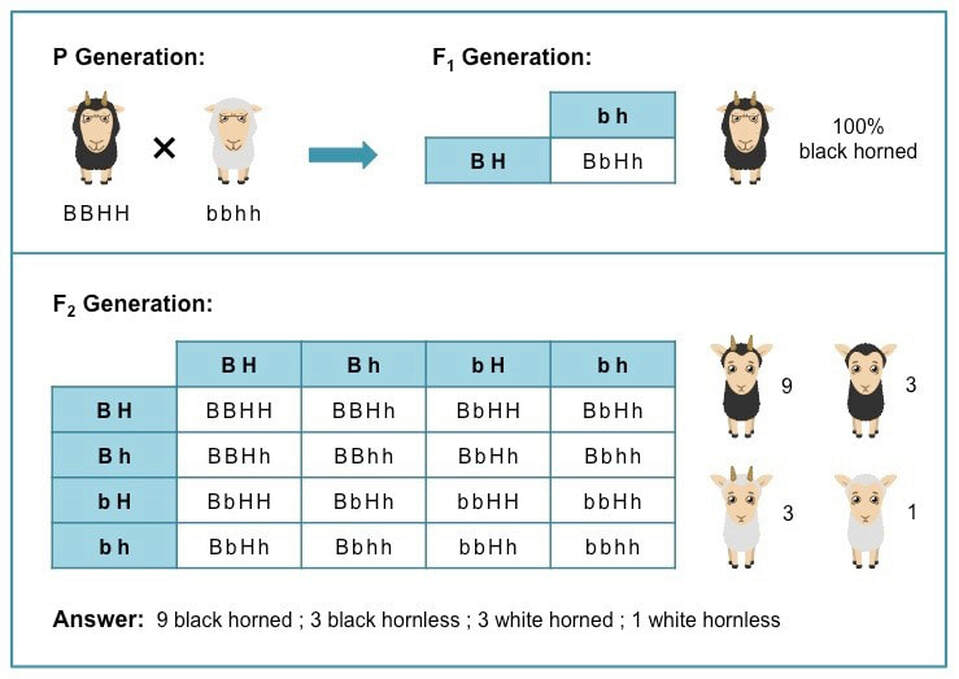
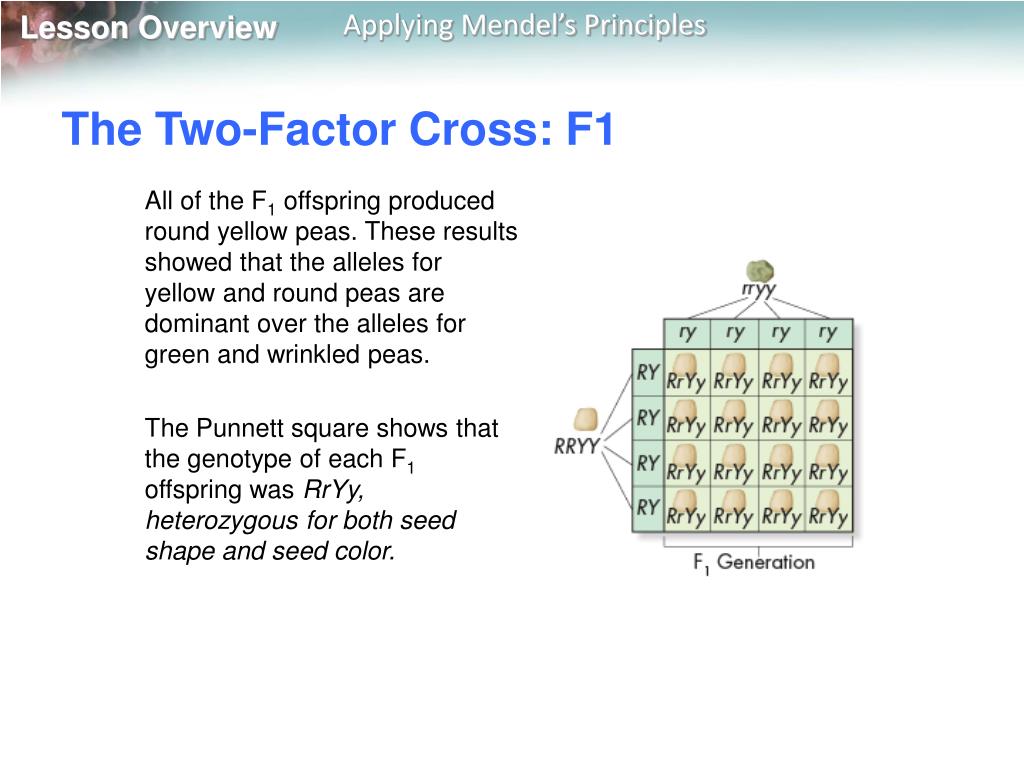
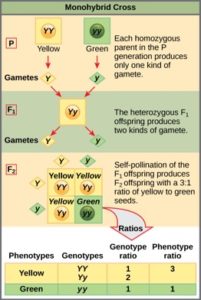
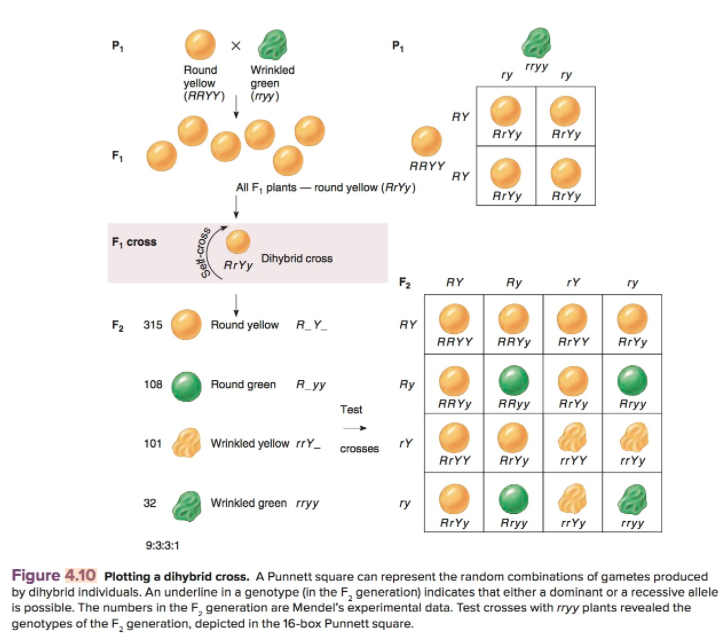
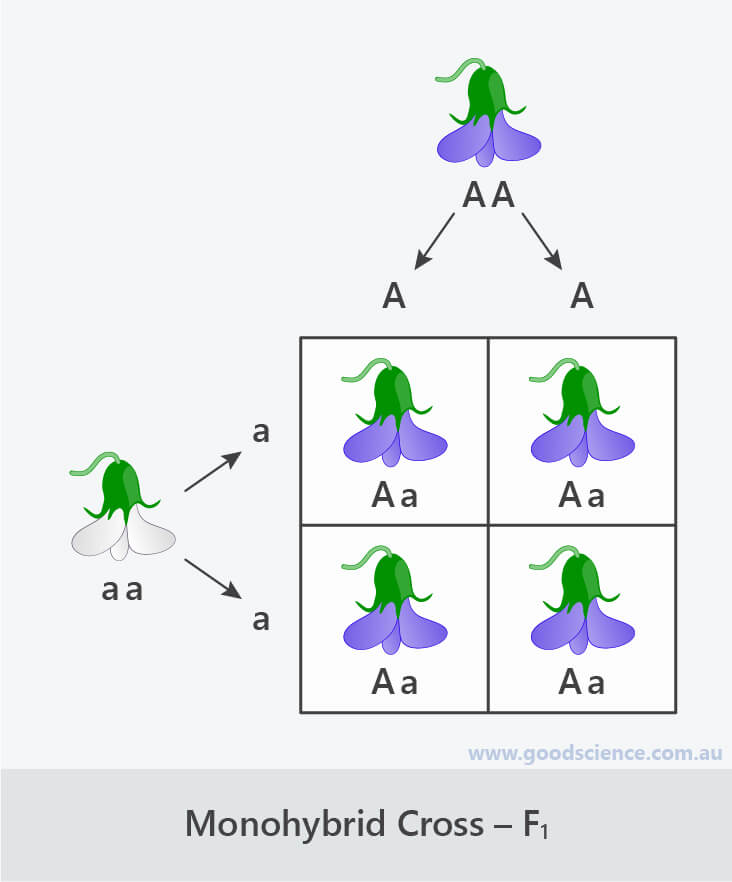
F1 Cross Punnett Square
Drag pink labels onto the pink targets to indicate the alleles carried by the gametes sperm and egg.
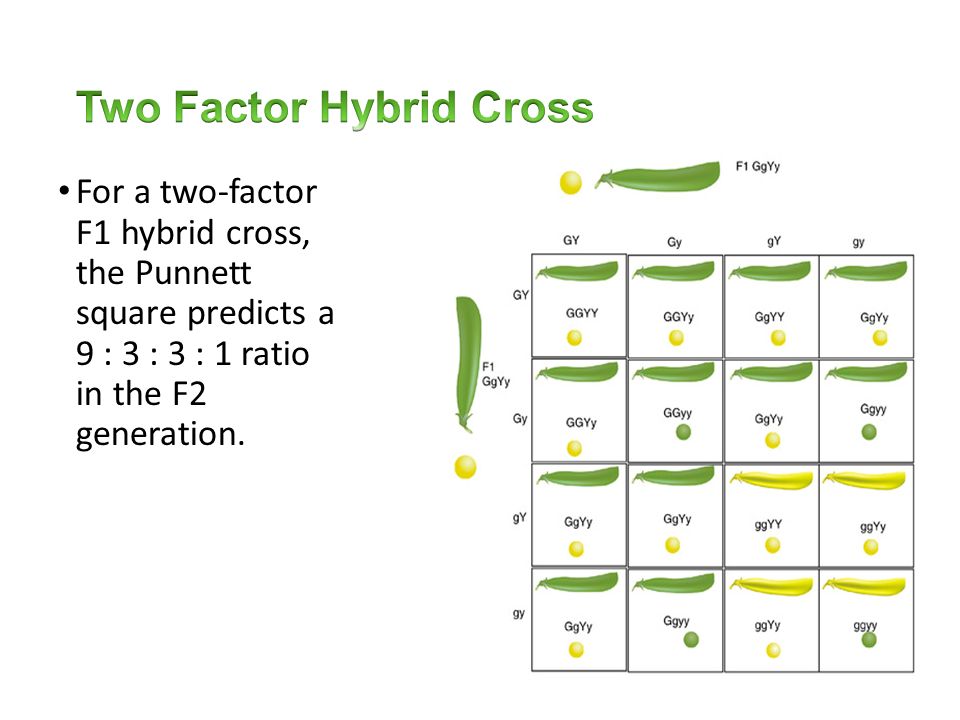
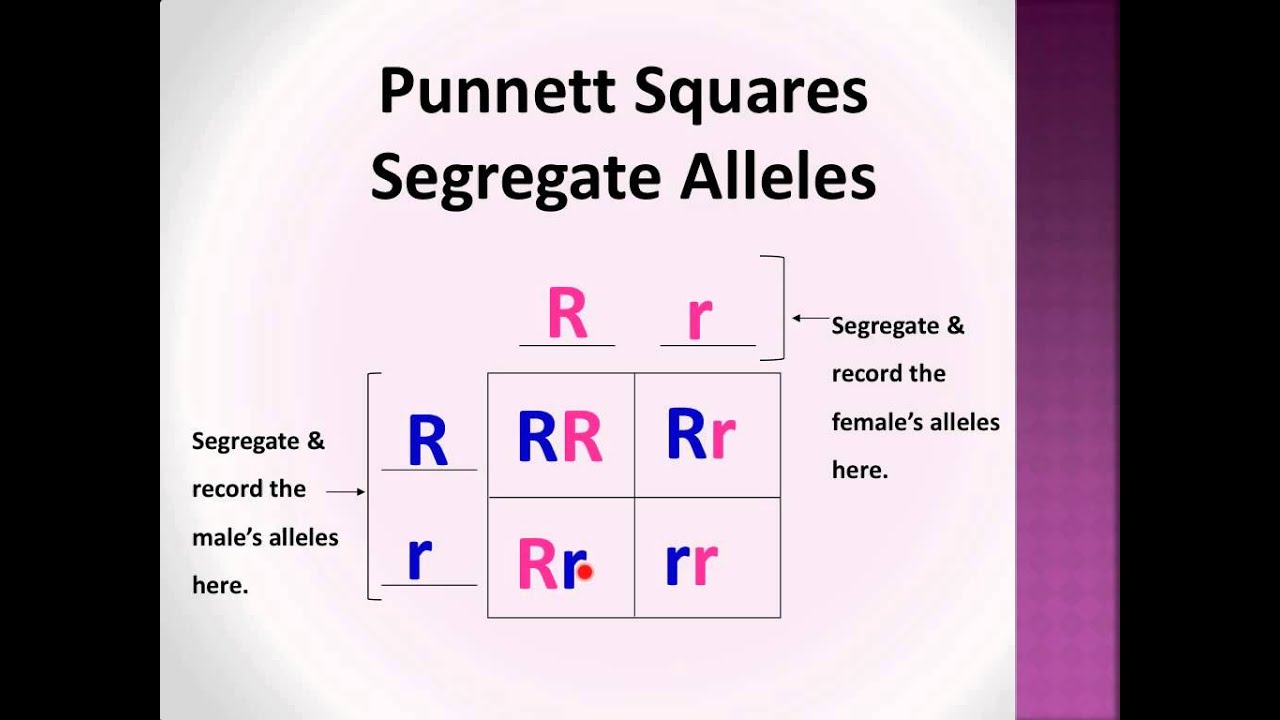
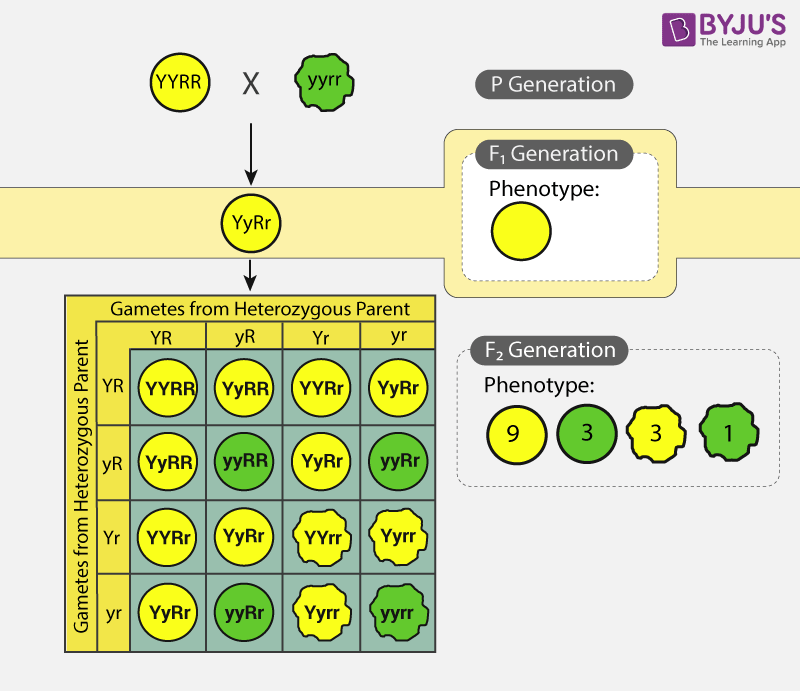
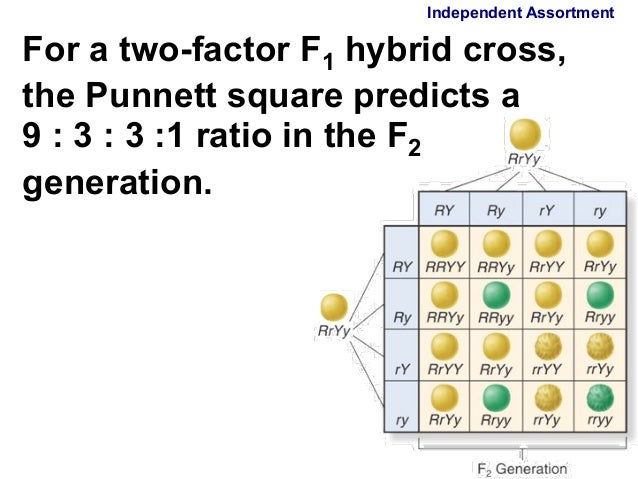
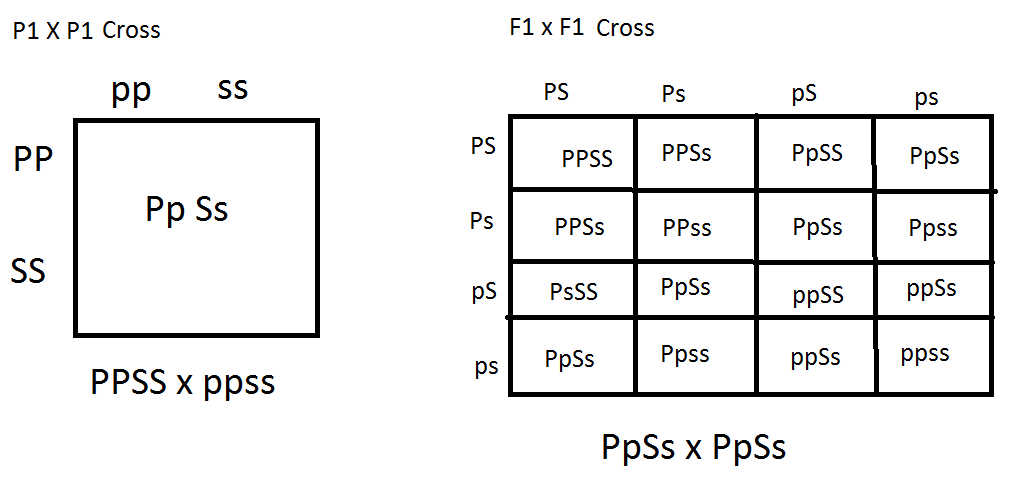
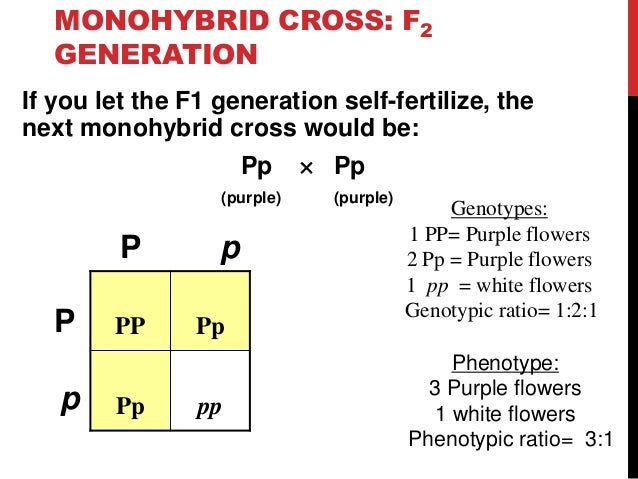
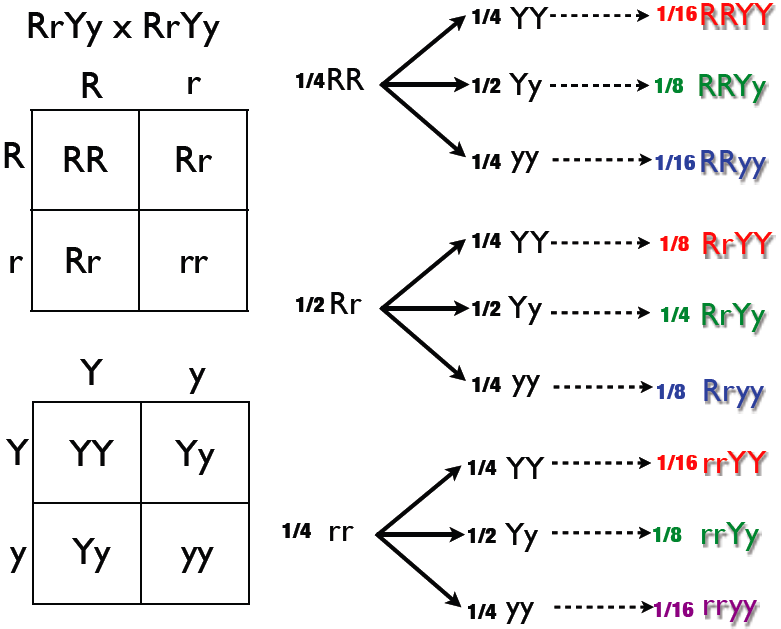
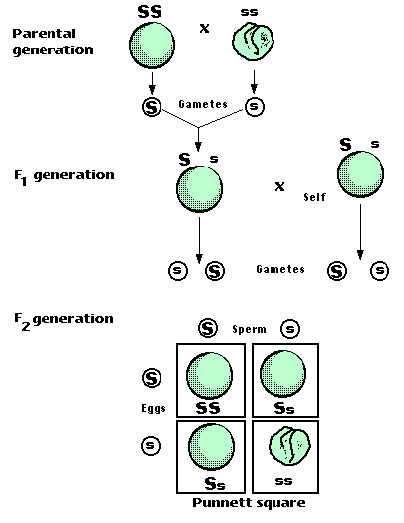
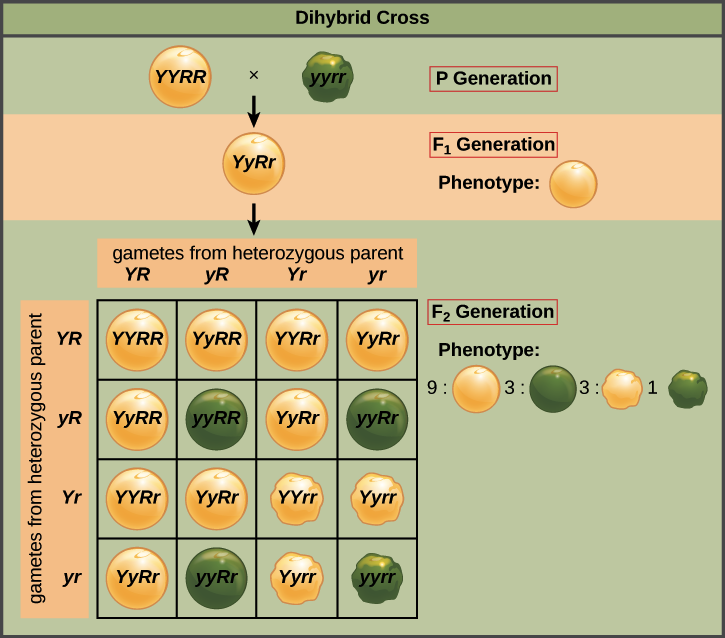
F1 cross punnett square. Reginald crundall punnett a mathematician came up with these in 1905 long after mendels experiments. Above the second punnett square shows the cross between the peas of the f1 generation. A punnett square for a tetrahybrid cross contains 256 boxes with 16 phenotypes and 81 genotypes. Geneticists write the alleles that each parent can contribute to the offspring along the sides of the square.
From punnett square in the offspring we have genotype ratio and probability. Student to fill in the blanks a alleles a alleles v f1 parent genes student fill in blank asked by cato on july 8 2012. Punnett square cheat sheet below is a sampling of punnett square problems that you will be expected to solve. This screencast explains punnett squares p f1 f2 generations.
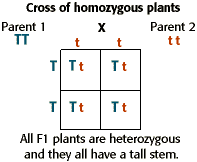
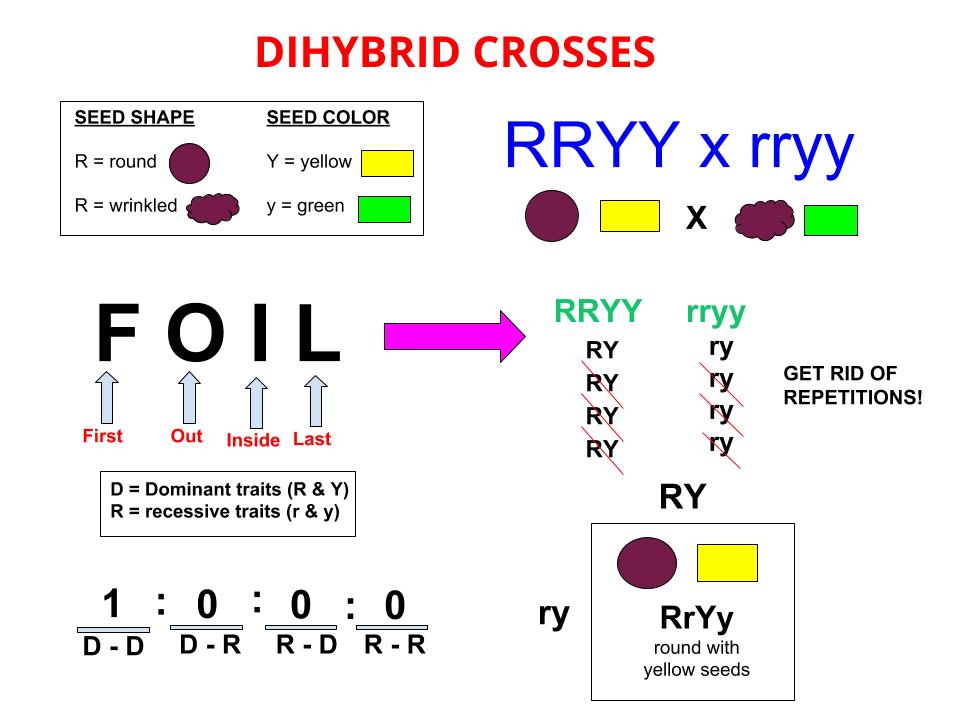
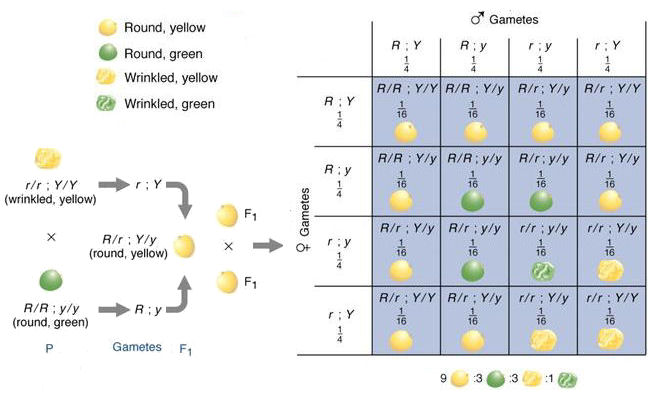
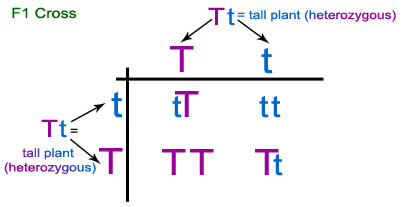
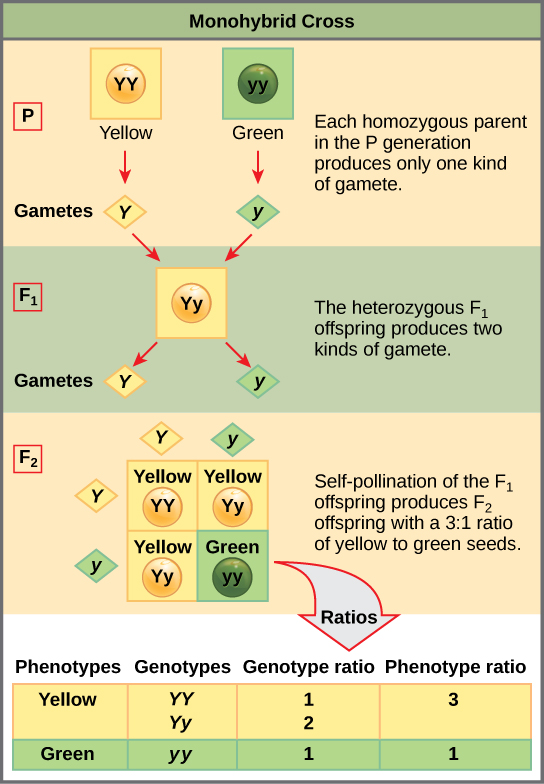
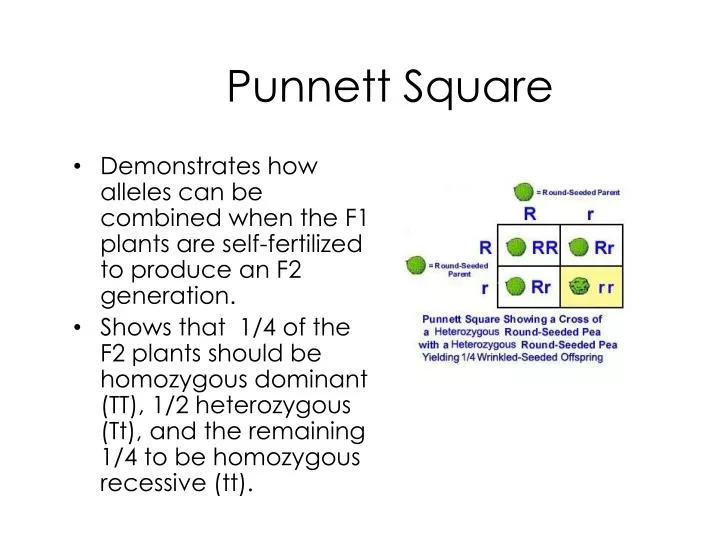
125gg this typical genotypes ratio 121 for a monohybrid crossdominant allele will mask the recessive allele that means that the organisms with the genotypes gg and gg have the same phenotype. The self cross of the f1 generation can be analyzed with a punnett square to predict the genotypes of the f2 generation. Given this complexity punnett squares are not the best method for calculating genotype and phenotype ratios for crosses involving more than one trait. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations to complete the punnett square for morgans f1 x f1 cross.
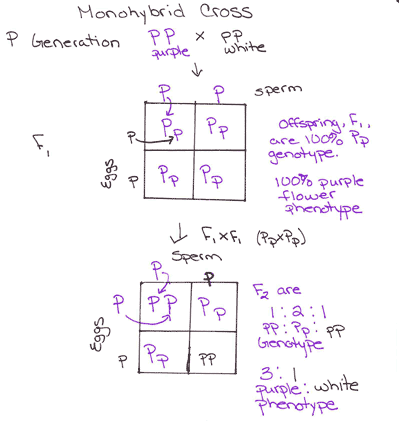
It is not known if a tall pea plant is homozygous or heterozygous a hybrid. This punnett square shows the cross between plants with yellow seeds and green seeds. Creating a punnett square and using it to determine traits of offspring is called performing a cross. Lets take a look at how punnet squares work using the yellow and green peas example from mendels garden experiments.
The cross between the true breeding p plants produces f1 heterozygotes that can be self fertilized. Punnett squares punnett squares are a useful tool for predicting what the offspring will look like when mating plants or animals. In order to do this you will also have to understand the meaning of the terms below. You decide to do a test cross to find.
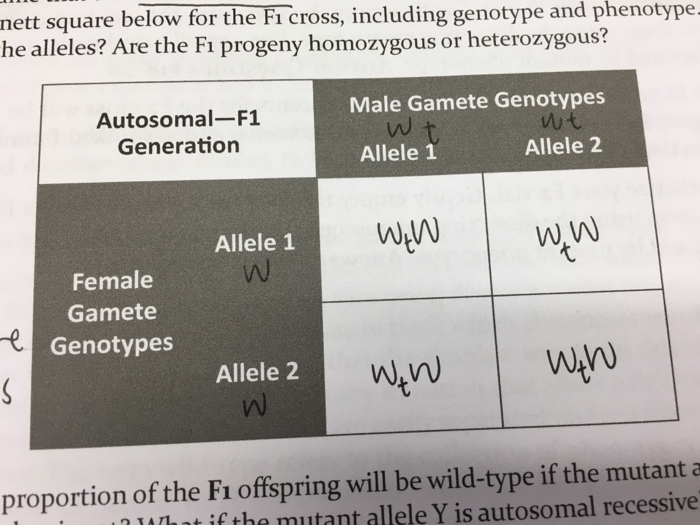
Each parent has two alleles for a trait and passes one along to its offspring. Punnett square for f1 cross c expected genetic outcomes f1 parent genes. A tool called a punnett square helps geneticists predict what kinds of offspring might result from a particular genetic cross. Tt or tt phenotype.
The physical characteristics of the particular trait. The punnett square below shows morgans cross of the f1 males with the f1 females.



/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg)