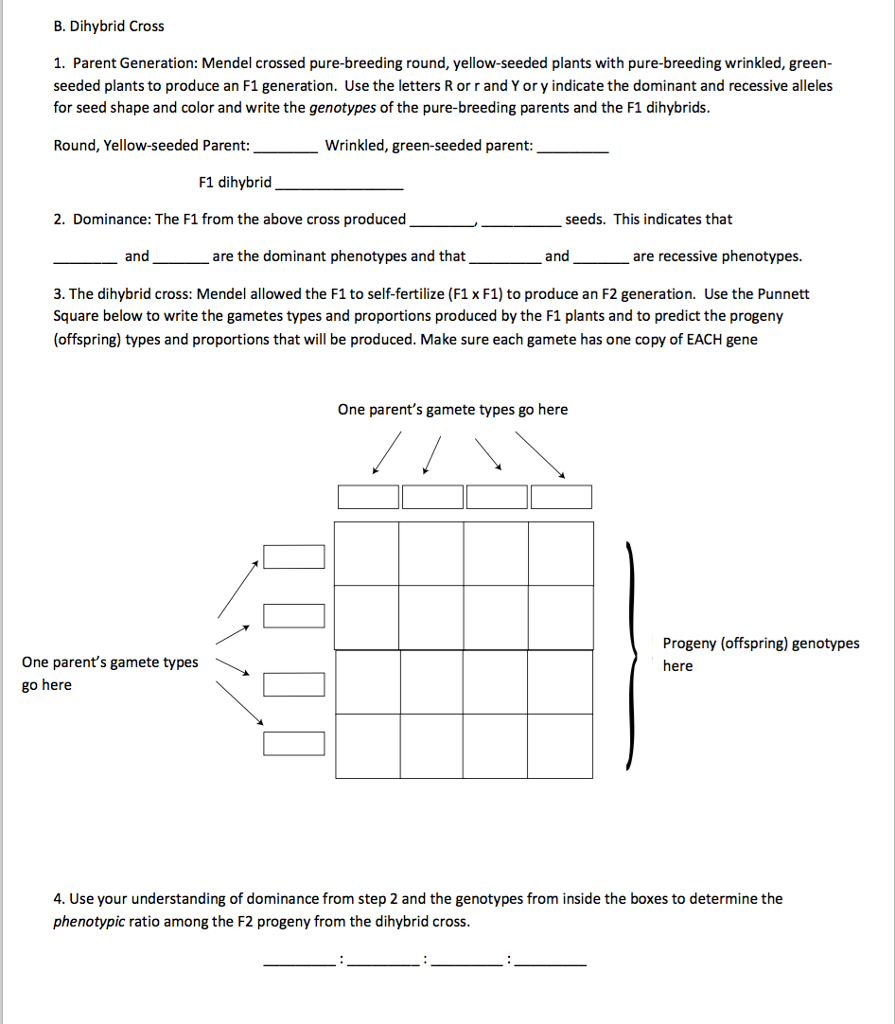
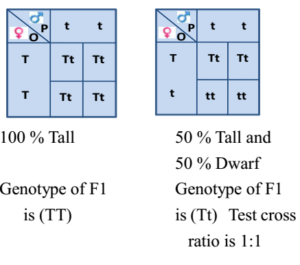
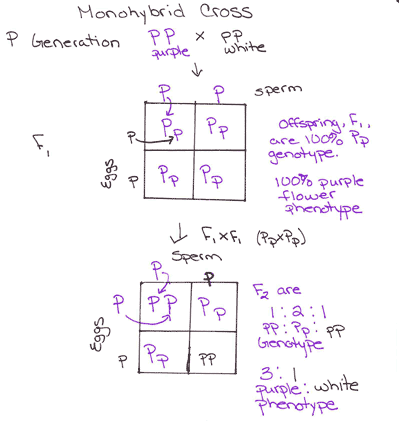
F1 Generation Ratio
It comes as handy if you want to calculate the genotypic ratio the phenotypic ratio or if youre looking for a simple ready to go dominant and recessive traits chartmoreover our punnet square maker allows you to calculate the probability that a rare.
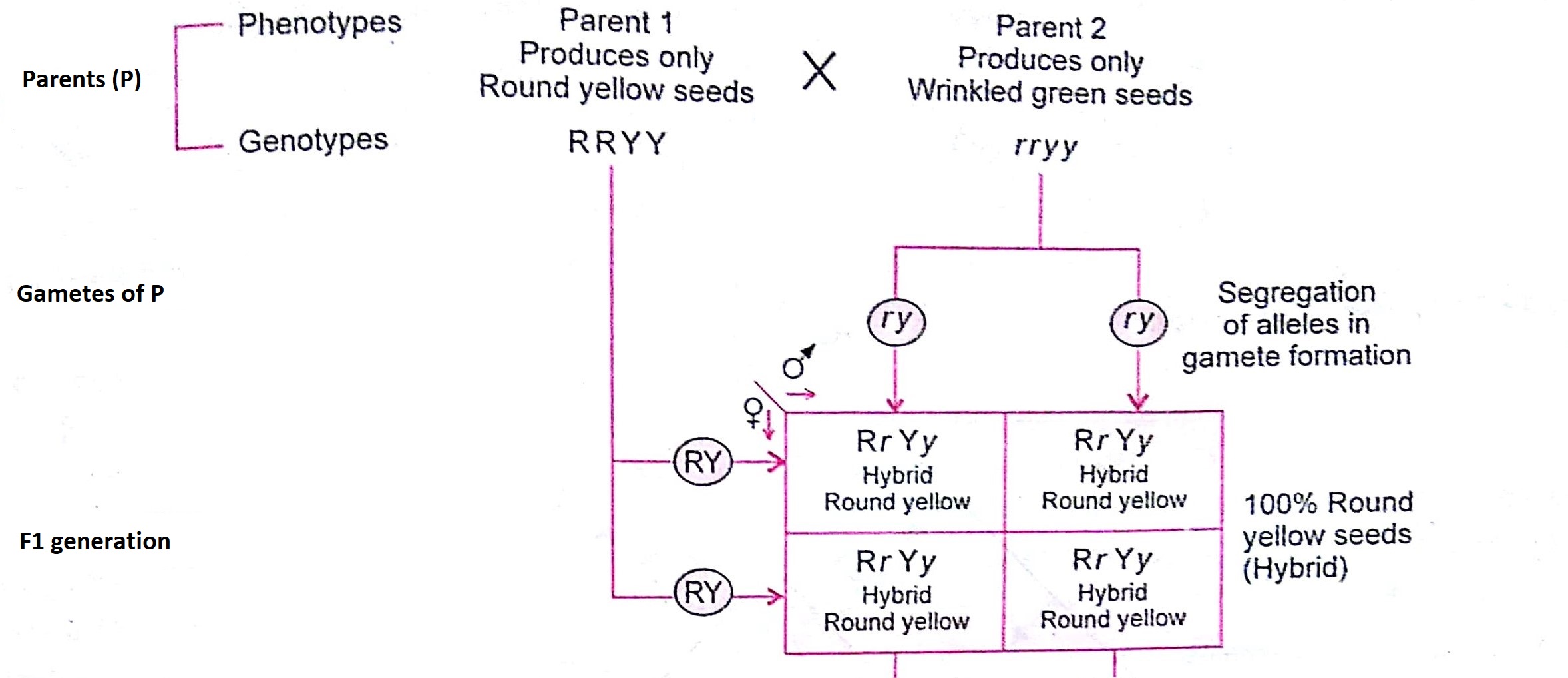
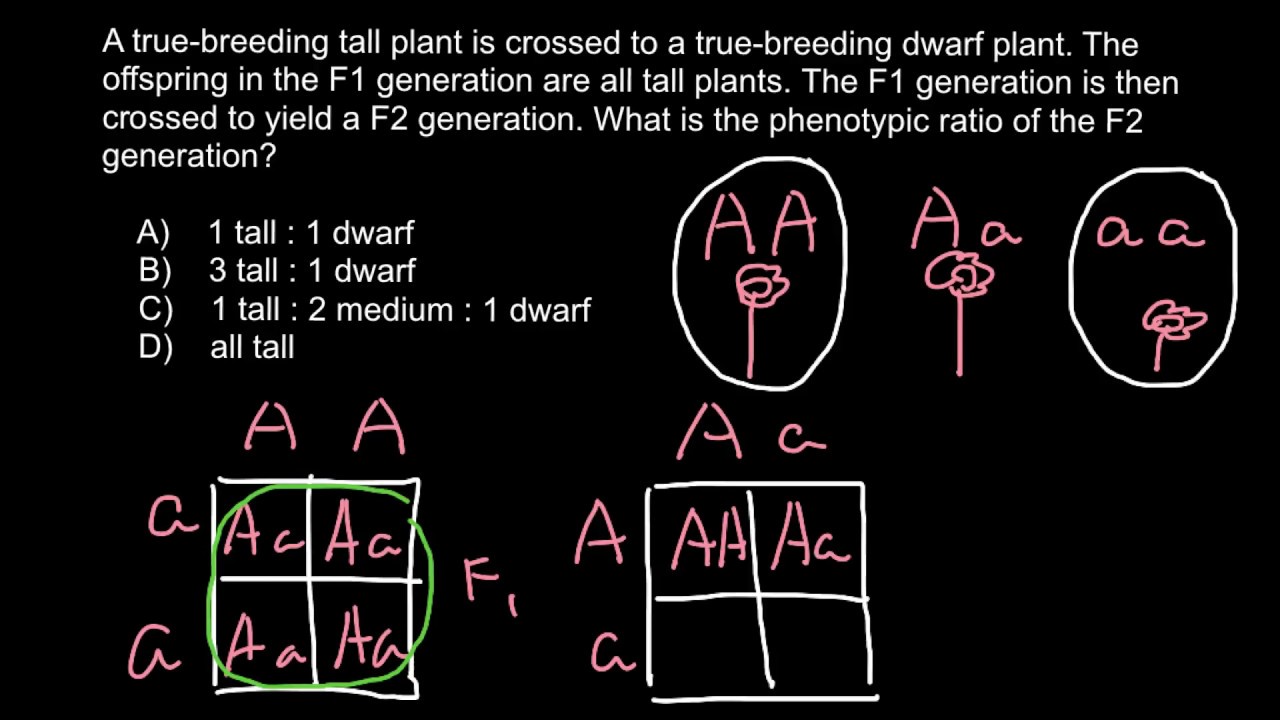
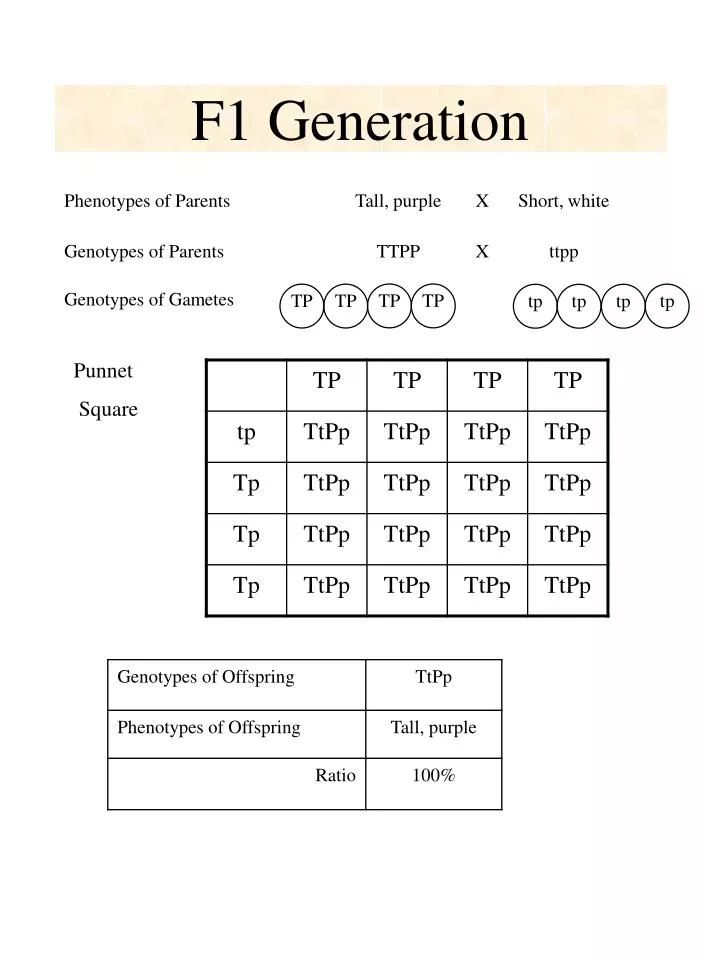
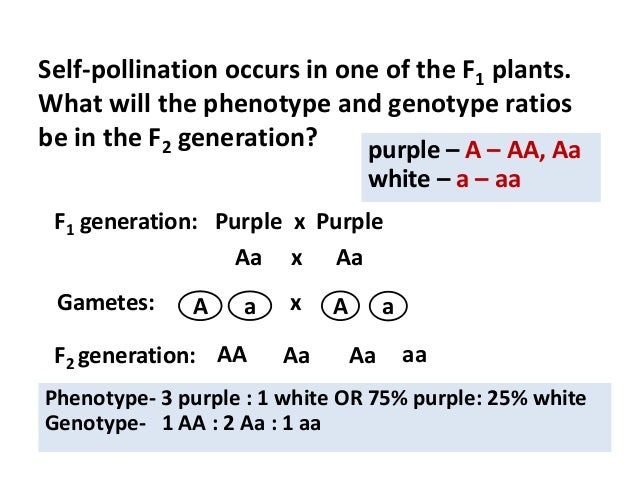
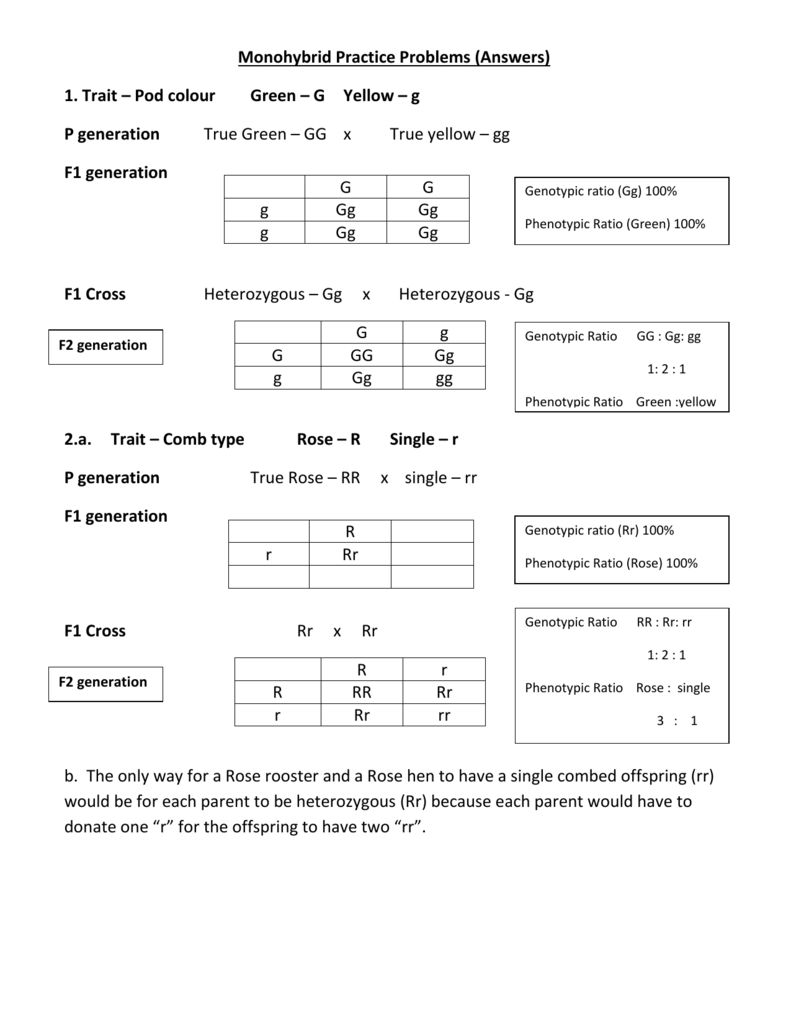
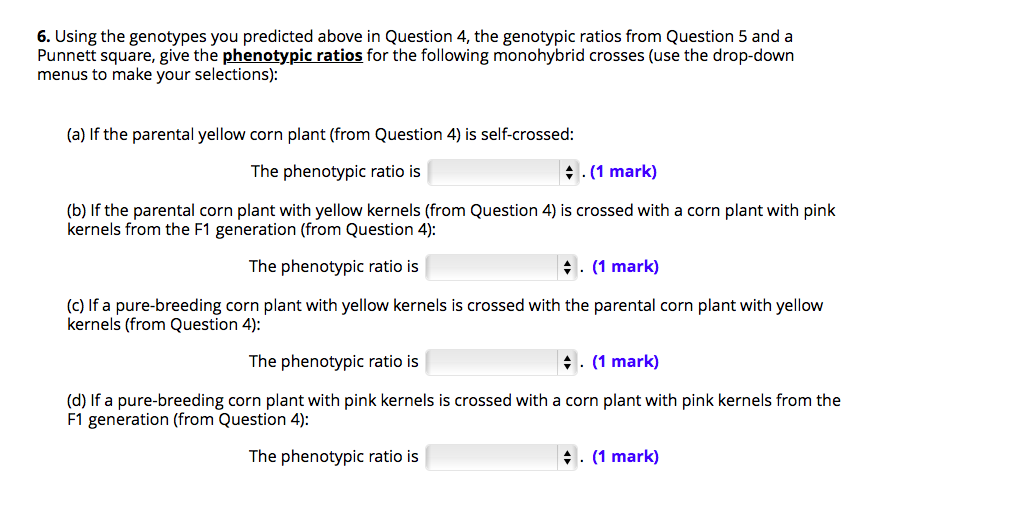
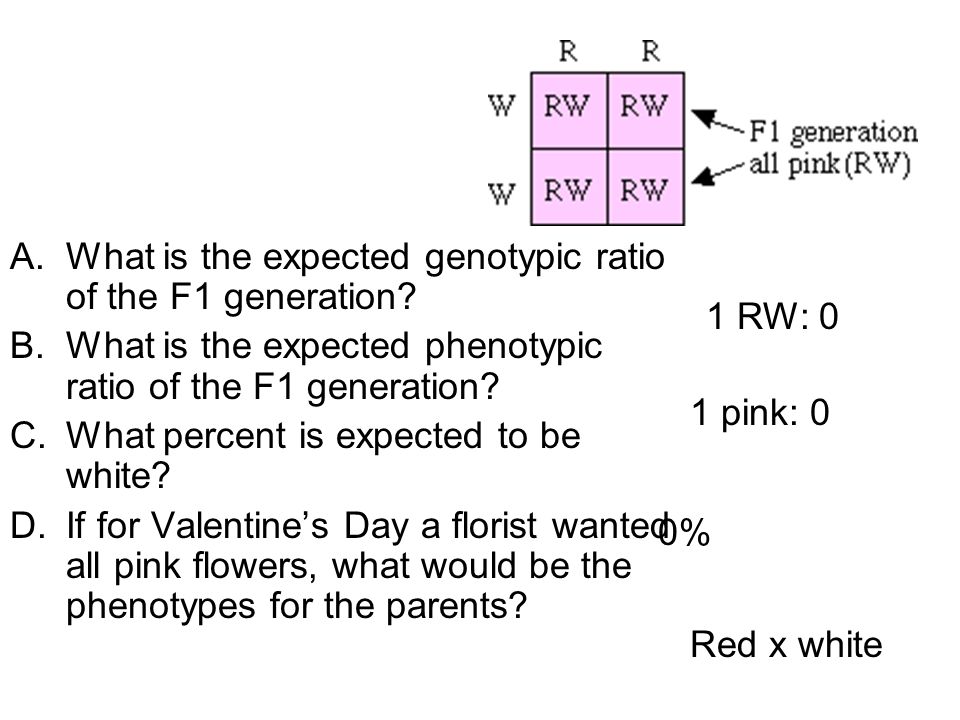
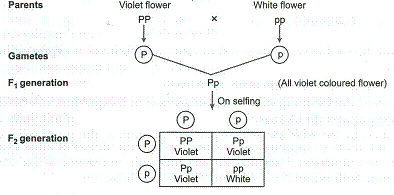
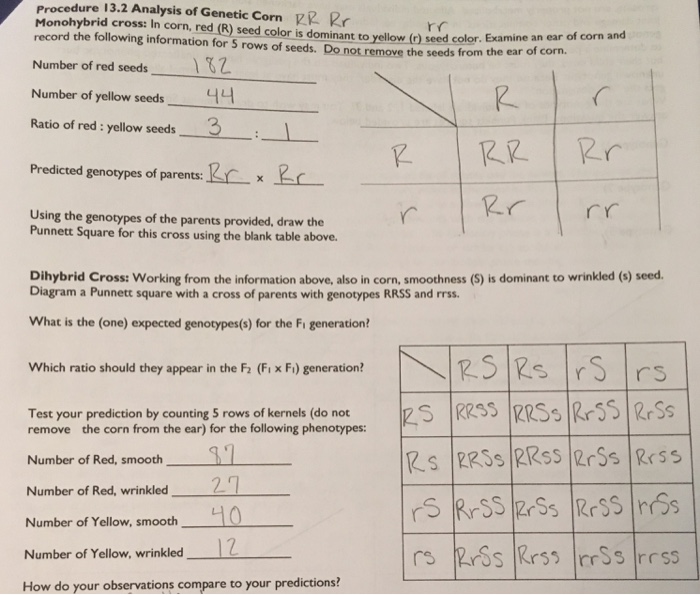
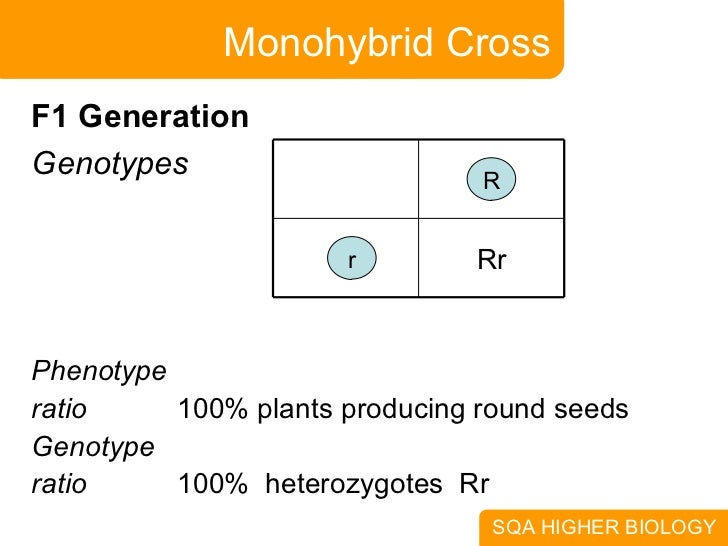
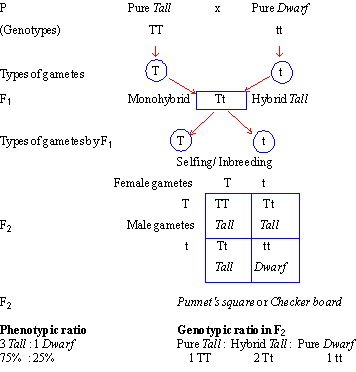
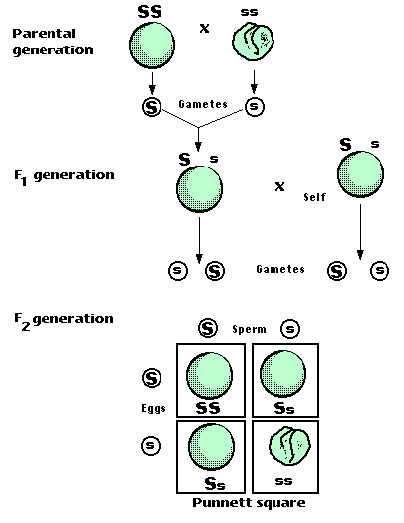
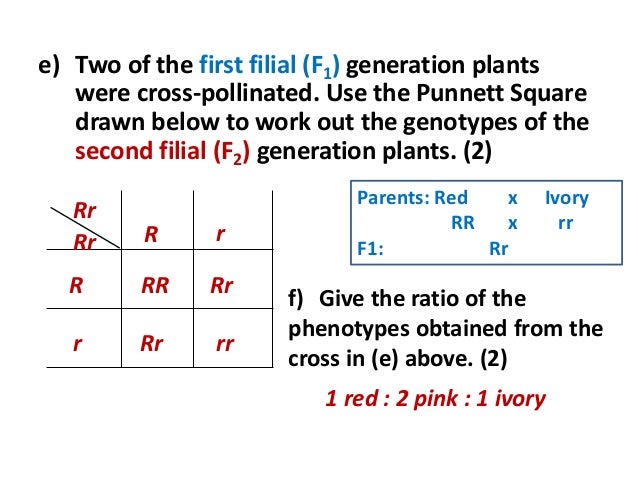
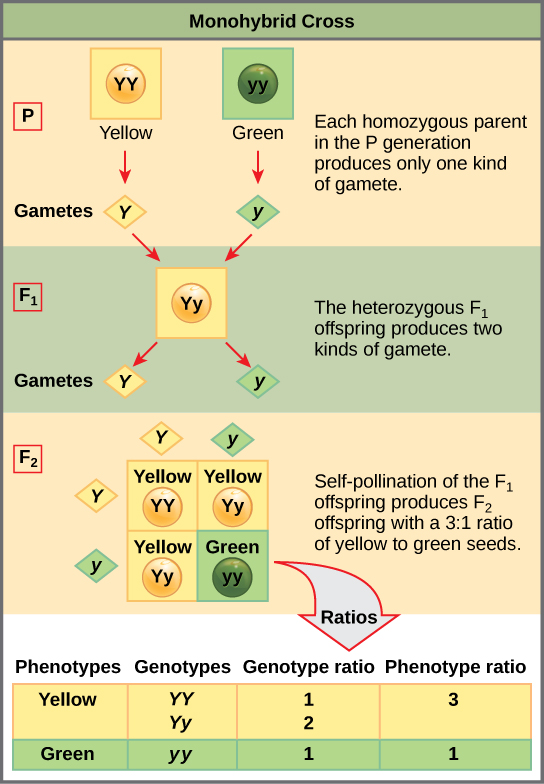
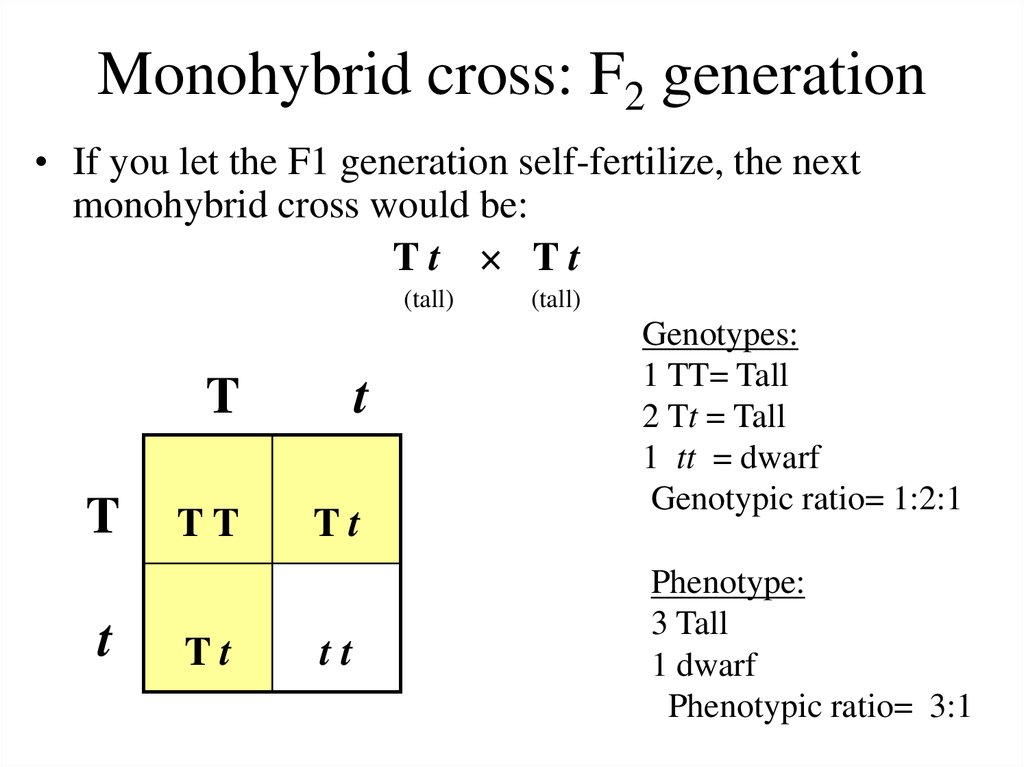
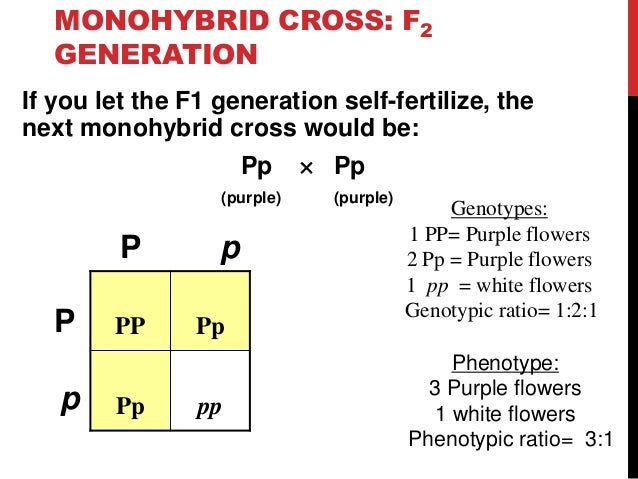
F1 generation ratio. Based on the results it was confirmed that a ratio could be formulated according to the phenotype of the f2 generation that is 31. Download the pdf of f1 vs f2 generation. The second generation the f2 produced 2459 red eyed females 1011 red eyed males and 782 white eyed males. As in a dihybrid cross the f1 generation plants produced from a monohybrid cross are heterozygous and only the dominant phenotype is observed.
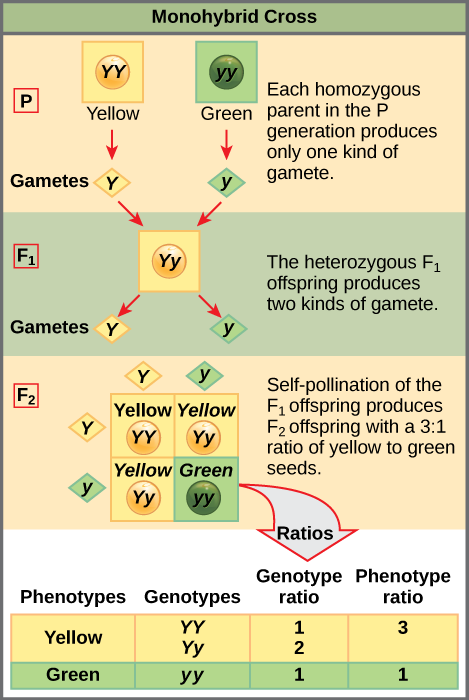
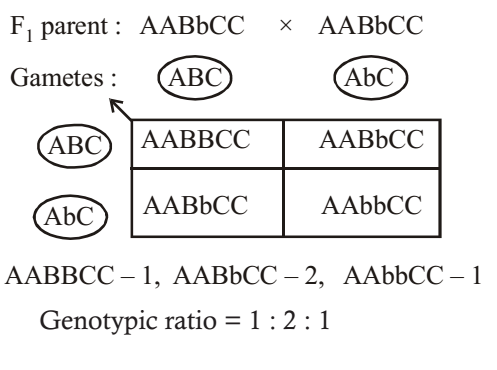
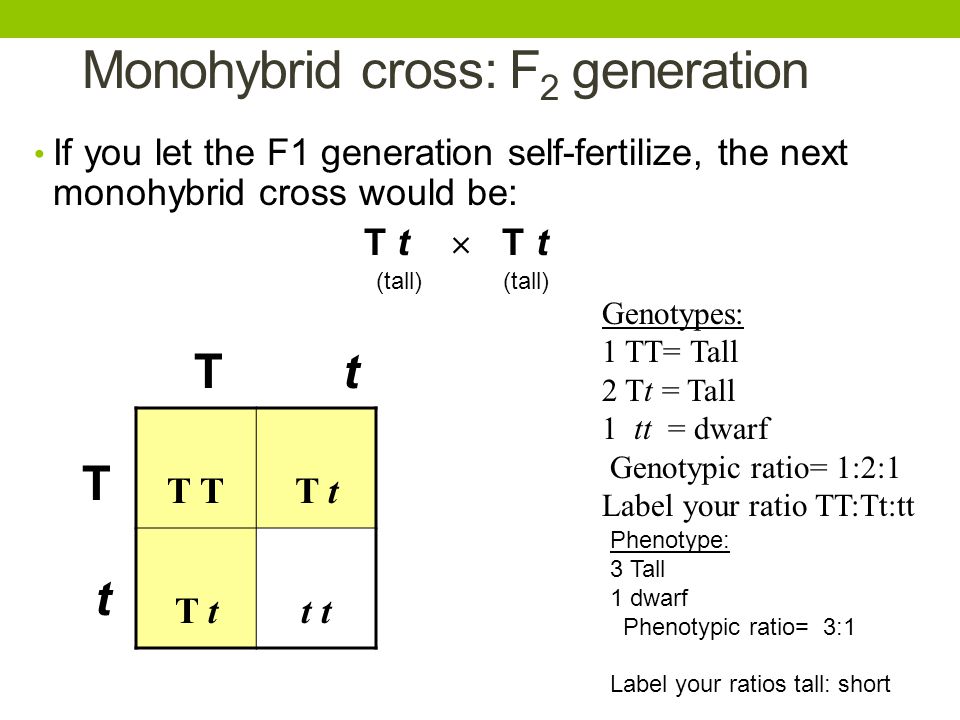
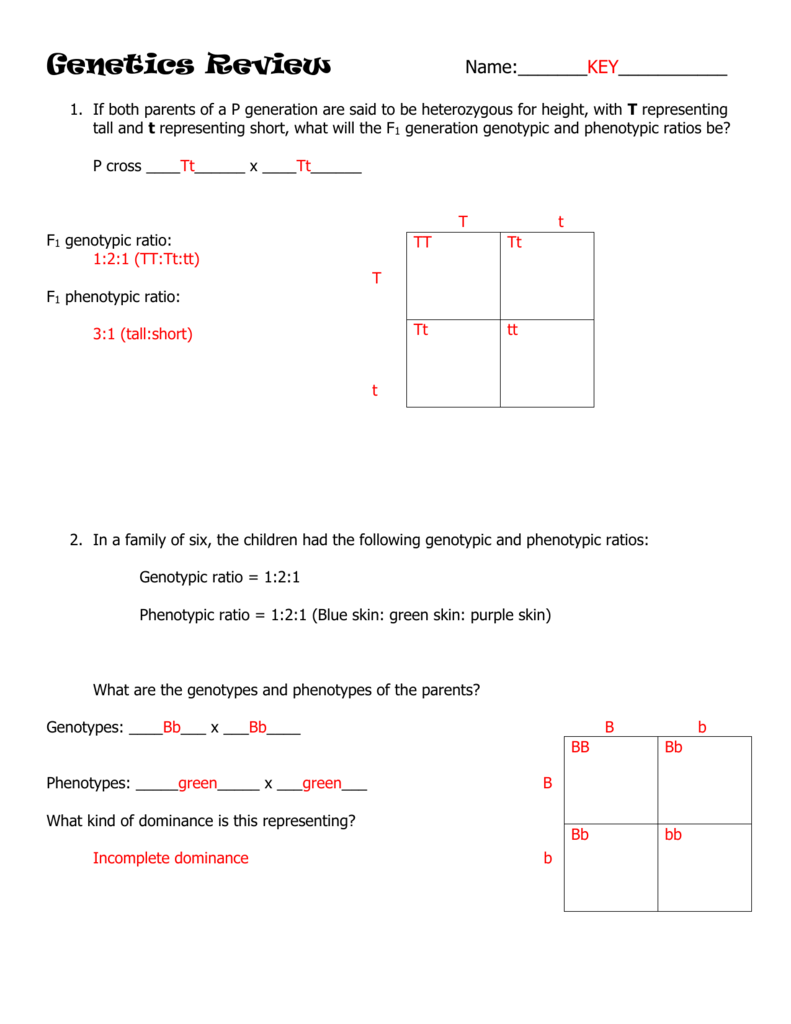
Well for the genotype. F2 generation is developed as a result of cross breeding of two f1 generation offspring together. The phenotypic ratio of the resulting f2 generation is 31. First generation is 100 heterozygous ww x ww all ww.
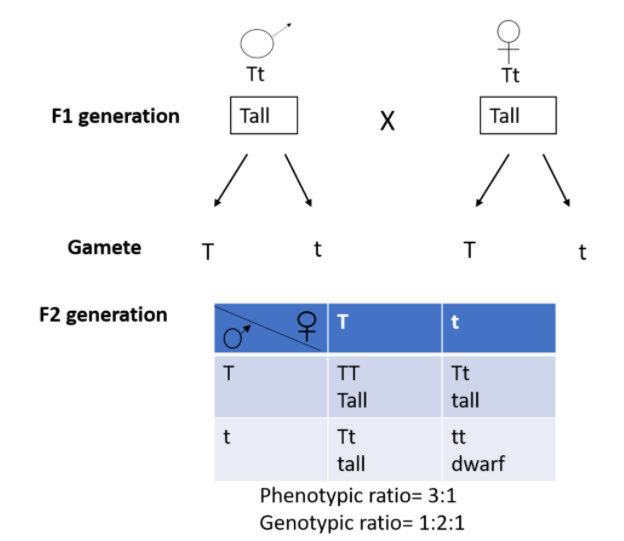
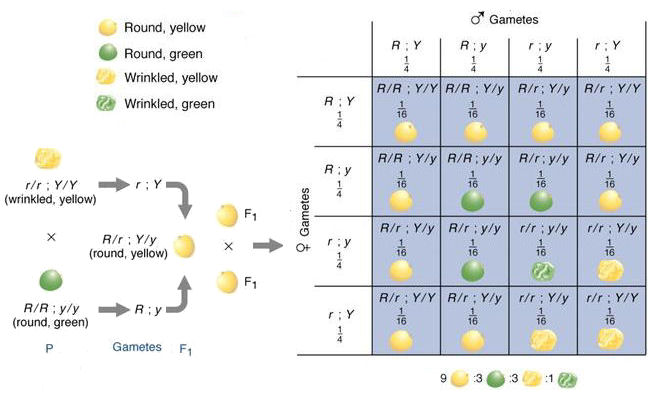
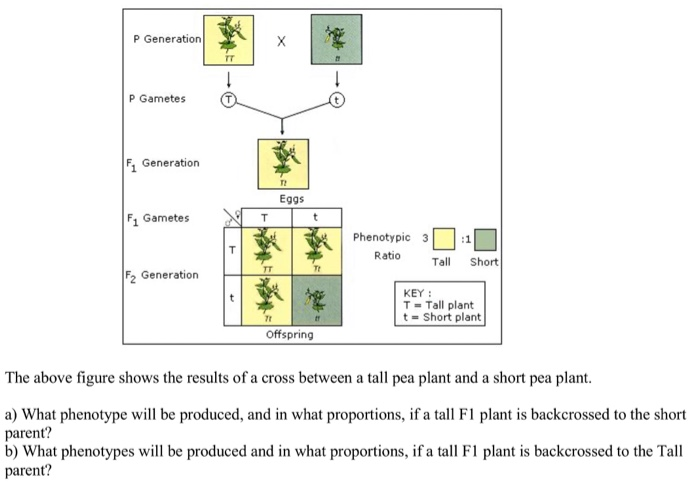
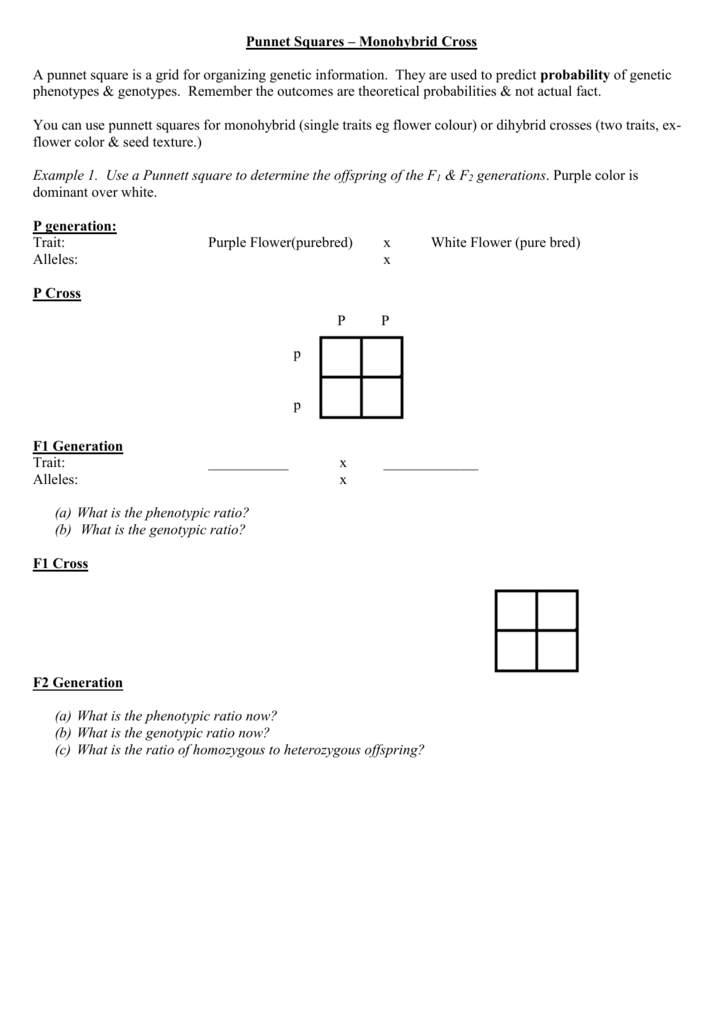
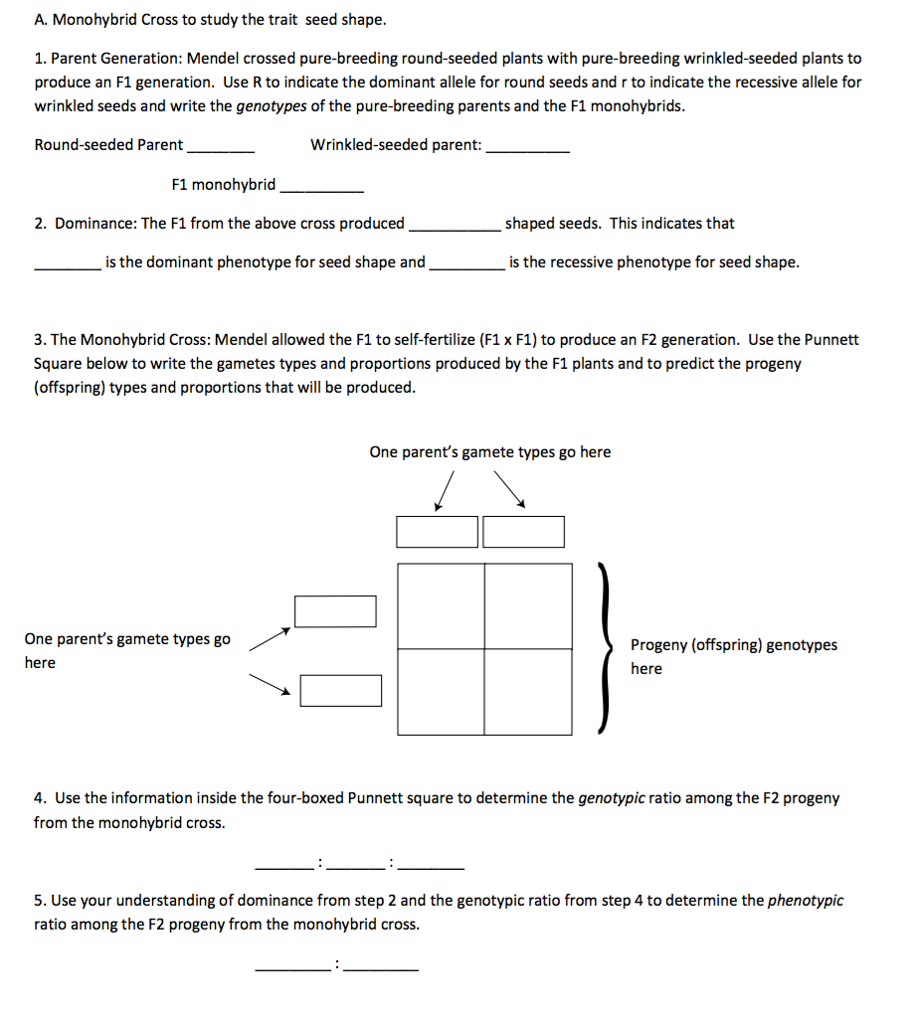
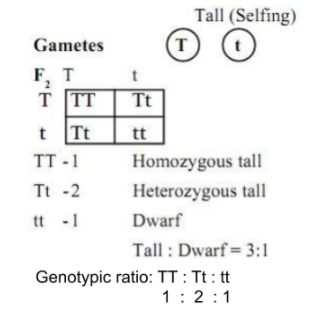
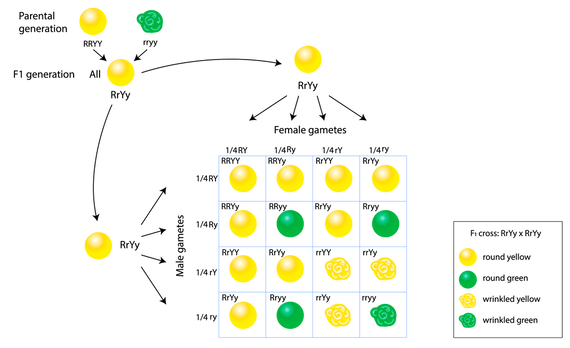
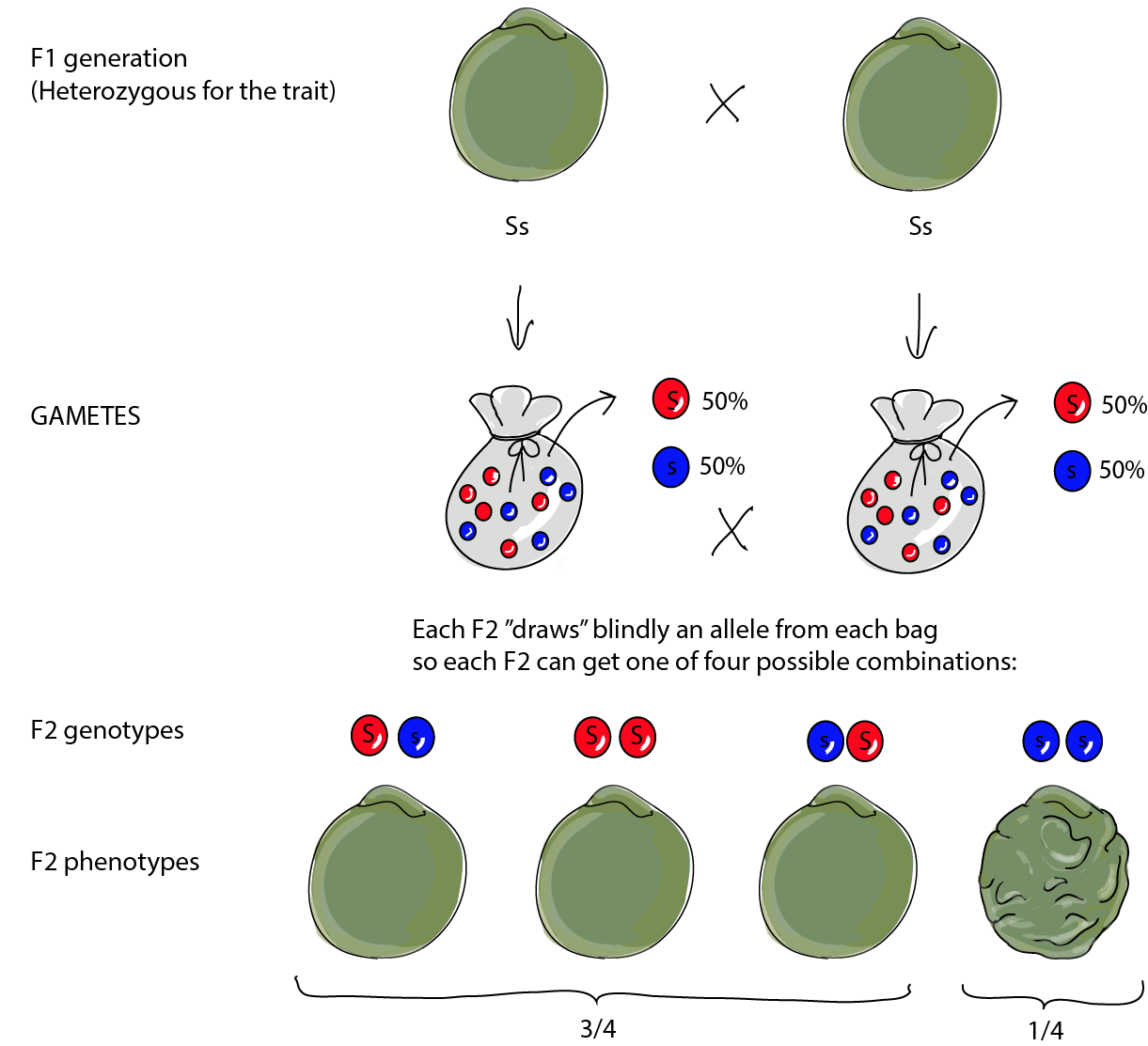
As we saw last time if we start with true breeding parents one homozygous dominant one homozygous recessive all of the f1 progeny will be heterozygous and show the dominant phenotype and then these will give rise to a 31 ratio of phenotypes in the f2 generation in a monohybrid cross and to a 9331 ratio of phenotypes in the f2 generation in a dihybrid cross. For the phenotypic ratio there needs to be info about the traits. One third 193565 of the round f1 seeds produced only round seeds in the f3 generation but two thirds 372565 of them produced both types of seeds in the f3 andonce againin a 31 ratio. Mendel showed that the 31 ratio of yellow pod to green pod plants could only be obtainable if both parents carried a copy of both the yellow and green alleles and that the yellow allele had to be dominant over green.
One third of the round seeds and all of the wrinkled seeds in the f2 generation were homozygous and produced only seeds of the same phenotype. This is the difference between f1 and f2 generation. Modern scientists now describe the cross of mendels f1 generation as a monohybrid cross. How does the inheritance of traits work.
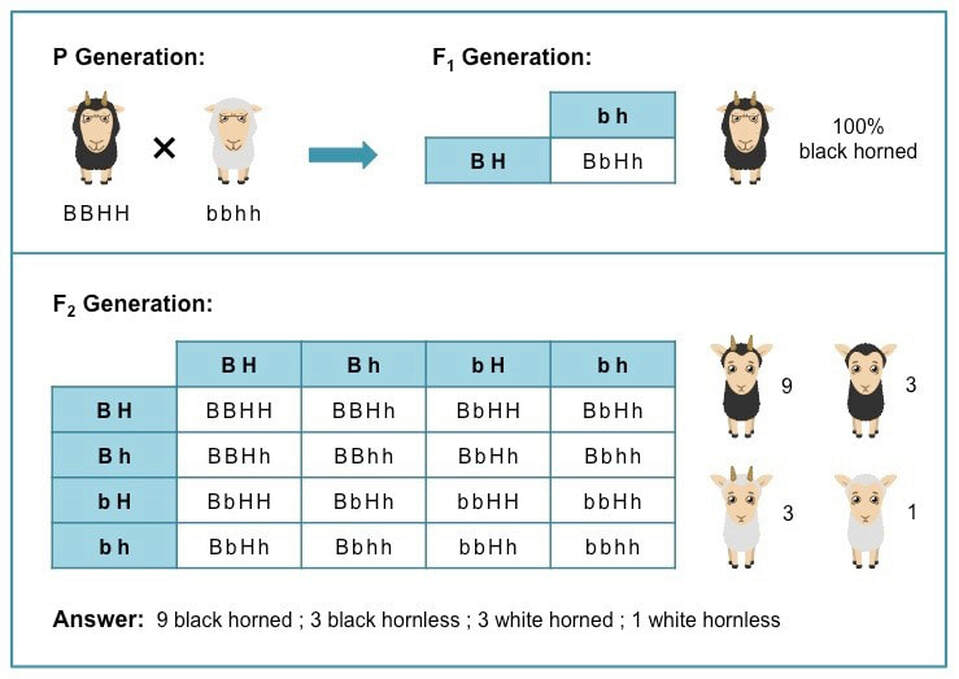
Next generation is ww x ww 1 ww. F1 generation example if you are crossing two parents that are true breeding meaning they each have homozygous traits one has dominant traits the other has recessive traits the f1. The first generation the f1 produced 1237 red eyed offspring and three white eyed flies all males. The phenotypic ratio is 9331 whereas the genotypic ratio is 121242121.

















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dihybrid_cross_ratios-58ef9ddd5f9b582c4d02ceb2.jpg)


































.PNG)