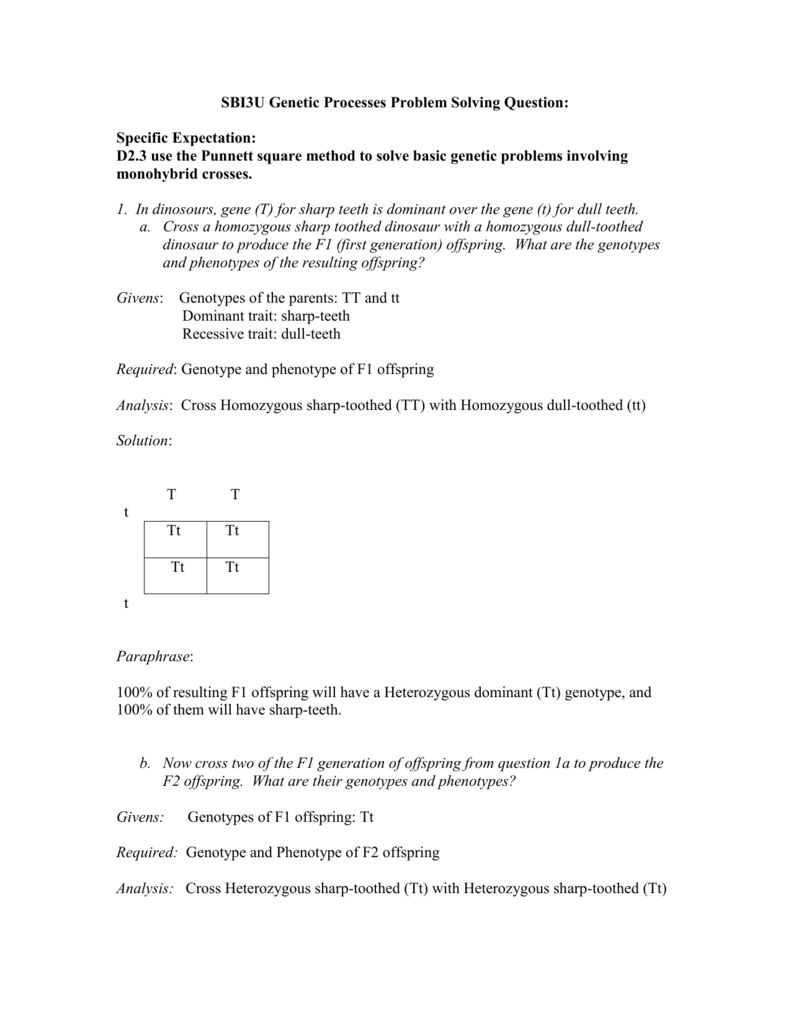
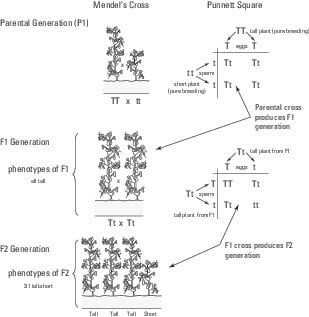
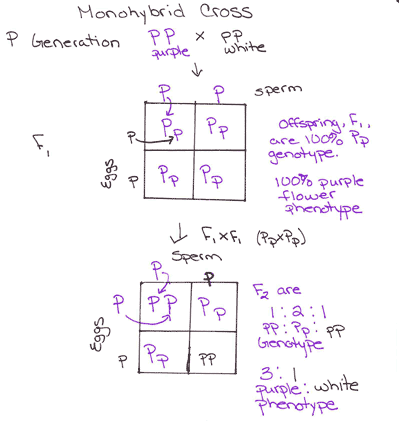
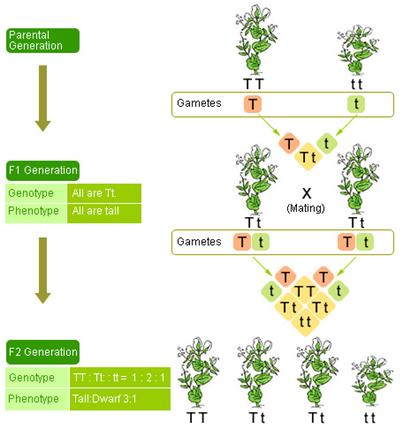
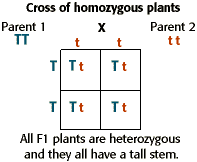
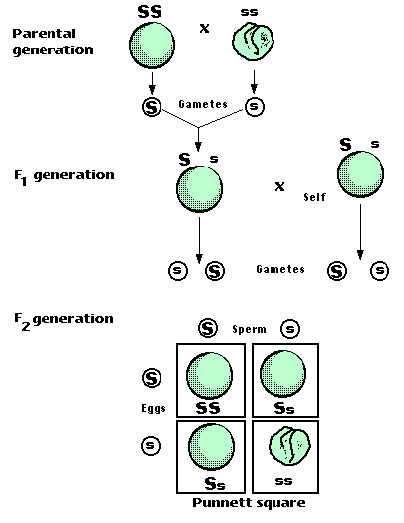
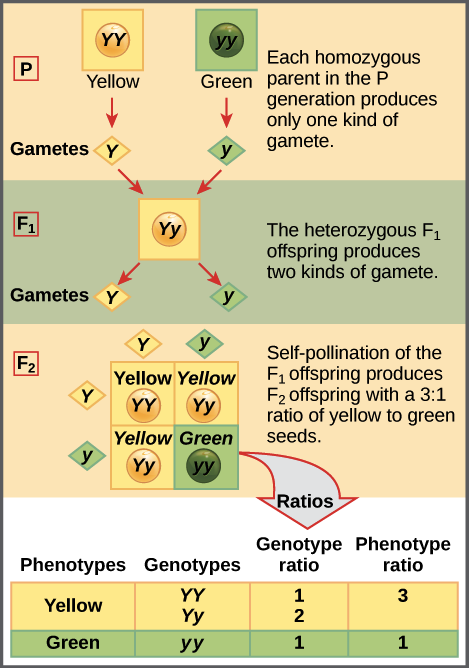
The cross between the true breeding p plants produces f1 heterozygotes that can be self fertilized.
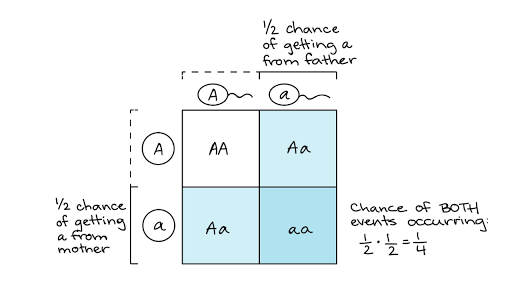
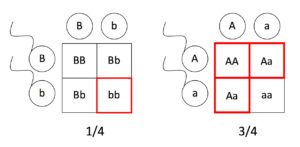
F1 offspring punnett square. It will show you every possible combination of offspring that result from a cross. The physical characteristics of the particular trait. Punnett square crosses are based on meiosis a biological process where parents pass on alleles to sex cells which they later transmit to their offspring. This screencast explains punnett squares p f1 f2 generations.
A punnett square so named after its creator reginald c. Lets think about x linked diseases disorders that are inherited only via the female line of the familyevery woman has two different x chromosomes inherited from her parents. Creating a punnett square and using it to determine traits of offspring is called performing a cross. Punnett is a chart drawn to determine the probable results of a genetic cross.
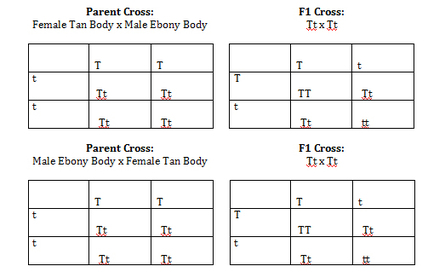
A punnett square allows the prediction of the percentages of phenotypes in the offspring of a cross from known genotypes. Our punnett square maker works on autosomal alleles chromosomes 1 22 but it can be used for other things. Each parent has two alleles for a trait and passes one along to its offspring. A punnett square shows the genotype s two individuals can produce when crossed.
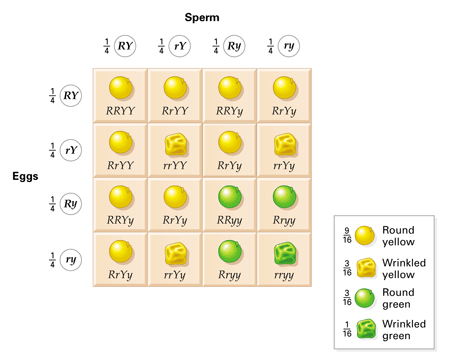
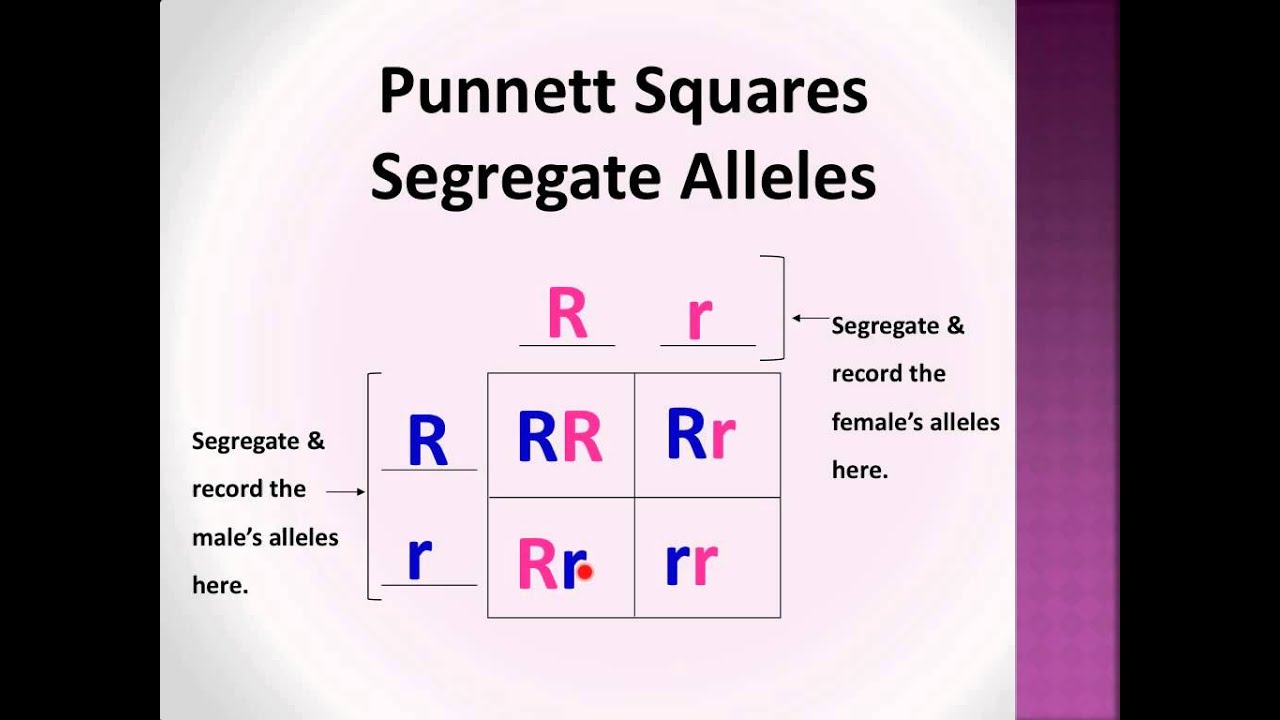
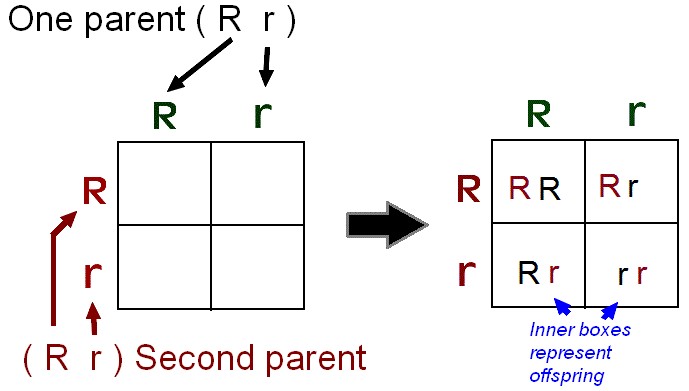
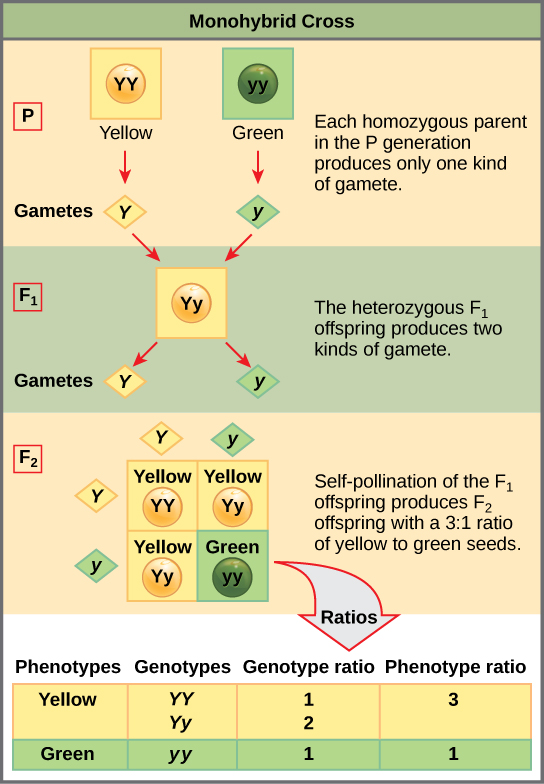
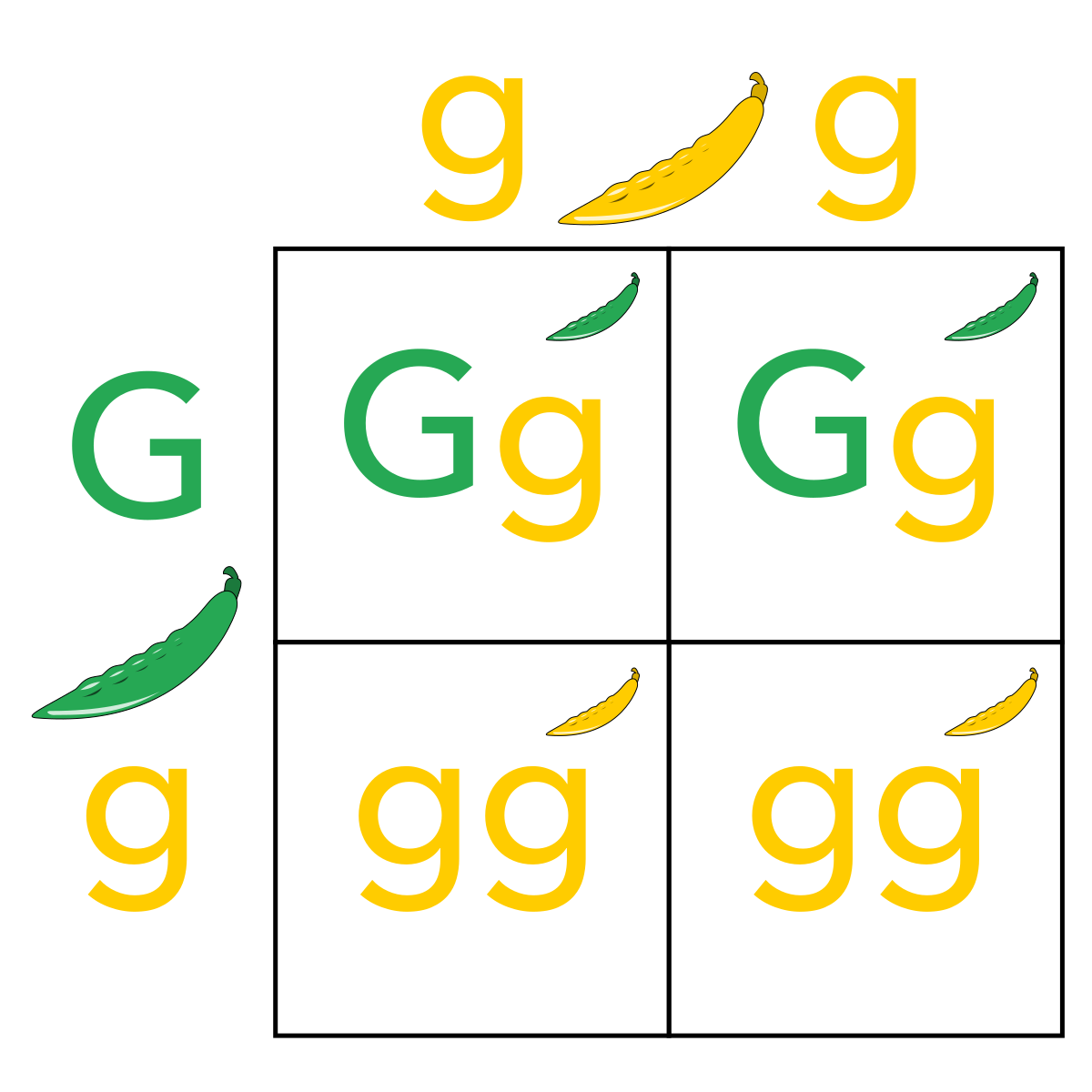
To draw a square write all possible allele combinations one parent can contribute to its gametes across the top of a box and all possible allele combinations from the other parent down the left side. This punnett square shows the cross between plants with yellow seeds and green seeds. Punnett square cheat sheet below is a sampling of punnett square problems that you will be expected to solve. Tt or tt phenotype.
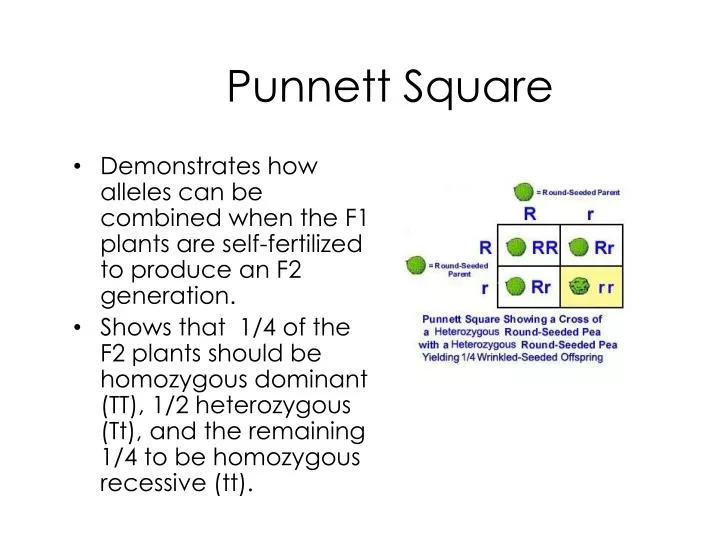
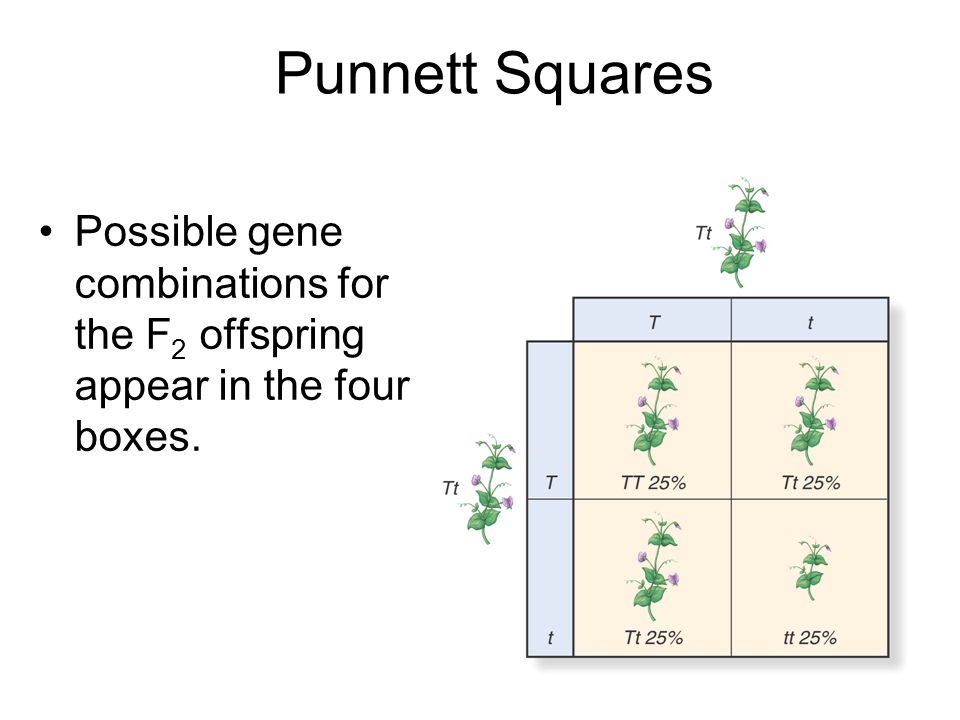
All offspring are yy and have yellow seeds. Each individual in the f1 generation is heterozygous carrying one of each allele. The letters that make up the individual. In order to do this you will also have to understand the meaning of the terms below.
In this case only one genotype is possible in the f1 offspring. Types of punnett squares. This information is transferred to the punnett square and the possible genotypes are extracted. The allele combinations along the top and sides become labels for rows and columns within the square.
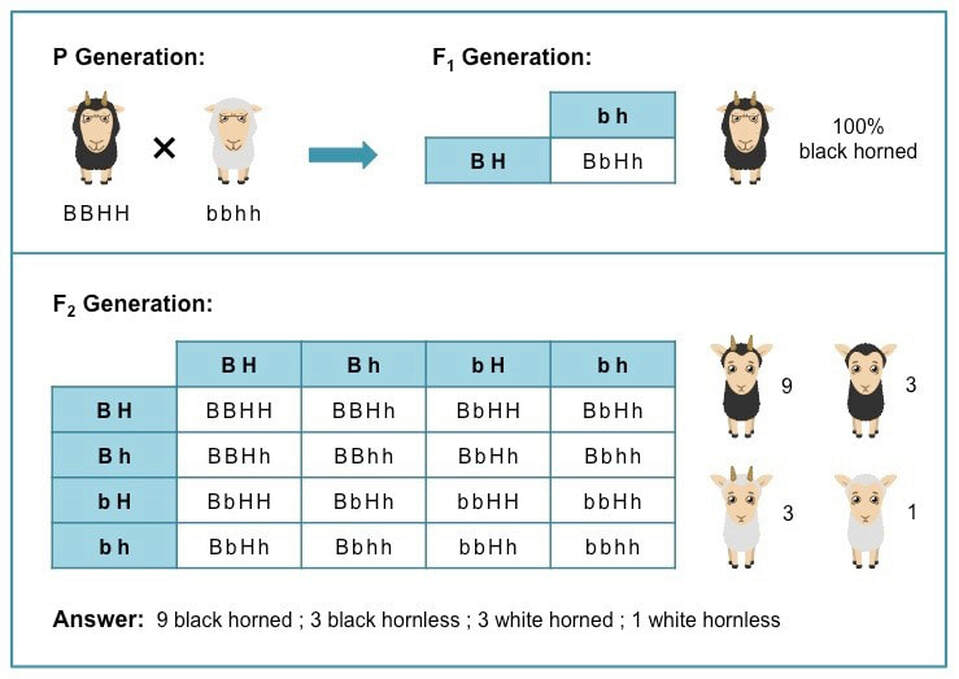
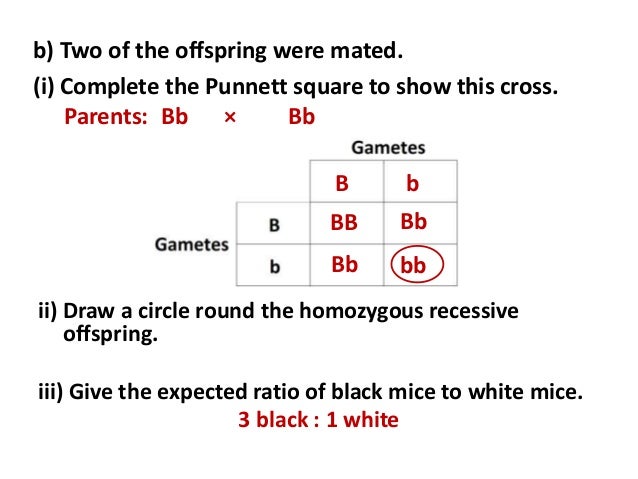
A punnett square can be used to determine a missing genotype based on the other genotypes involved in a cross.
















(39).jpg)




















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dihybrid_cross_ratios-58ef9ddd5f9b582c4d02ceb2.jpg)