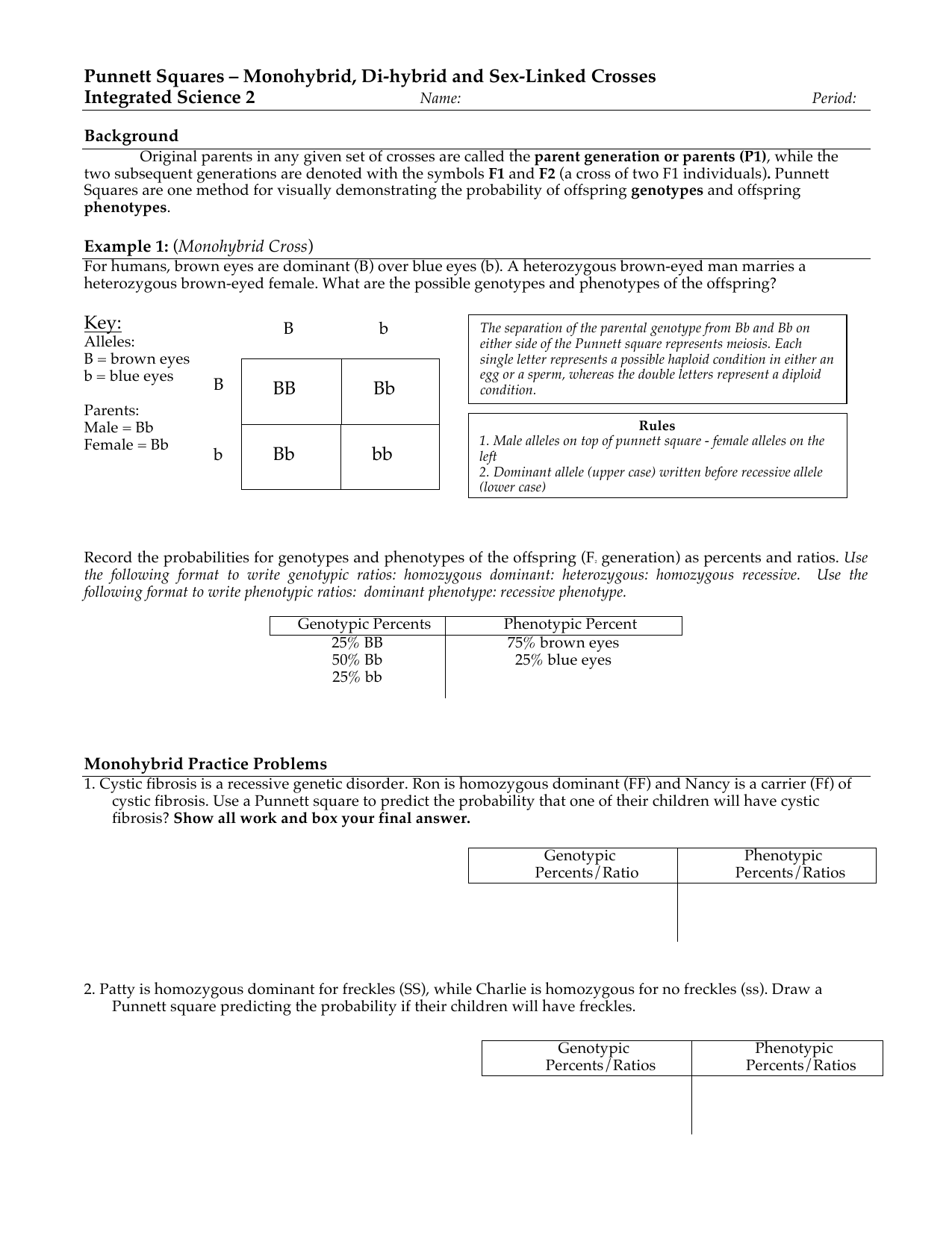
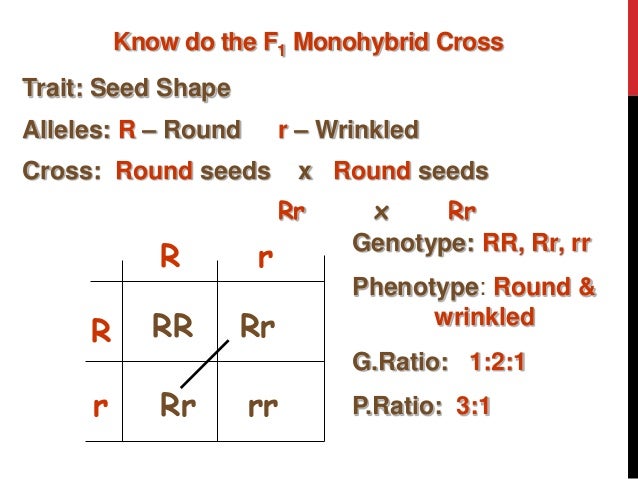
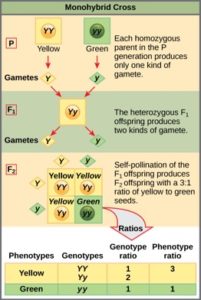
F1 Monohybrid Cross Example
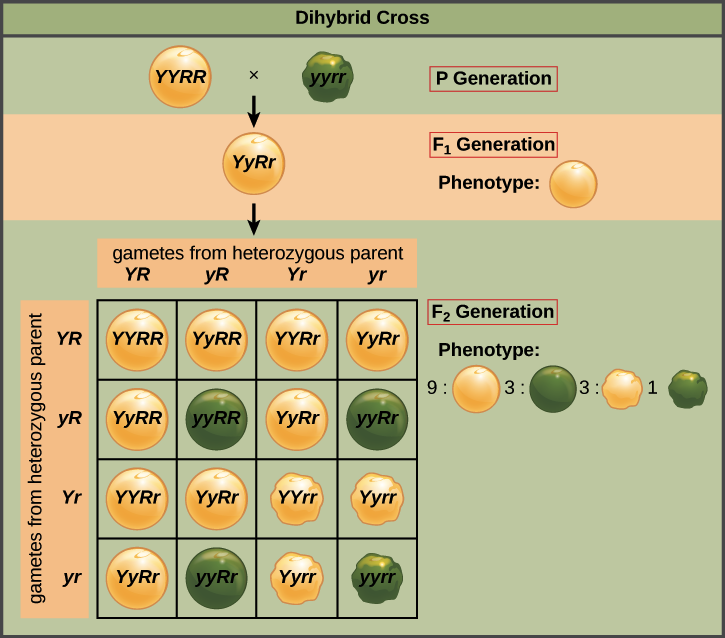
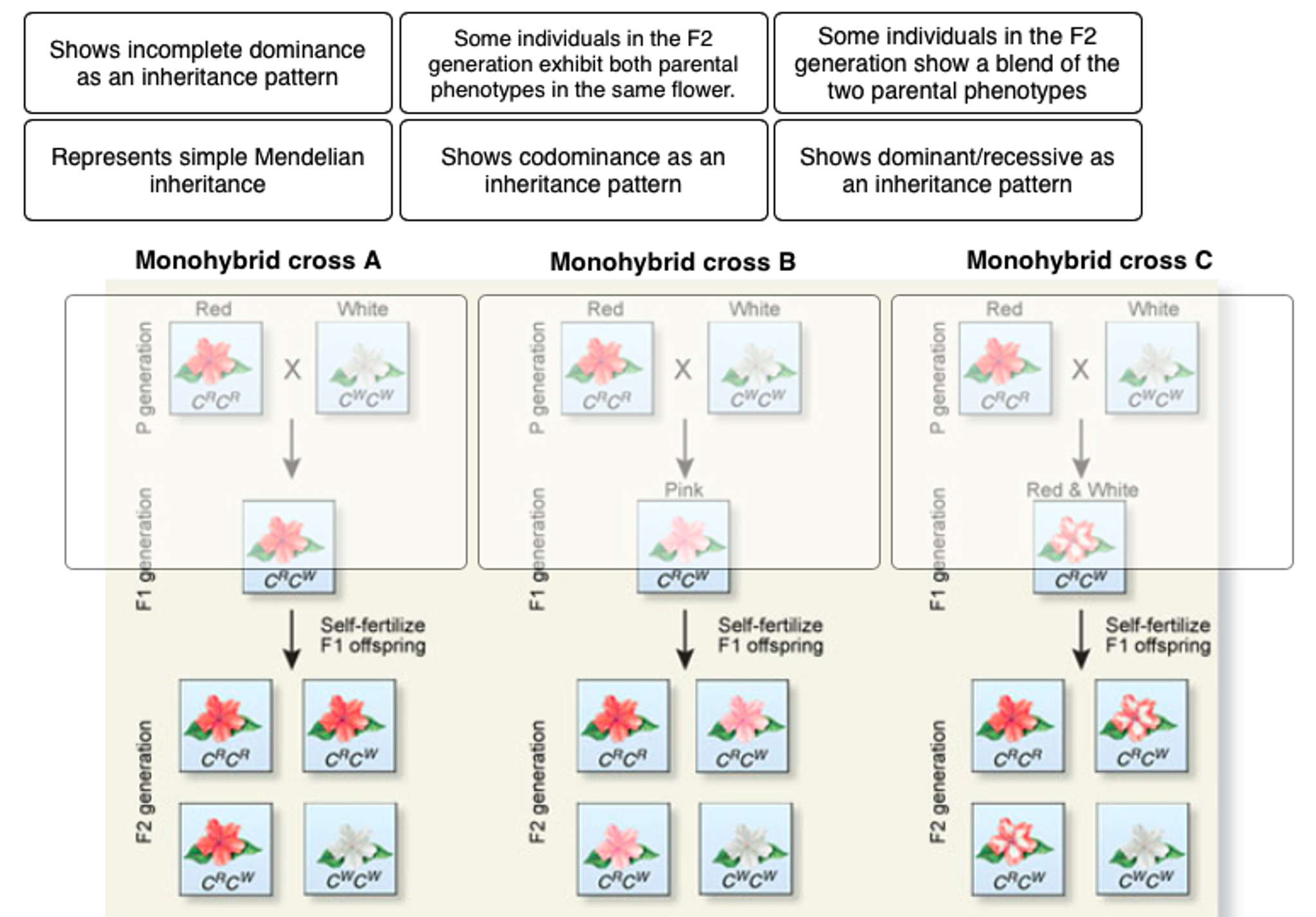
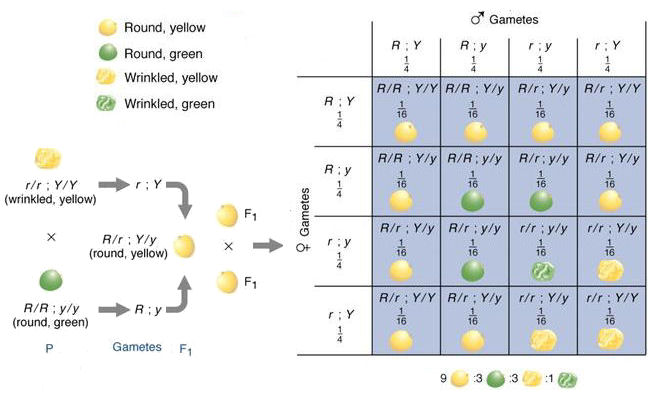
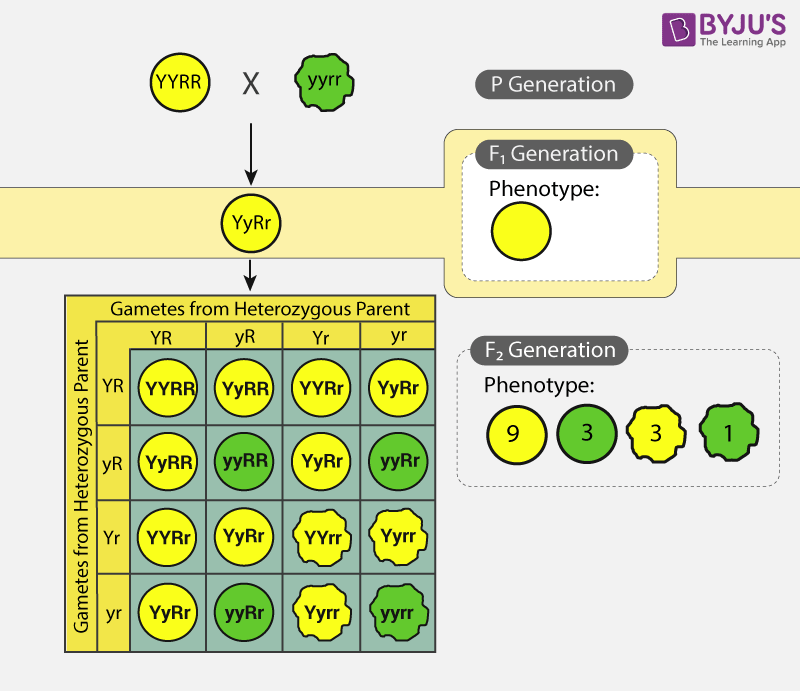
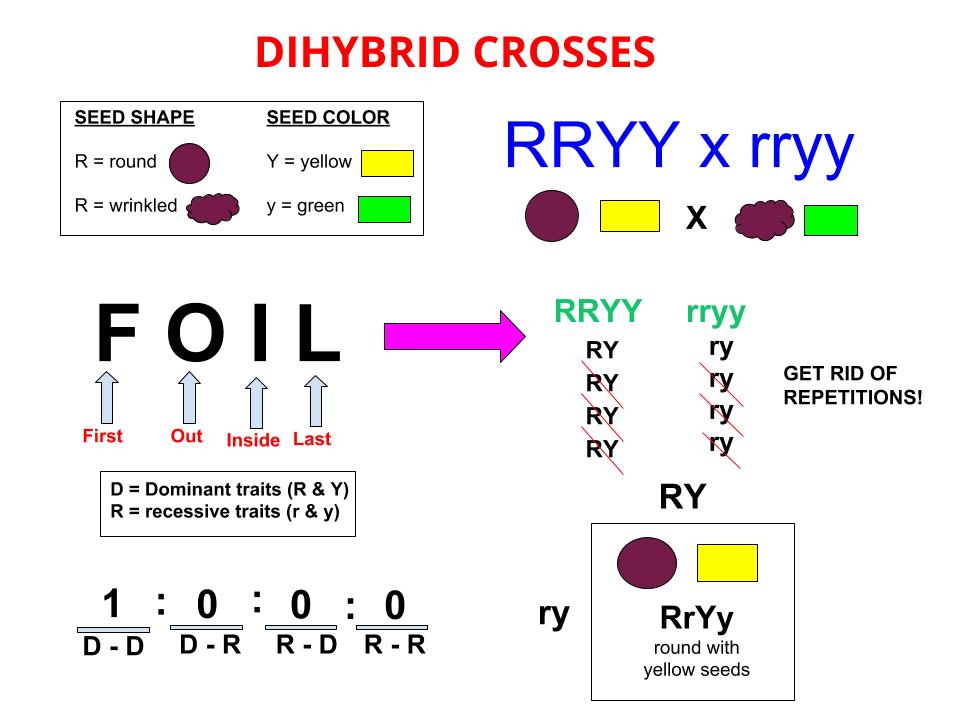
This cross only examined one trait however many more traits can be observed at once.
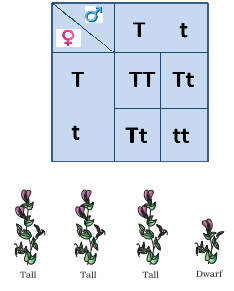
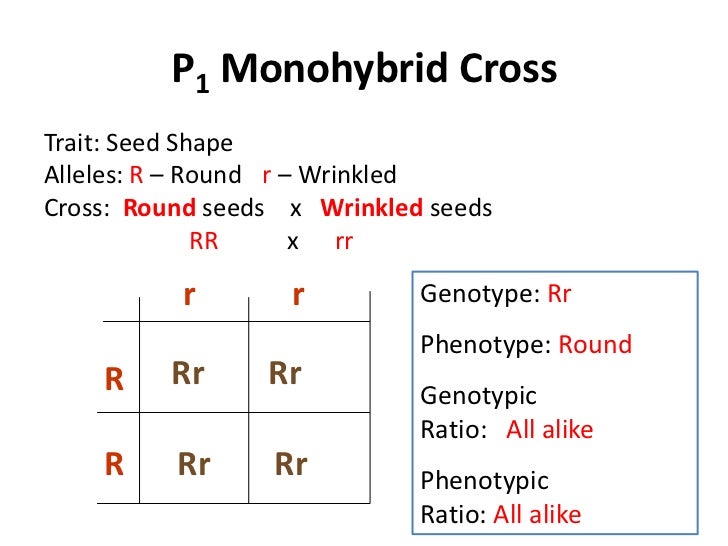
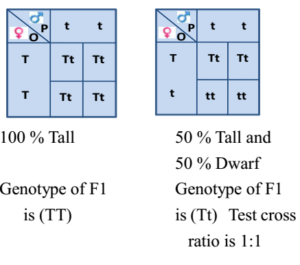
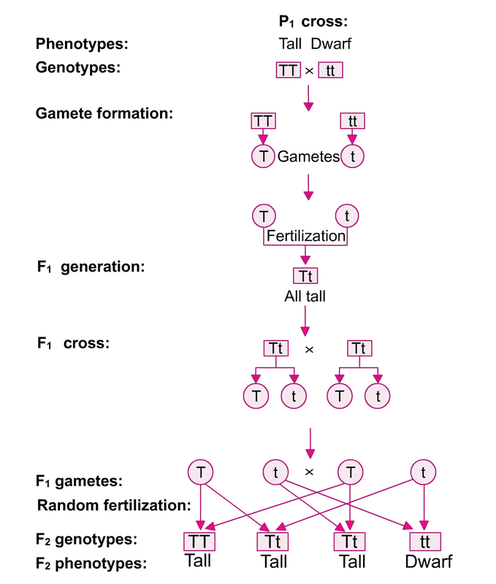
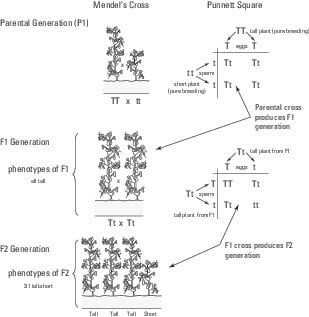
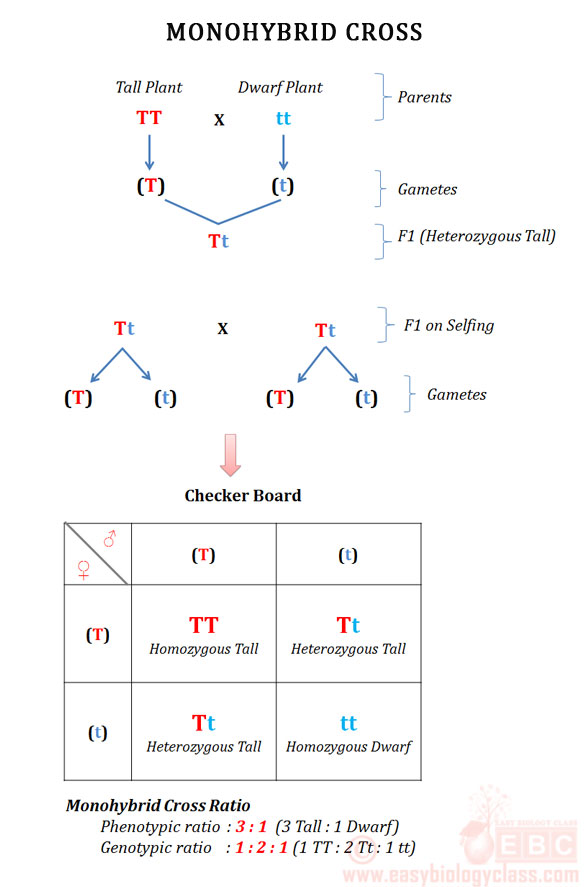
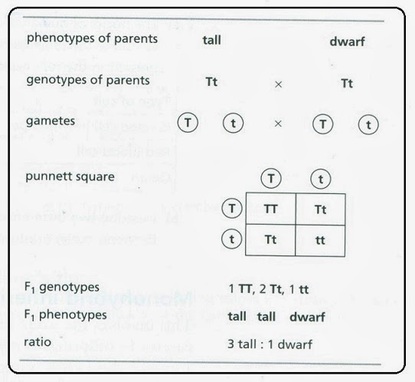
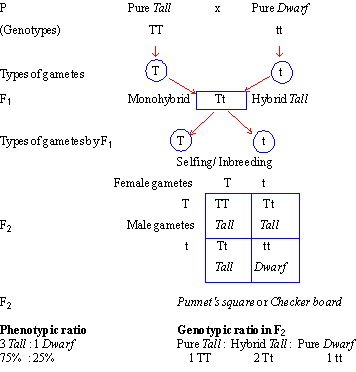
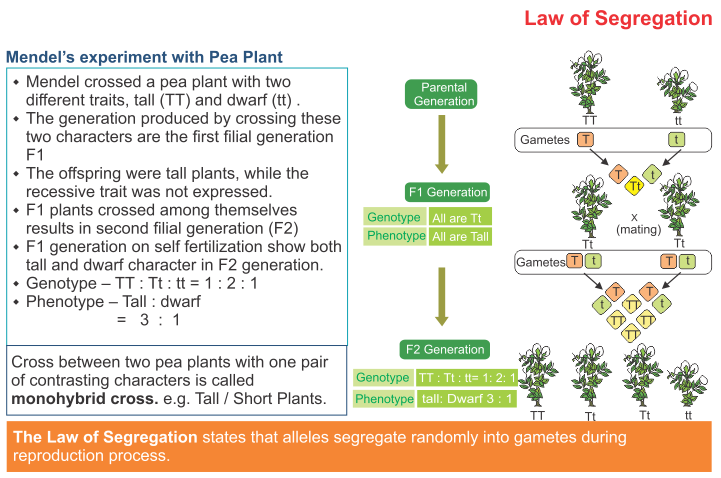
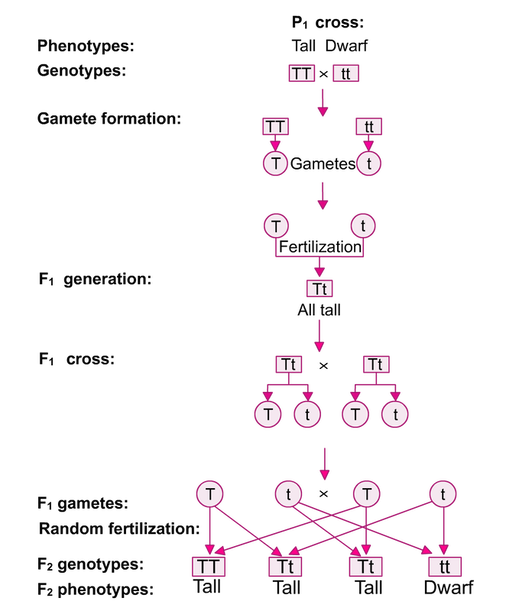
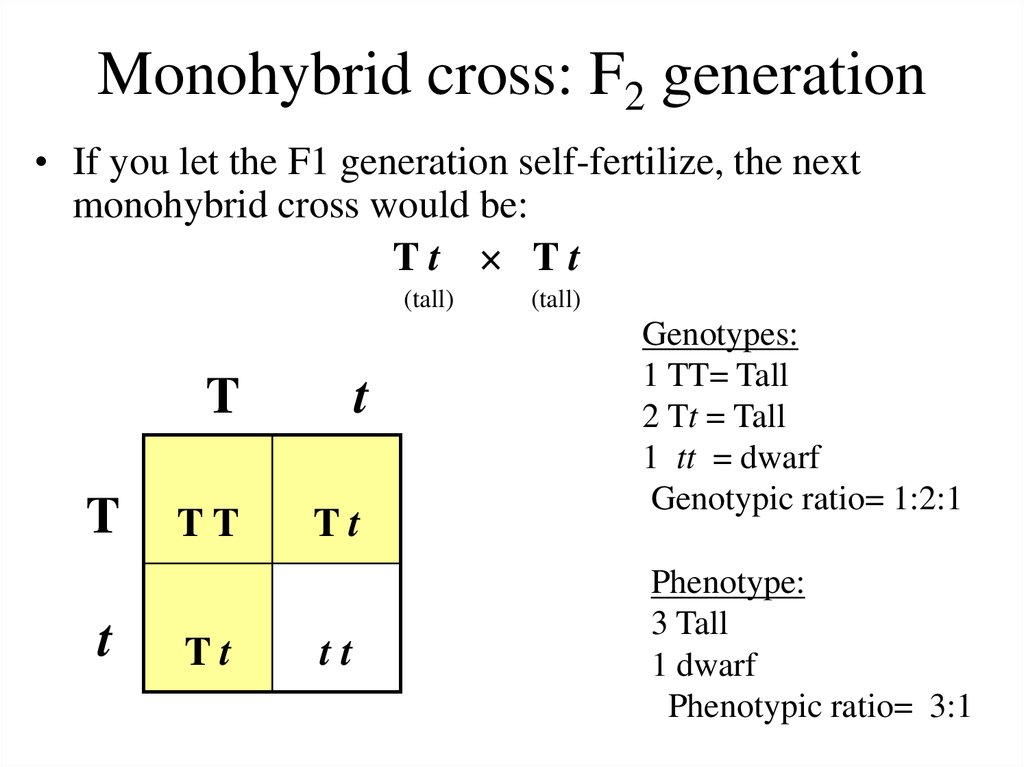
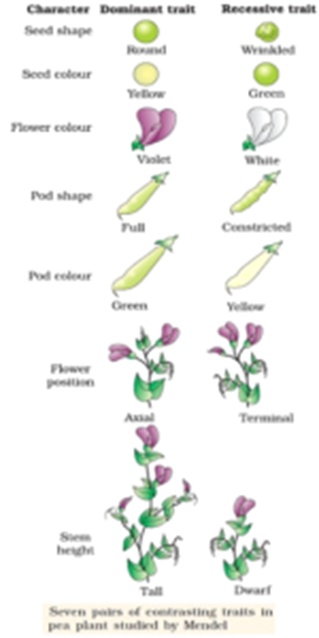
F1 monohybrid cross example. Tallness t gene is dominant over dwarfness t gene. The individuals in the cross all had one allele for green pods and one allele for yellow pods making them hybrids. Pure homozygous tall pea plant. For monohybrid cross mendel began with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits ie one tall and another dwarf.
The cross pollination of tall and dwarf plants resulted in tall plants. All the hybrid plants were tall. The form of a trait is the one that is not expressed in the f1 generation of a monohybrid cross bell when continuous traits are graphed in the form of a histogram with the phenotype on the x axis and the frequency of individuals with that phenotype on the y axis a shaped curve results. Gregor mendel focused on several different genetic traits but we will focus on one.
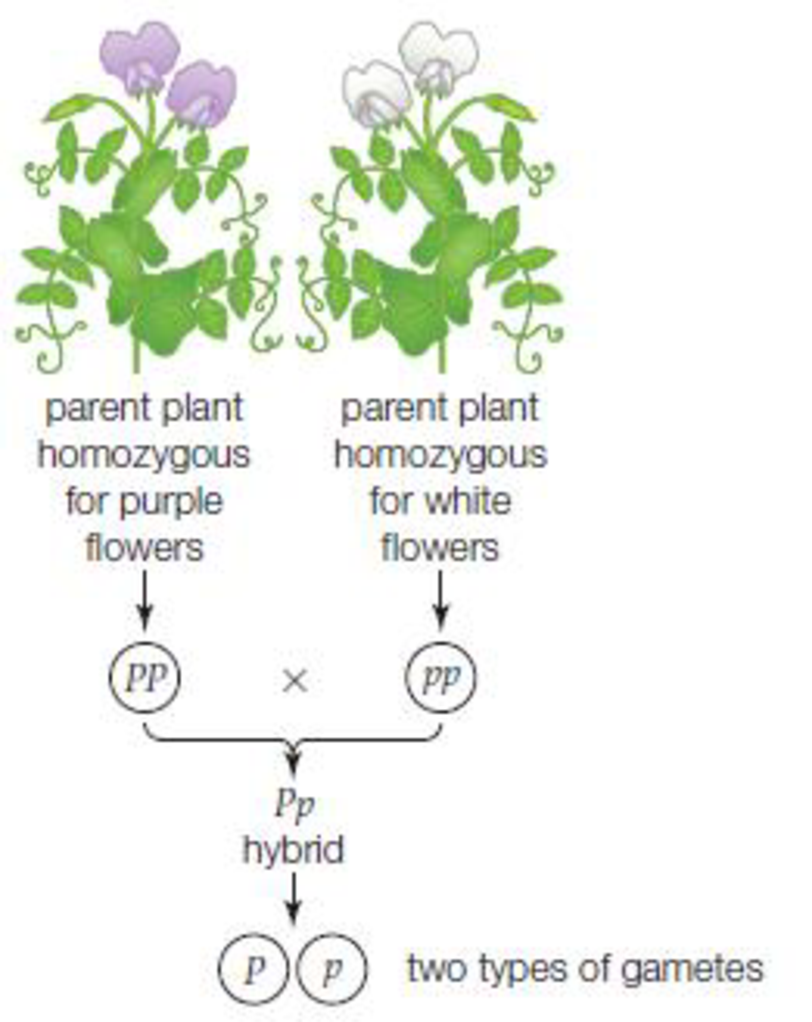
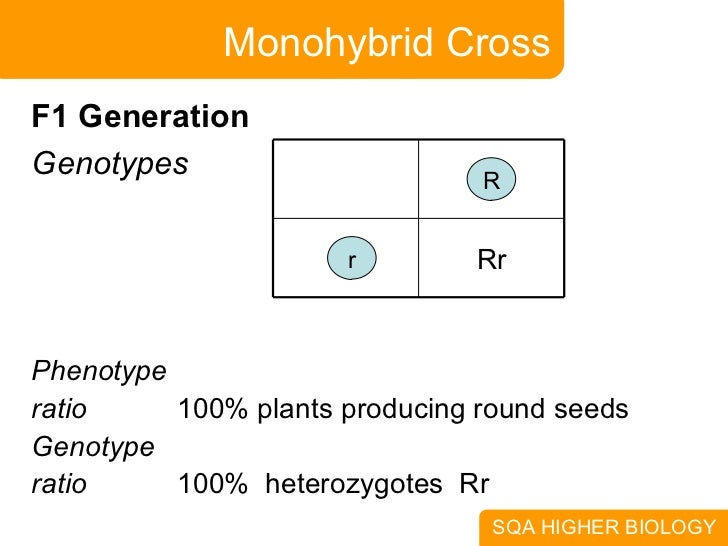
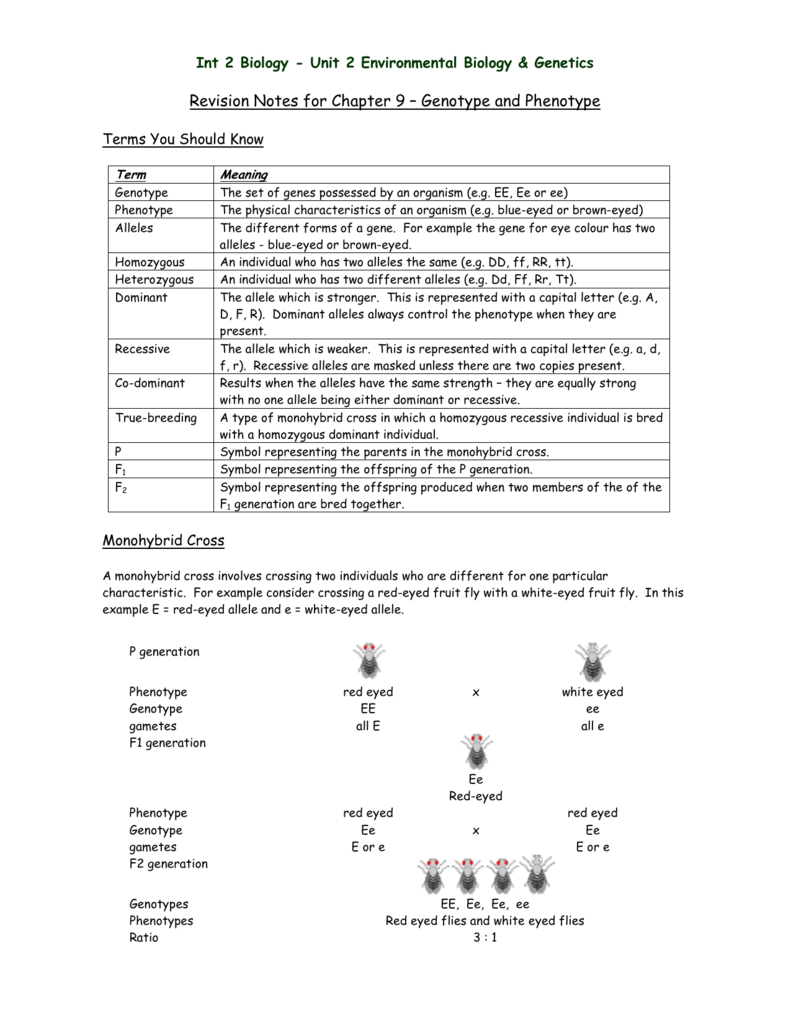
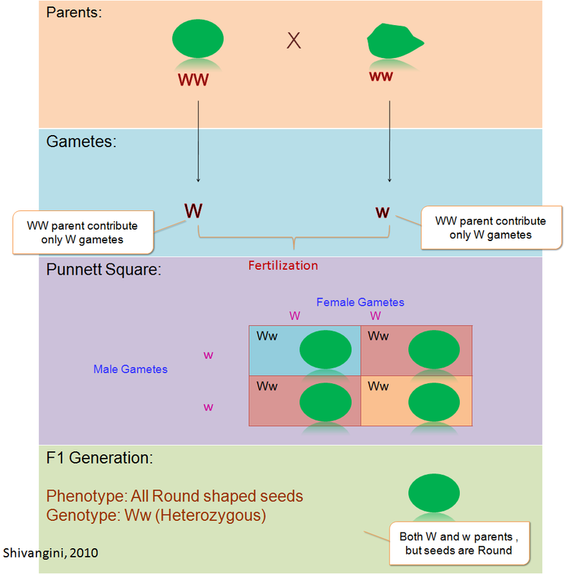
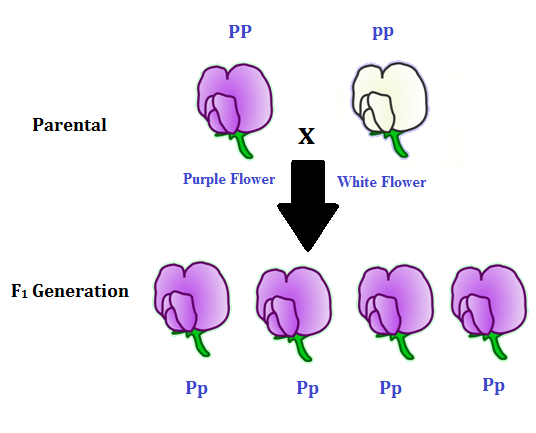
Peas are a variety of plant which can self fertilize meaning the male part of the plant can fertilize the eggs produced by the female part of the. When the father of genetics gregor mendel was first unfolding the secrets of pea genetics he started by producing lines of pure breeding peas. List of sixteen numerical problems on monohybrid cross. As in a dihybrid cross the f1 generation plants produced from a monohybrid cross are heterozygous and only the dominant phenotype is observed.
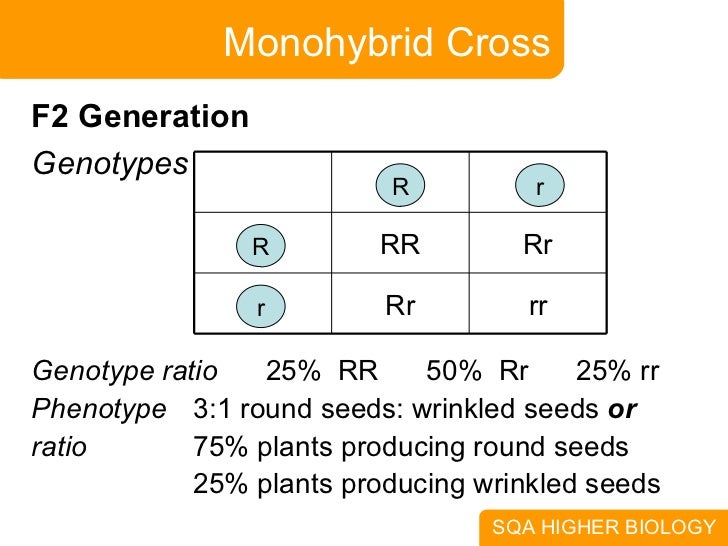
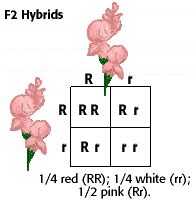
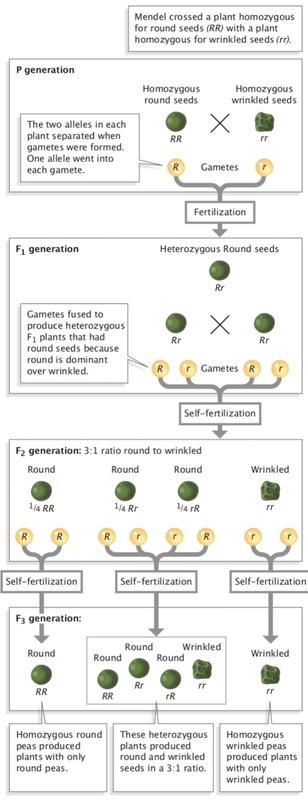
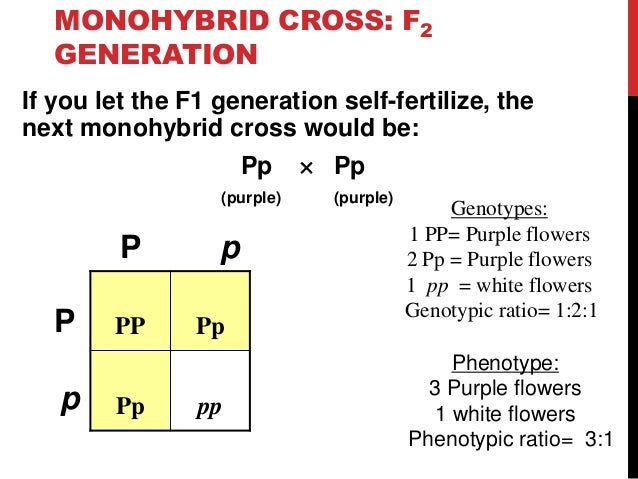
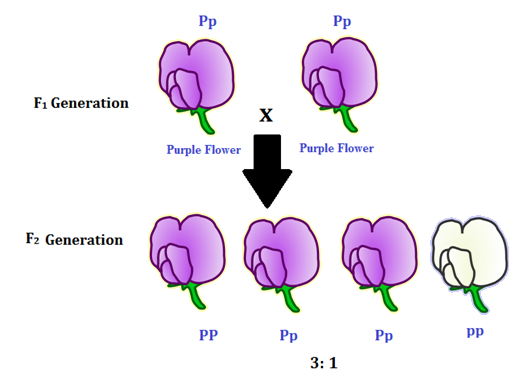
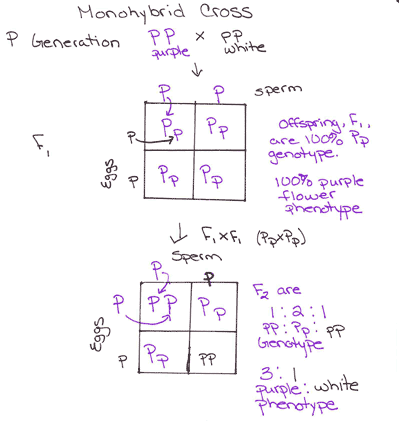
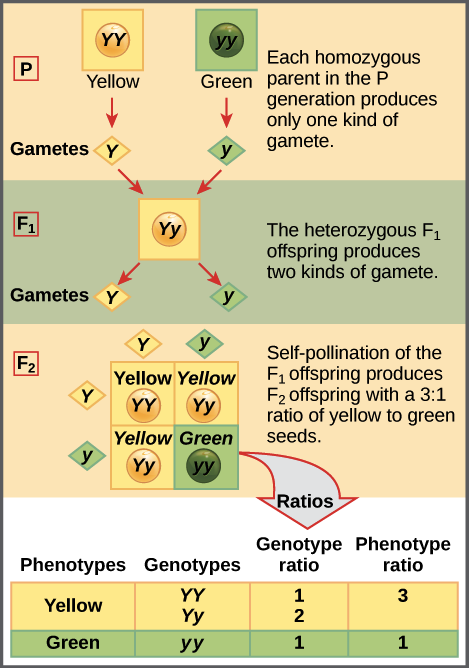
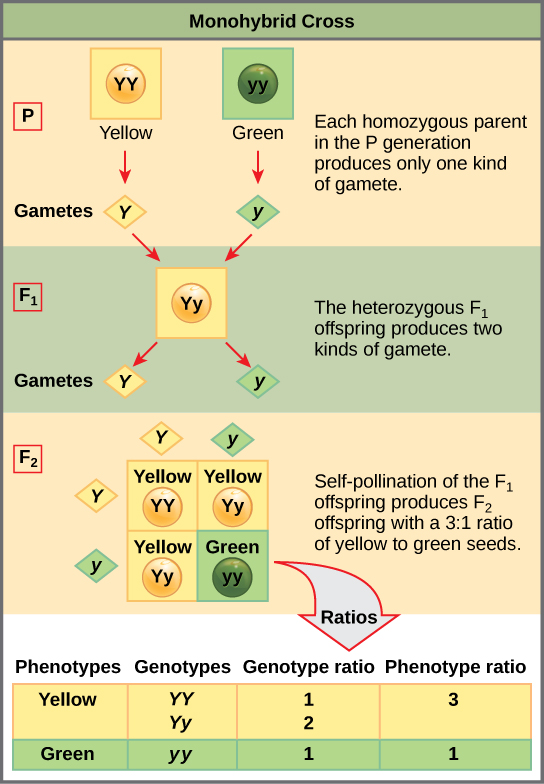
All of the f1 generation plants will have the genotype of ss heterozygous and all will be spherical seeded. About 34 exhibit the dominant phenotype and 14 exhibit the recessive phenotype. Examples of monohybrid cross gregor mendels peas. Although he did not know it at the time gregor mendel used monohybrid crosses to identify dominant and recessive traits in his landmark experiments with peas.
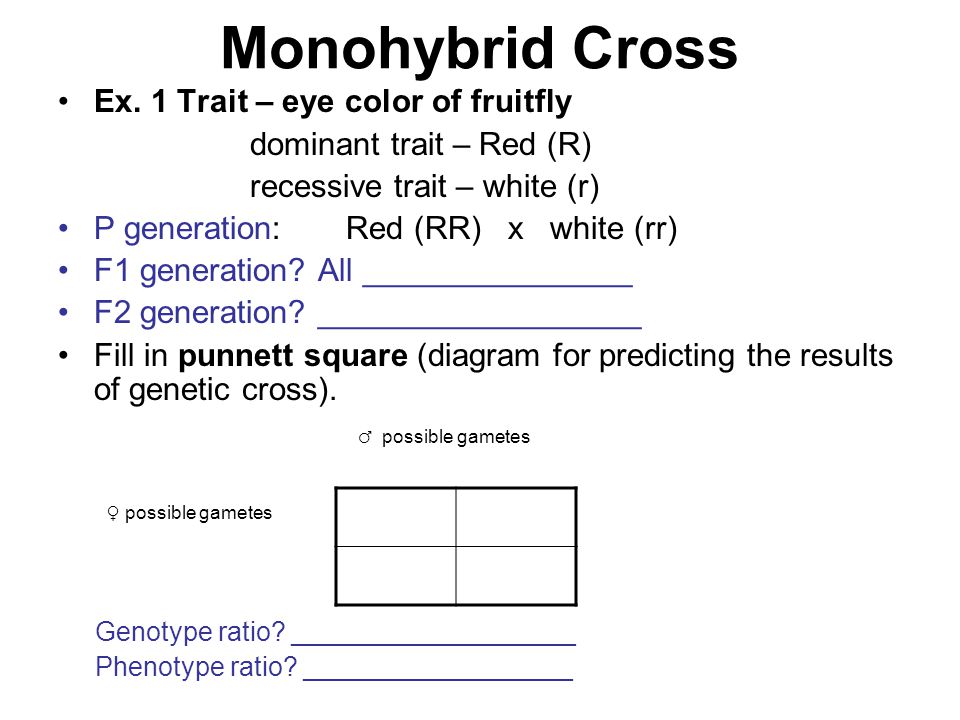
F1 generation f2 generation plants. Mendels experiment 1 tutorial to help answer the question. Monohybrid cross example gregor mendels peas. Modern scientists now describe the cross of mendels f1 generation as a monohybrid cross.
The phenotypic ratio of the resulting f2 generation is 31. Examples of f1 generation a monohybrid cross. Monohybrid cross problem set problem 3.

/genetic-crosses-56e97ae13df78c5ba057ca68.jpg)








.PNG)












/dihybrid_cross_2-58ef84973df78cd3fc70a061.jpg)













/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg)



.PNG)