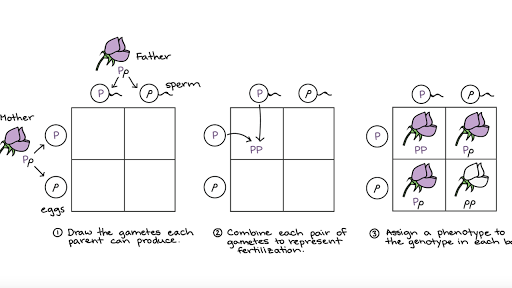
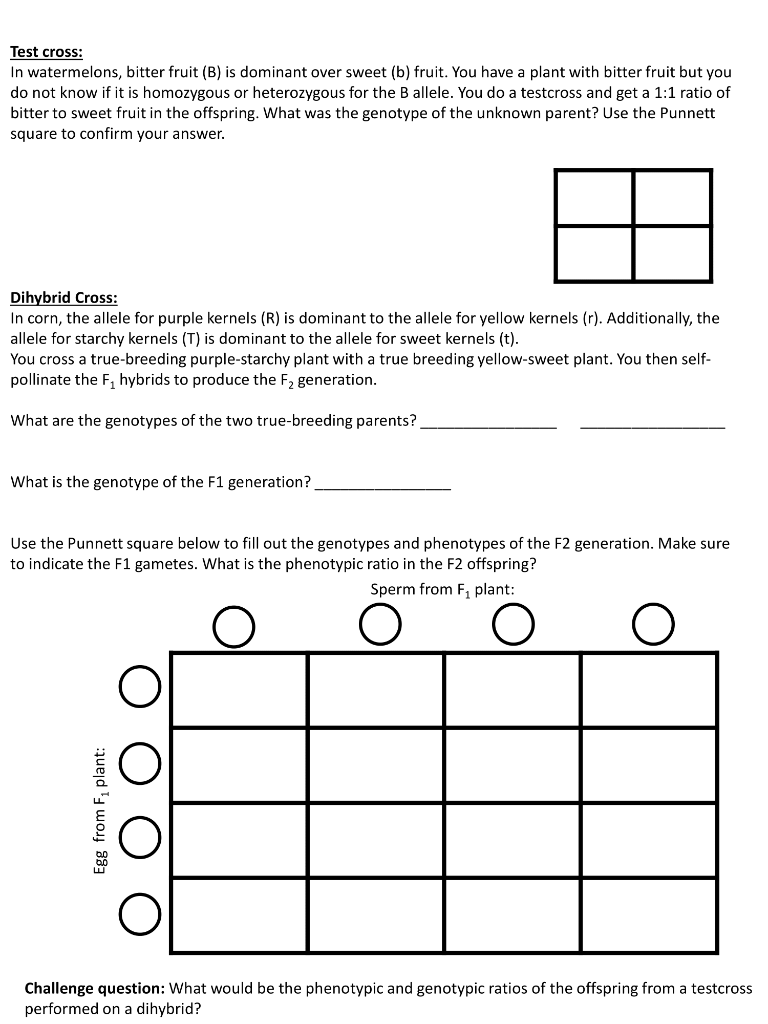
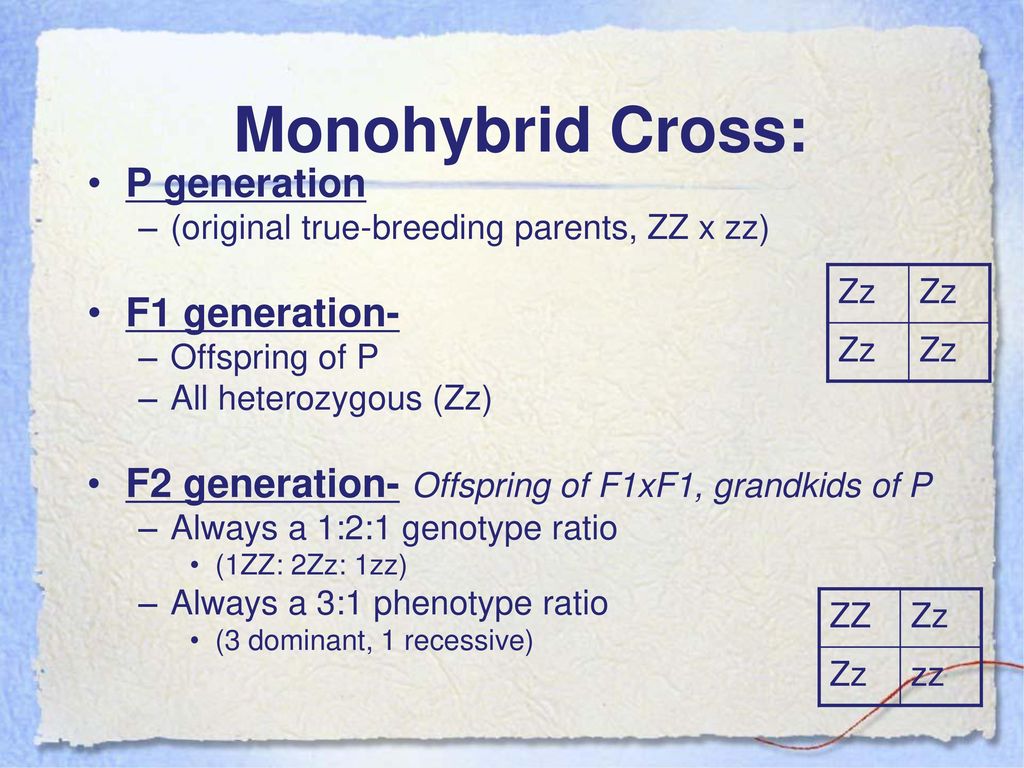
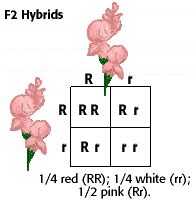
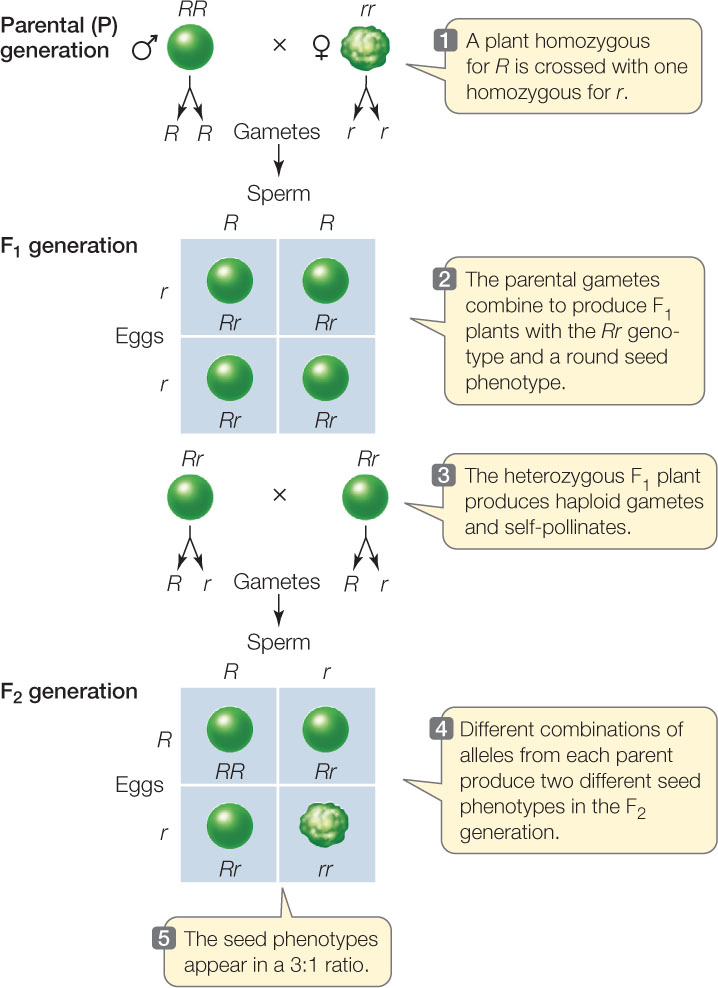
F1 Offspring Of True Breeding Parents With Different Phenotypes Are Always Heterozygous
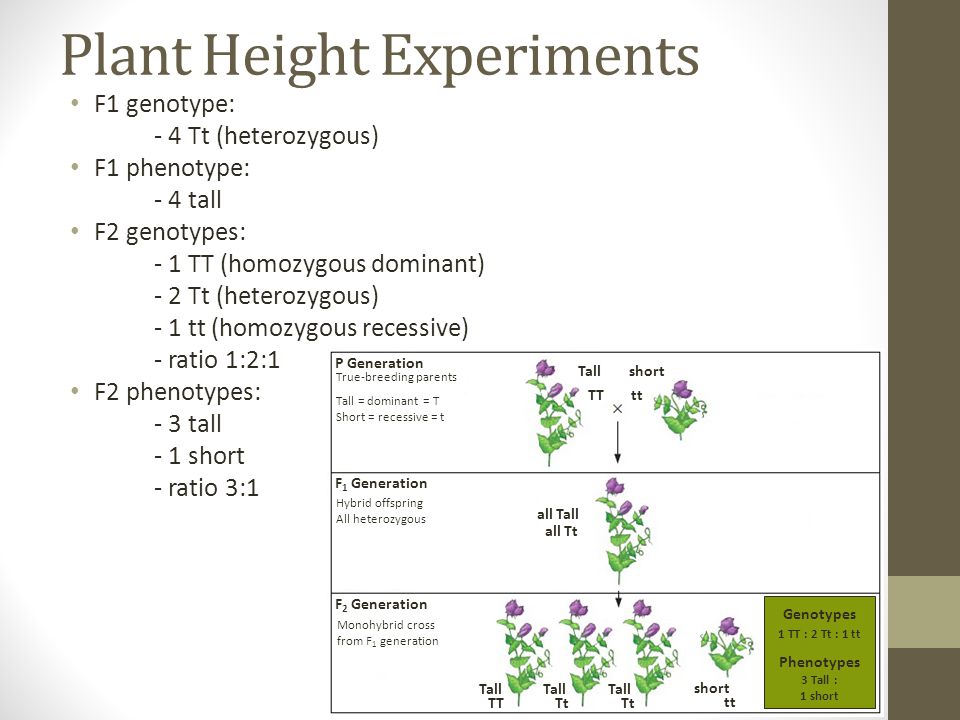
If the traits are inherited as dominant and recessive the f 1 offspring will all exhibit the same phenotype as the parent homozygous for the dominant trait.
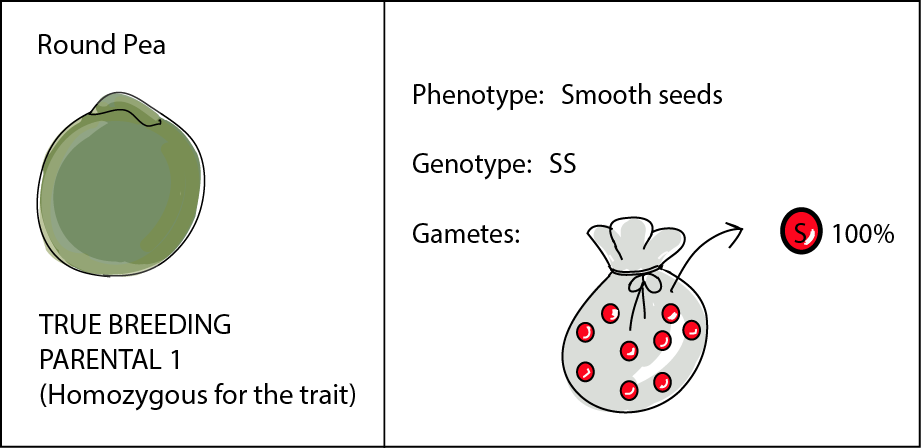
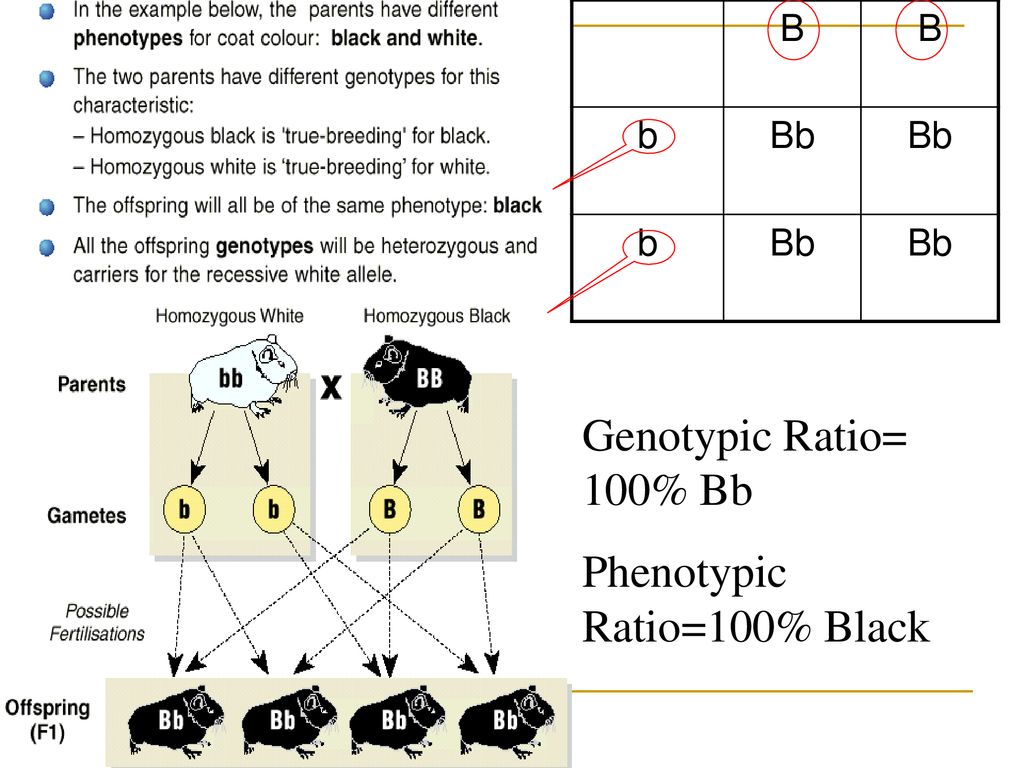
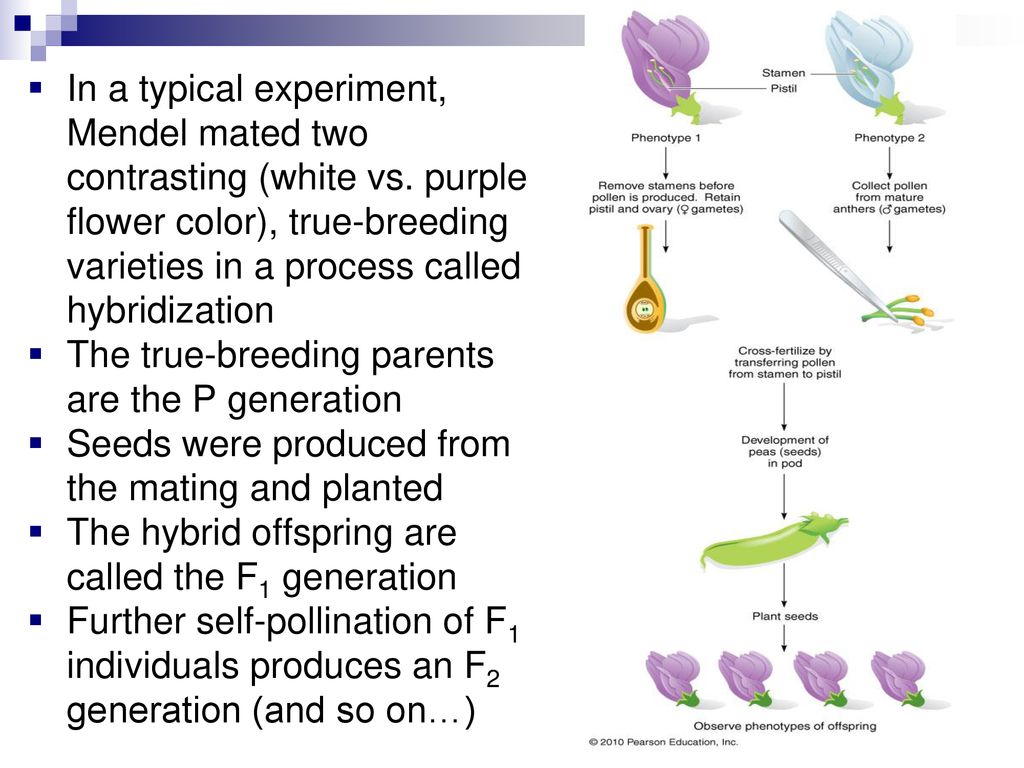
F1 offspring of true breeding parents with different phenotypes are always heterozygous. Start studying unit 5 mendelian genetics vocabulary. How many different types of gametes would be possible in this organism. O 4 why did all of the f1 offspring of mendels classic pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
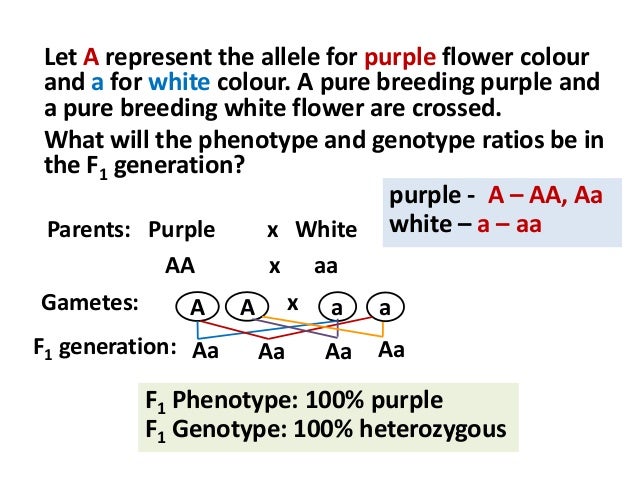
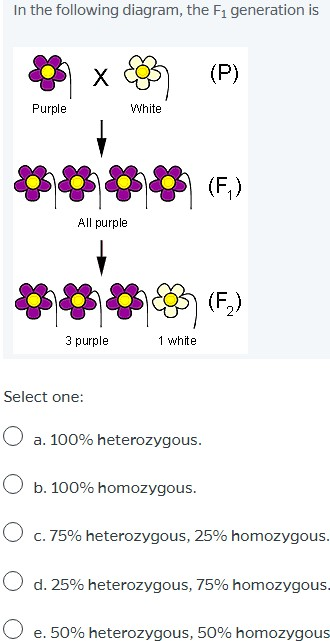
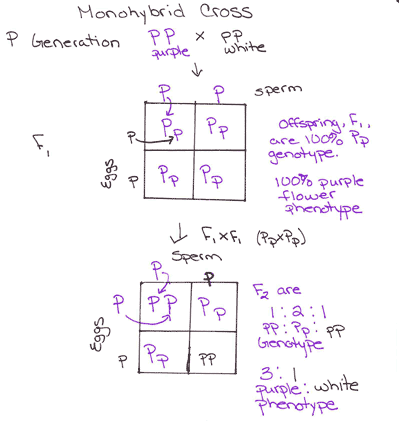
If you made a punnett square showing gregor mendels cross between true breeding tall plants and true breeding short plants the square would show that the offspring had a. When p plants with contrasting traits were cross fertilized all of the offspring were heterozygous for the contrasting trait meaning their genotype had different alleles for the gene being examined. A genotype that was different from that of both parents. Both a and b are dominant to o.
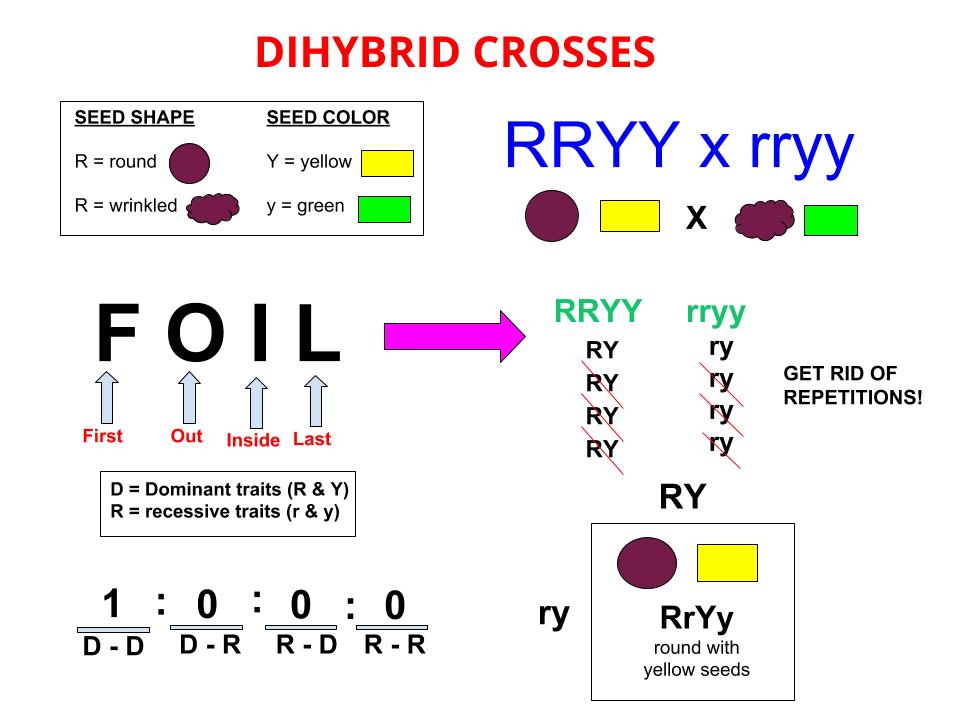
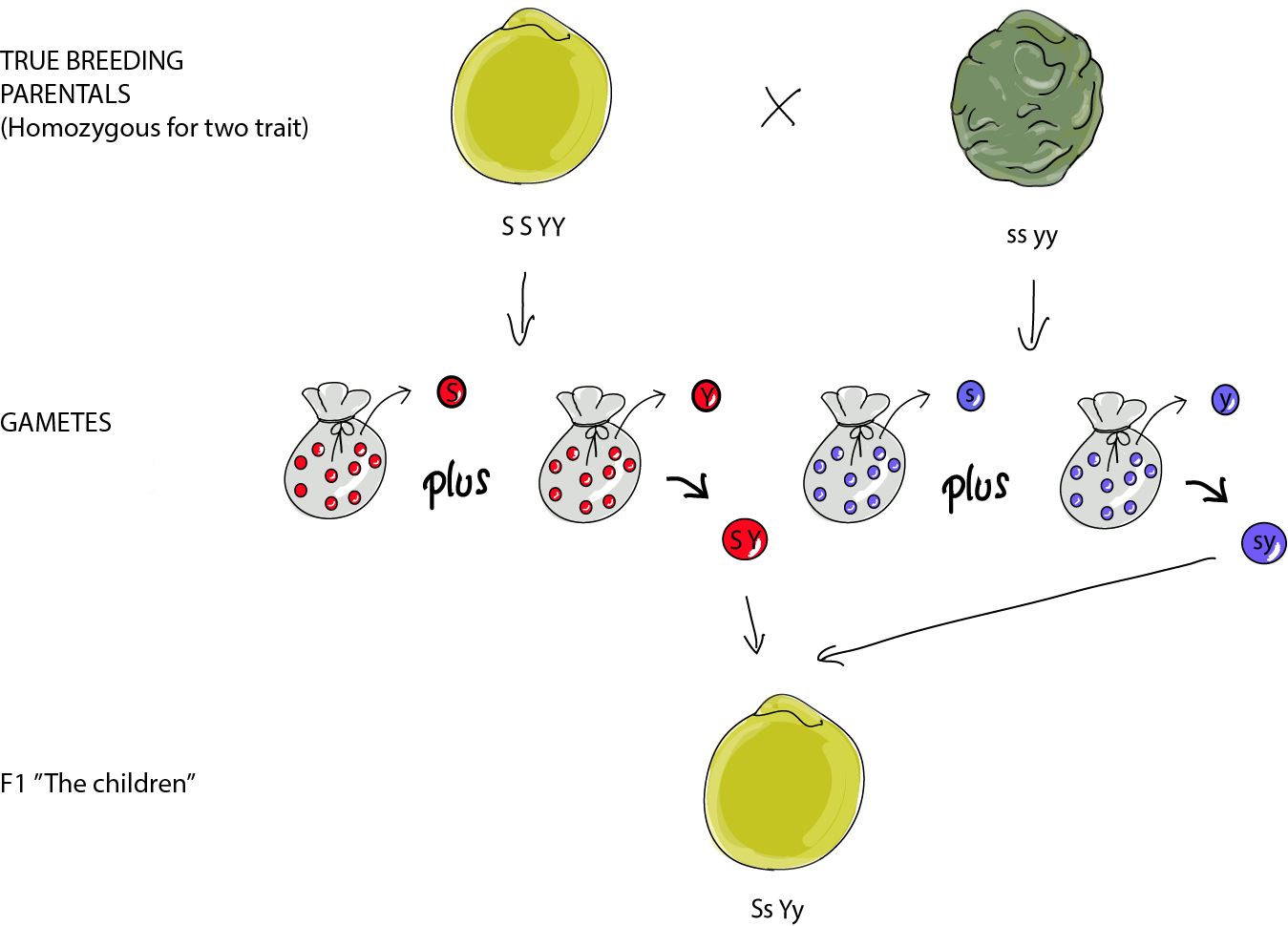
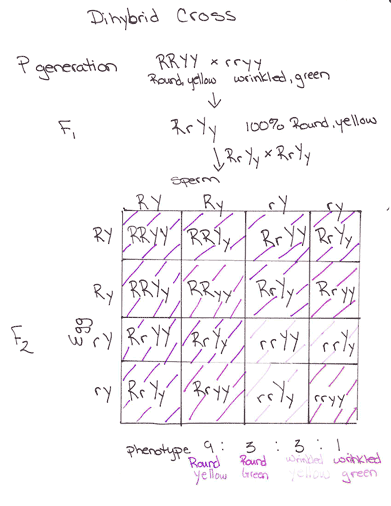
The offspring produced in the f1 generation of mendels experiment were this dihybrid crossing two true breeding homozygous dominant and recessive parents differing in two characters produces this type of individual in the f1 generation which are heterozygous for both characters. If a heterozygous blood type a parent iai and a heterozygous blood type b parent ibi mate one quarter of their offspring are expected to have the ab blood type iaib in which both antigens are expressed equally. The ia allele encodes the a blood group antigen ib encodes b and i encodes o. Therefore abo blood groups are an example of.
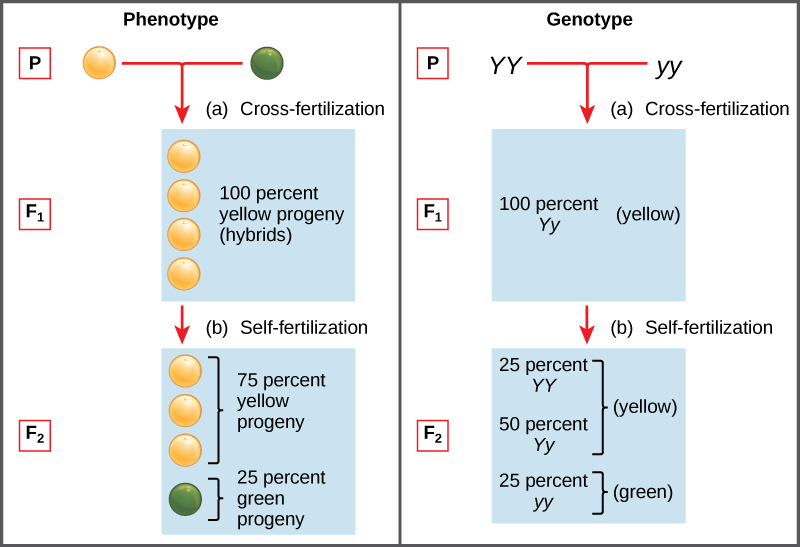
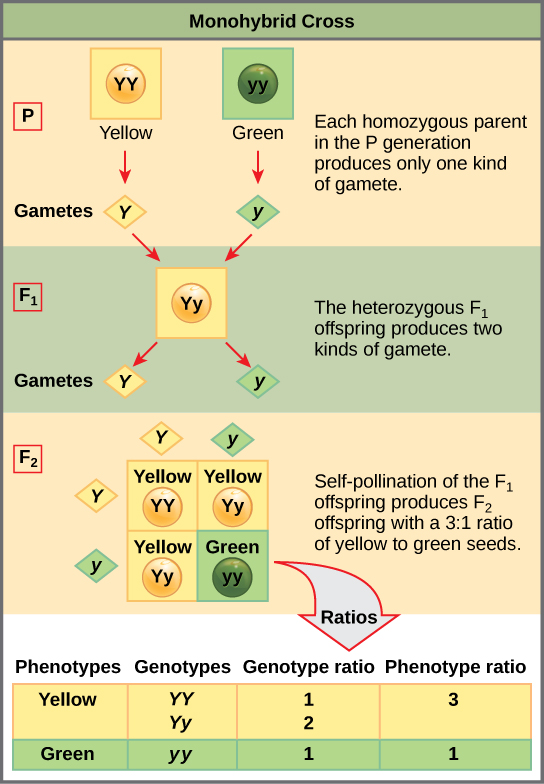
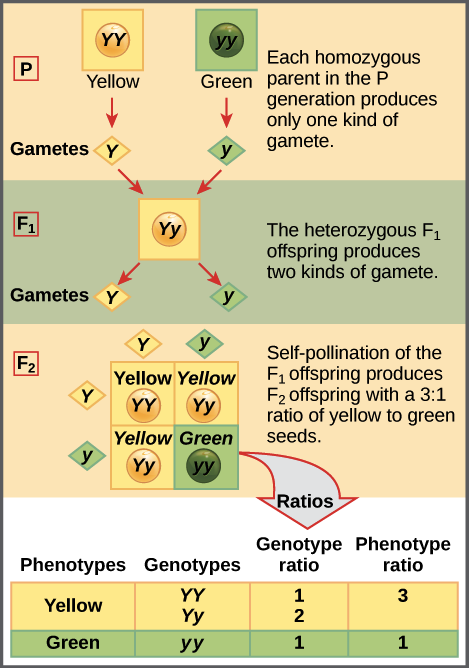
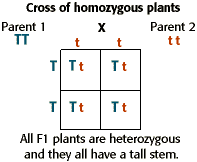
When true breeding or homozygous individuals that differ for a certain trait are crossed all of the offspring will be heterozygous for that trait. Heterozygous blood type a parent iai and a heterozygous blood type b parent ibi mate one quarter of their offspring will have ab blood type iaib in which both antigens are expressed equally. The offspring showed a combination of the phenotypes from each parent that were genetically dominant. Mendels discoveries involving the f1 and f2 generations laid the foundation for modern genetics.
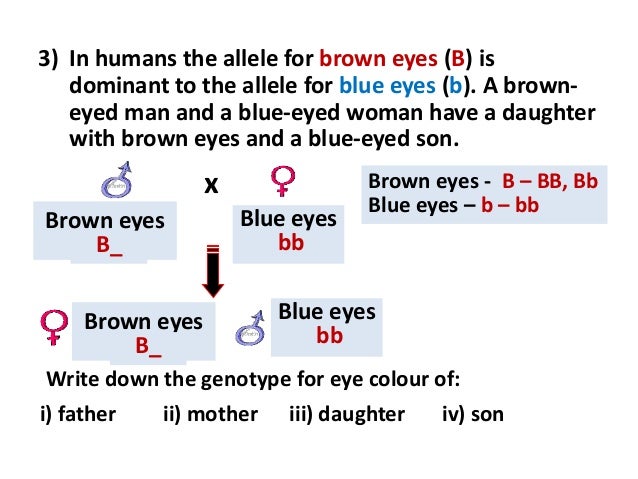
The genotype of one of the parents. If you are crossing two parents that are true breeding meaning they each have homozygous traits one has dominant traits the other has recessive traits the f1 generation will typically be. O one allele was dominant. A phenotype that was different from that of both parents.
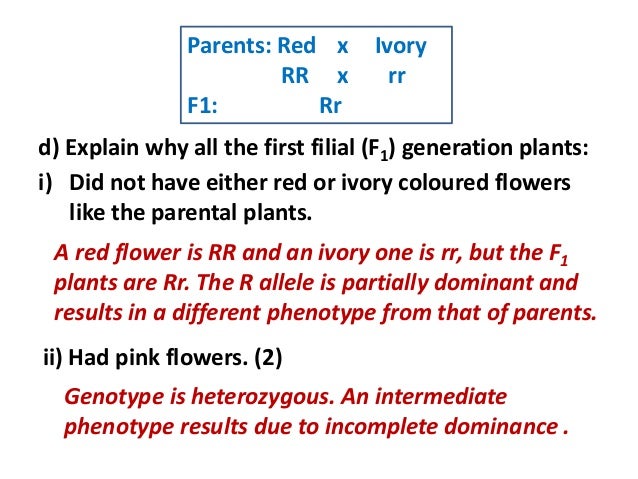
Multiple alleles and incomplete dominance b. Mendel crossed yellow seeded and green seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self pollinate to produce an f2. Codominance and incomplete dominance.


/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg)
















/genetic-crosses-56e97ae13df78c5ba057ca68.jpg)









/88168830-56a09a683df78cafdaa32734.jpg)





















/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg)