Dihybrid Cross F1 And F2
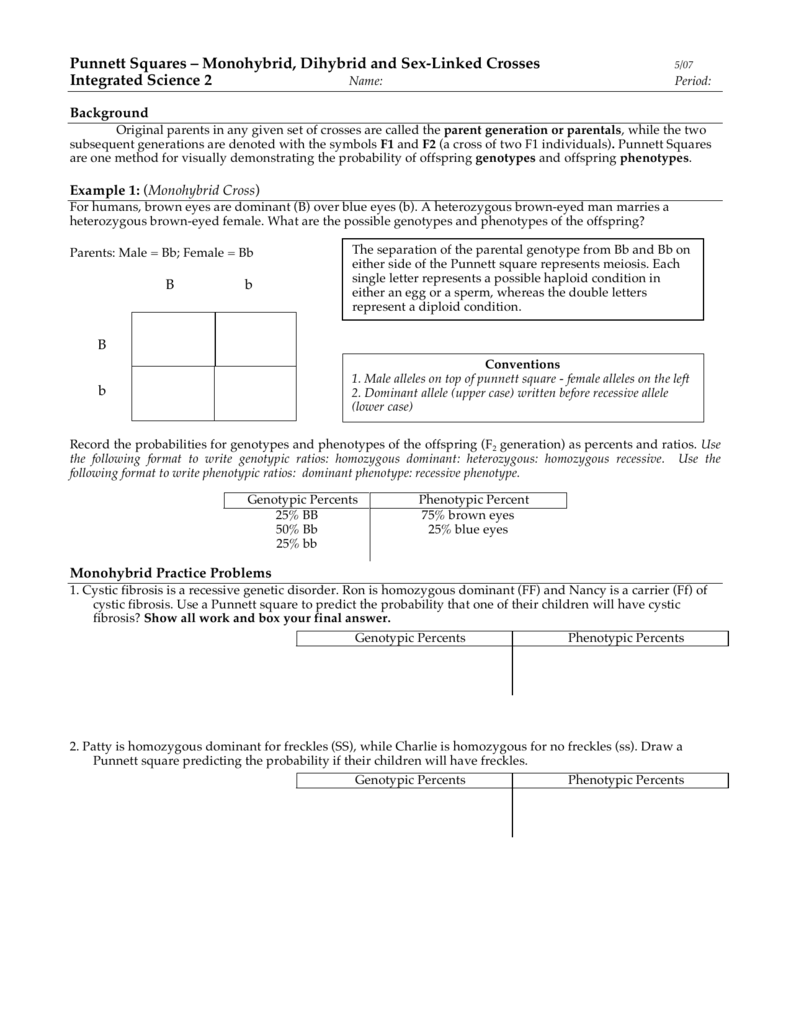
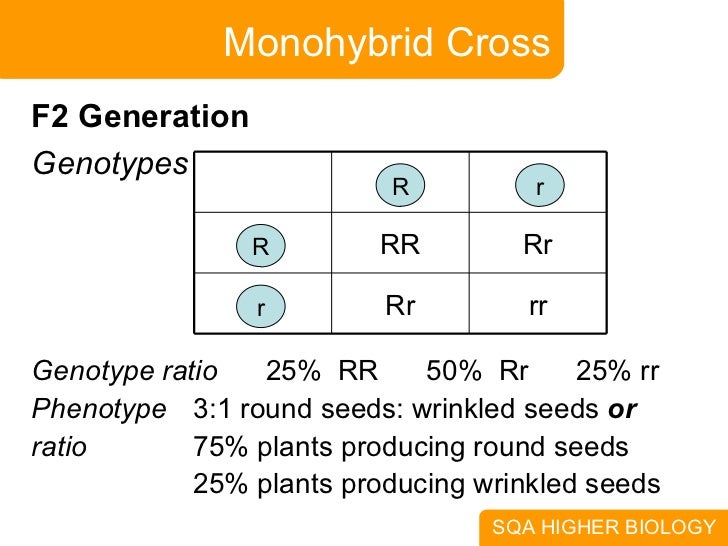
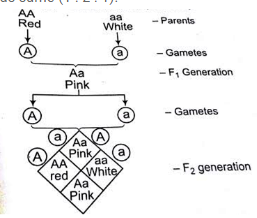
Thus in monohybrid cross f1 plants have similar genotype.

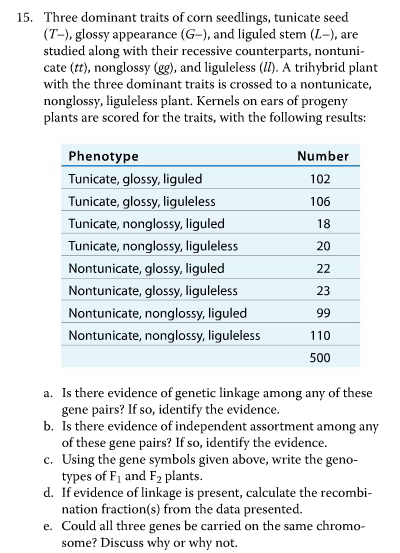
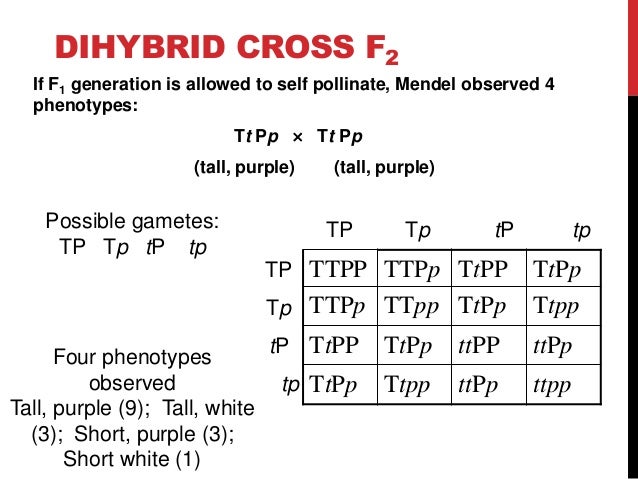
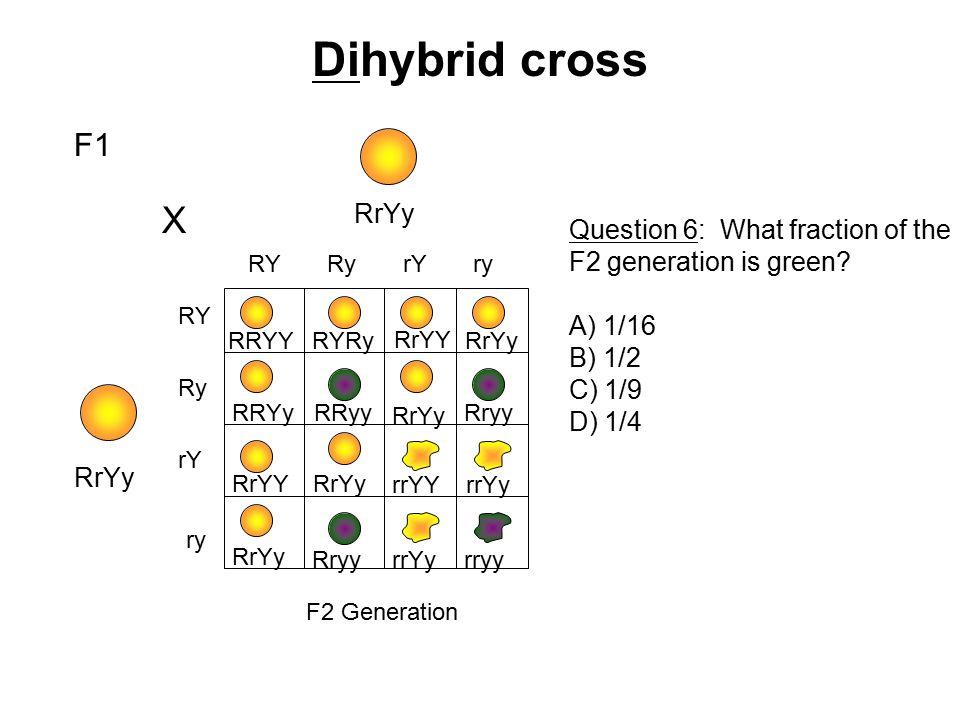
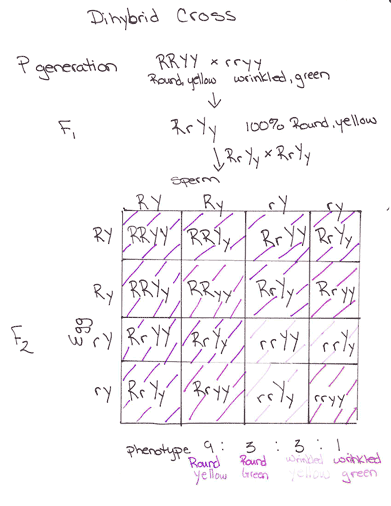
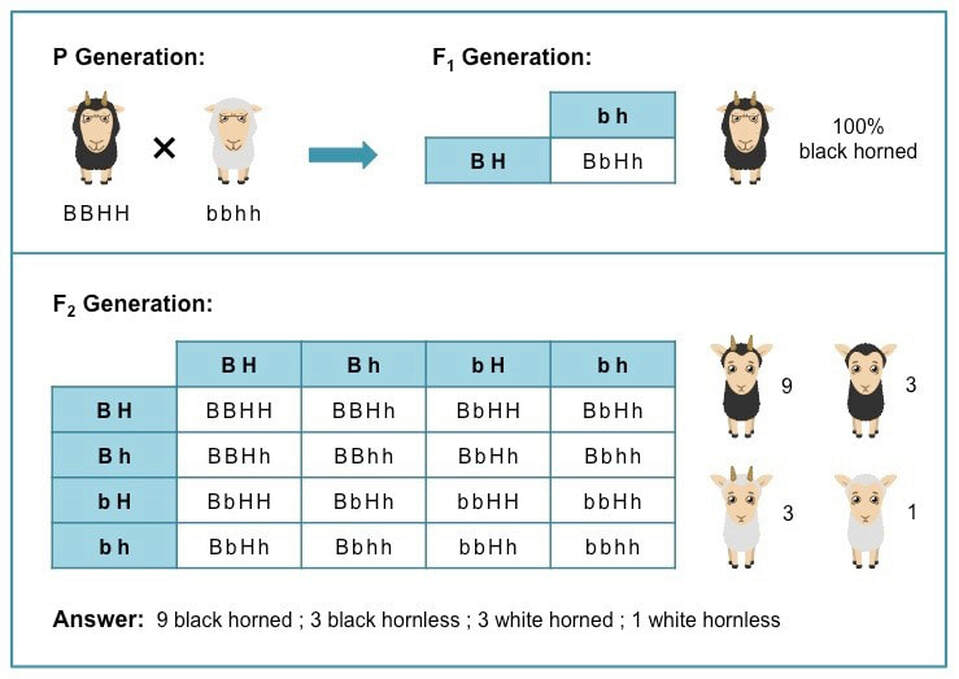
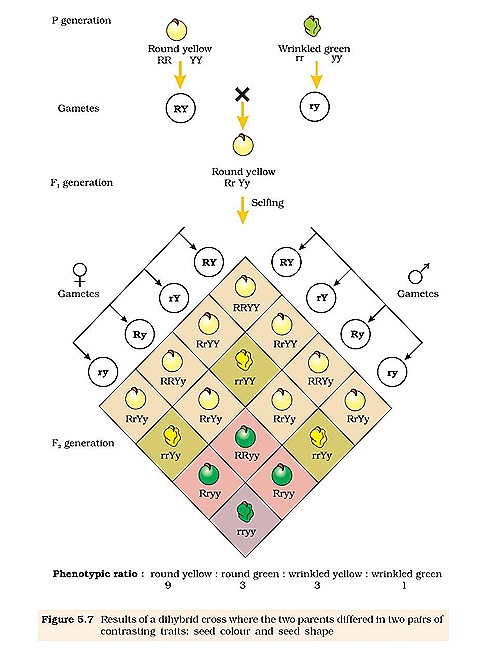
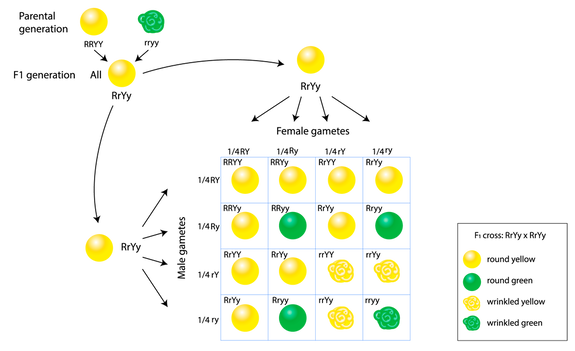
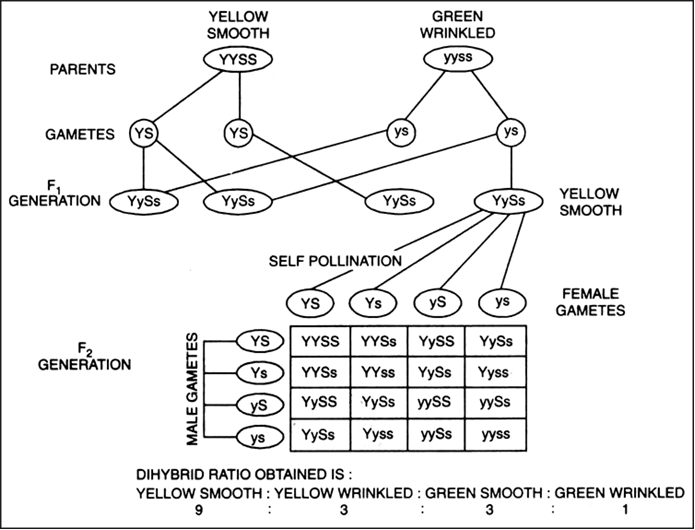
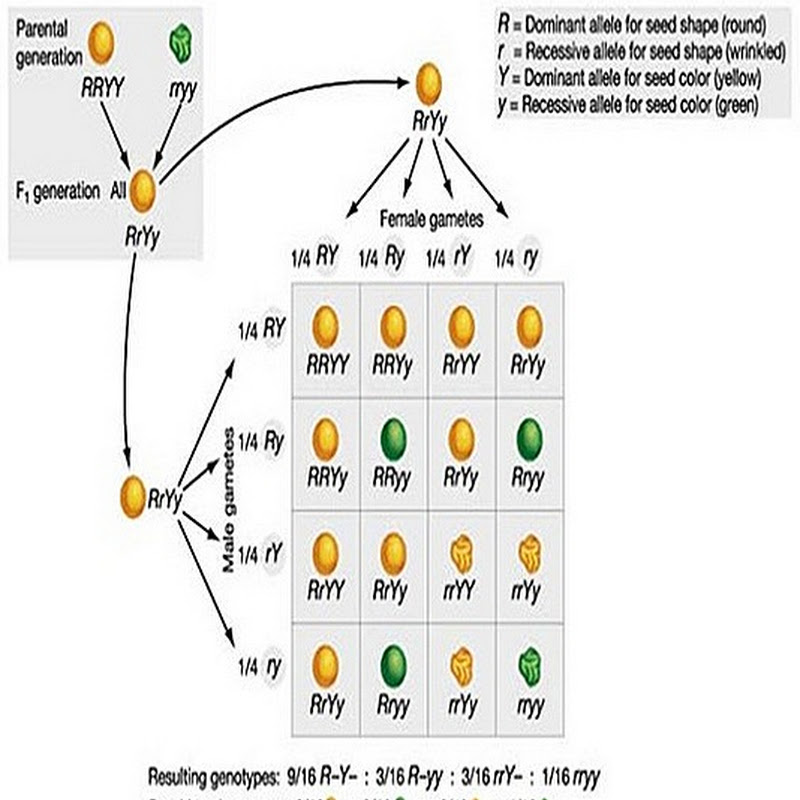
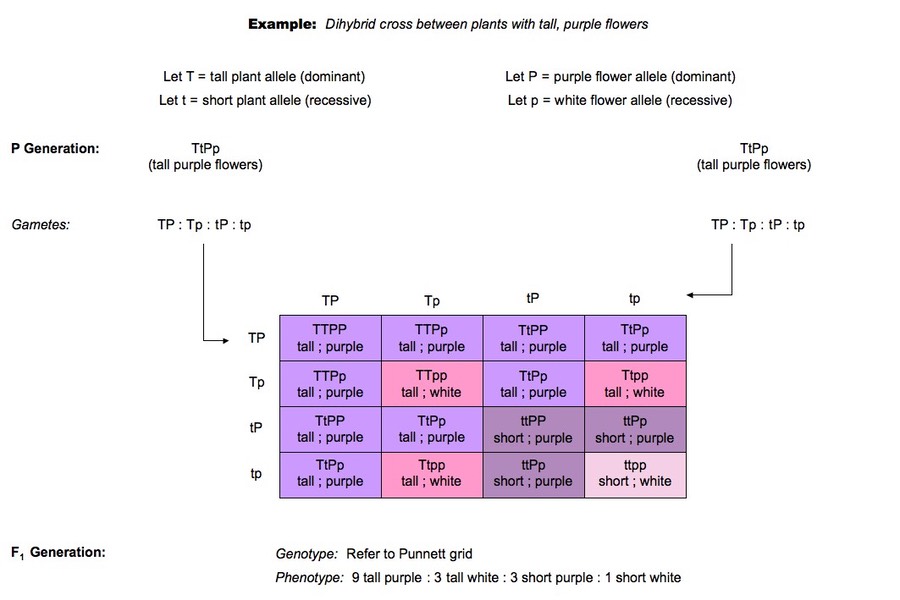
Dihybrid cross f1 and f2. The phenotypic ratio of the resulting f2 generation is 31. 316 tall plants with dented seeds. F1 and f2 generation are the two generations of the offspring of a dihybrid cross. Results of mendel os dihybrid crosses f2 generation contained both parental types and recombinant types f2 showed 4 different phenotypes.
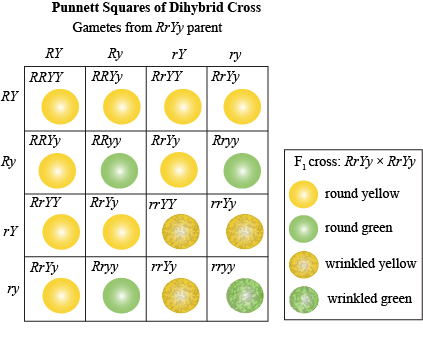
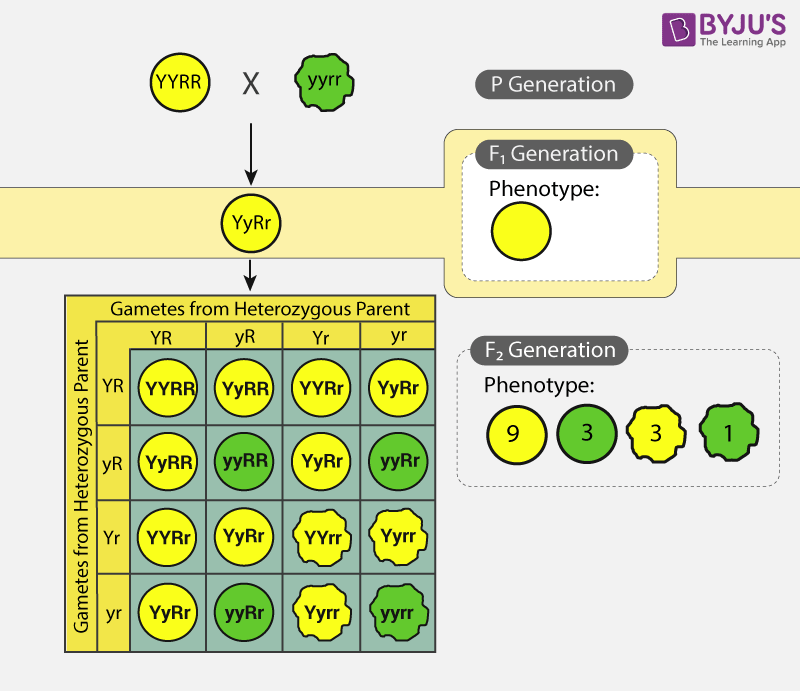
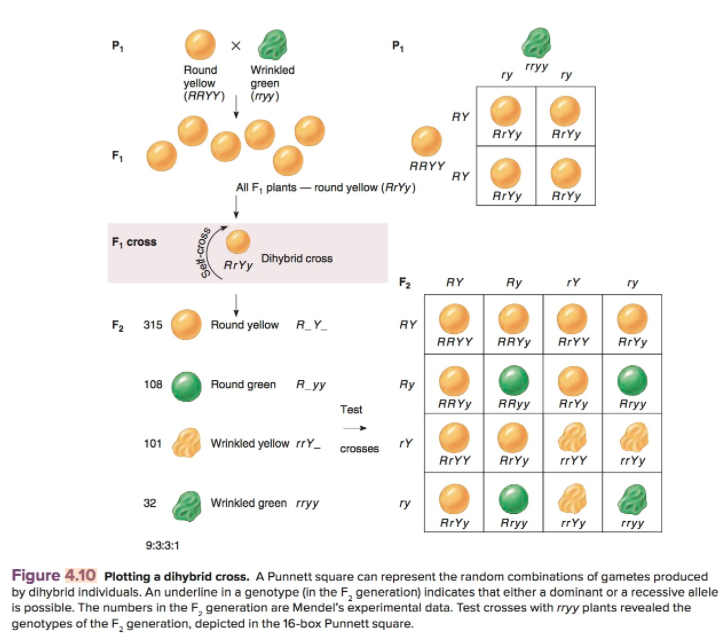
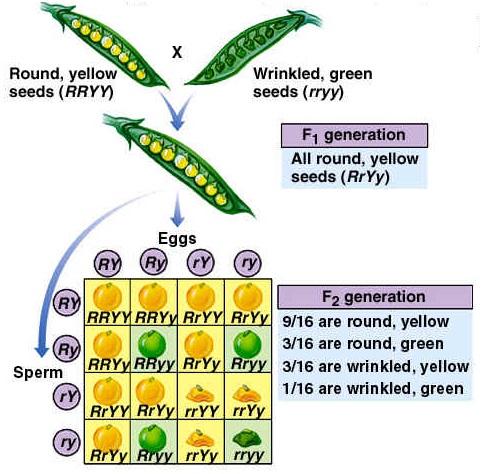
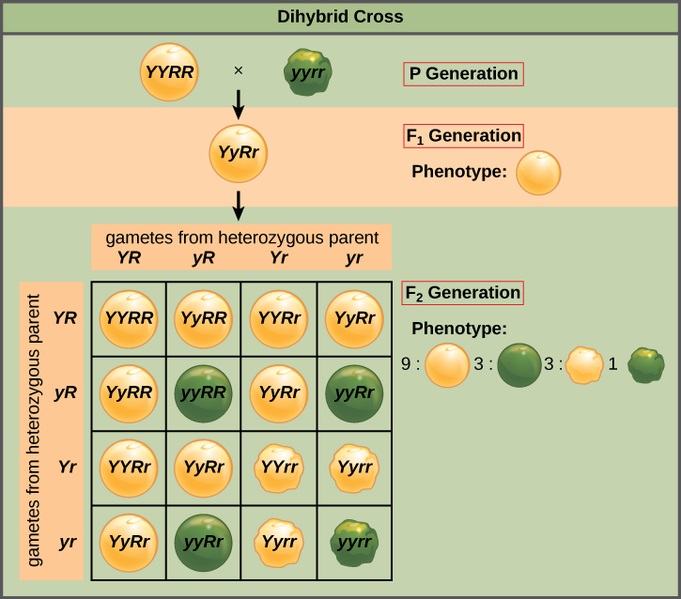
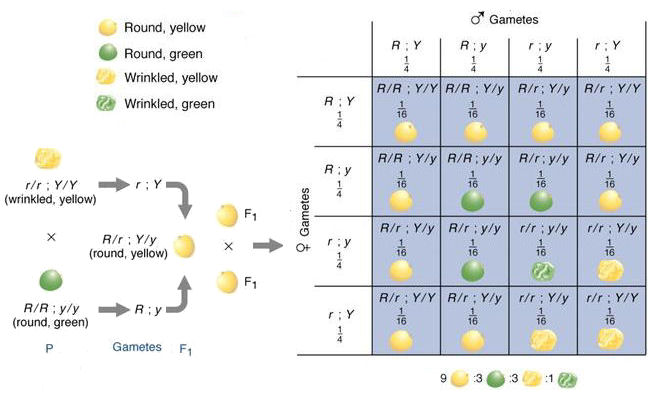
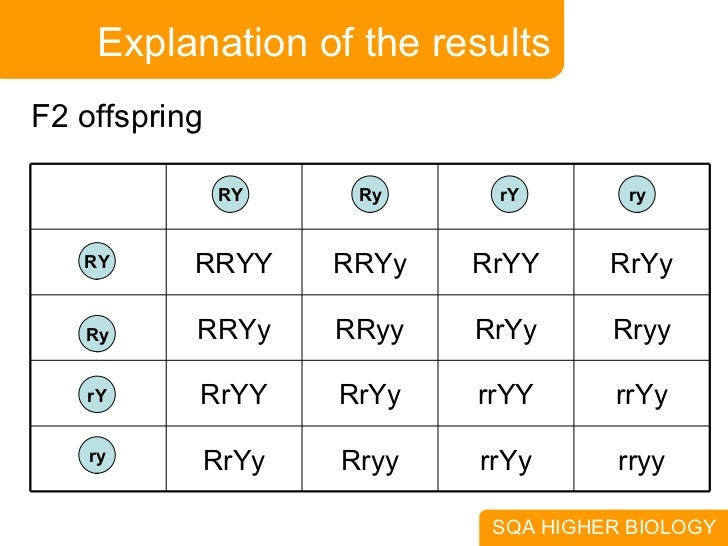
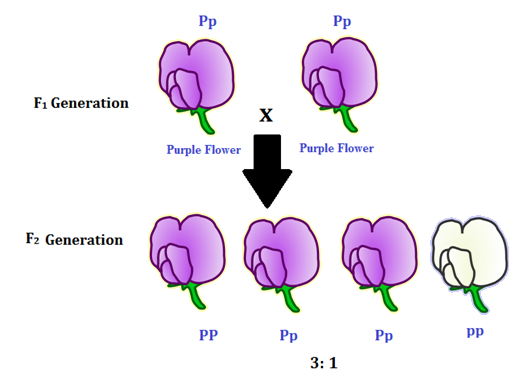
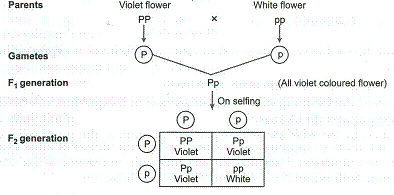
The round and. Self or cross f1 observe 9331 ratio note that the round green and wrinkled yellow phenotypic combinations observed in the parents did not stay together in the offspring. In the second cross the pollination was carried between the purple plants and the f2 results came as a ratio of 31 between purple and white plants. F2 offspring for unlinked alleles.
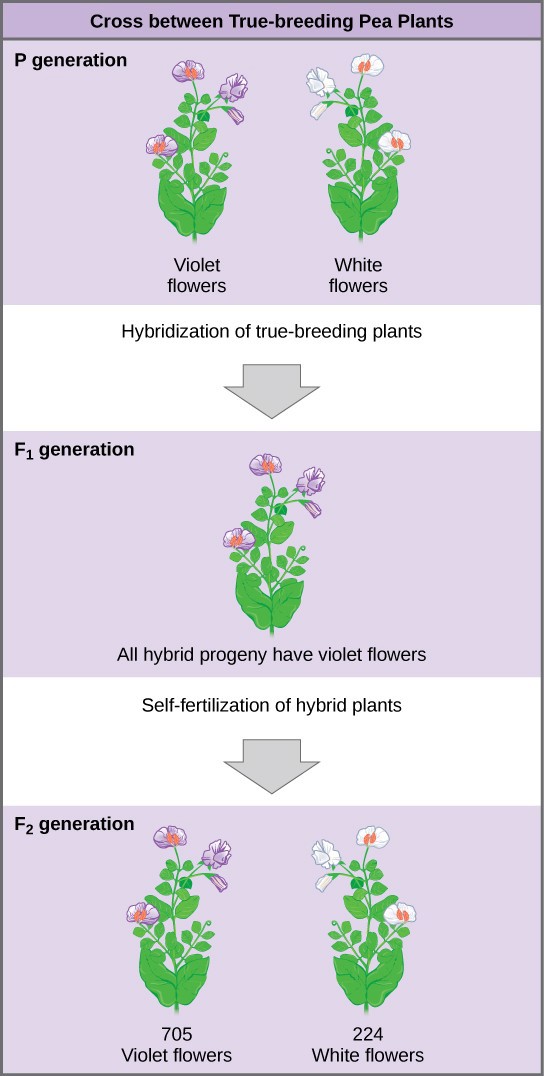
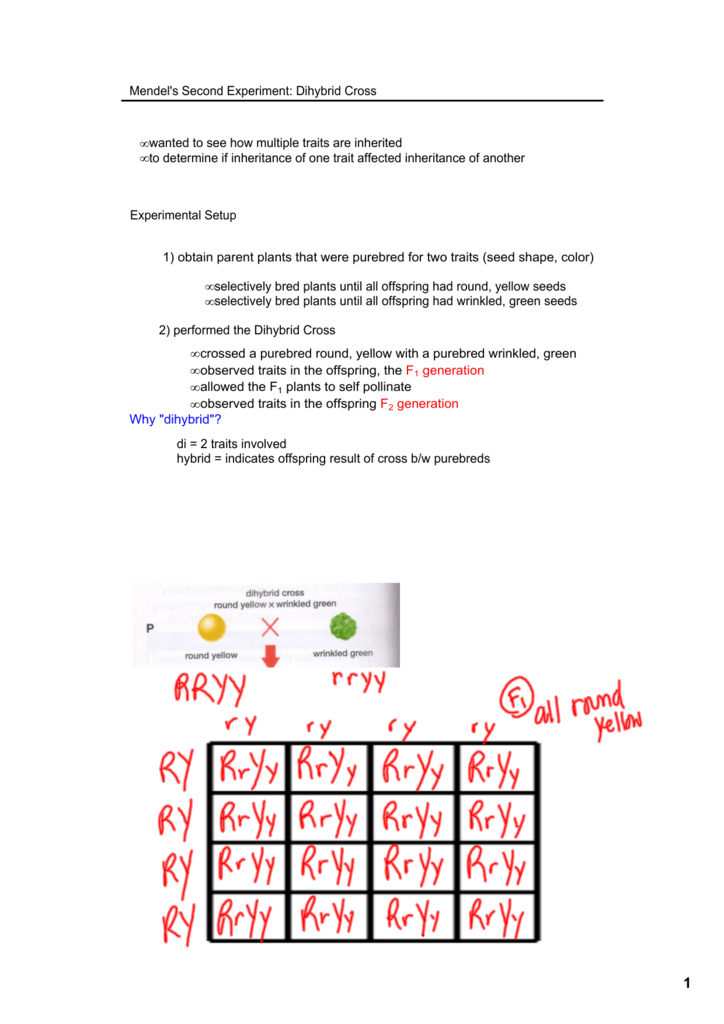
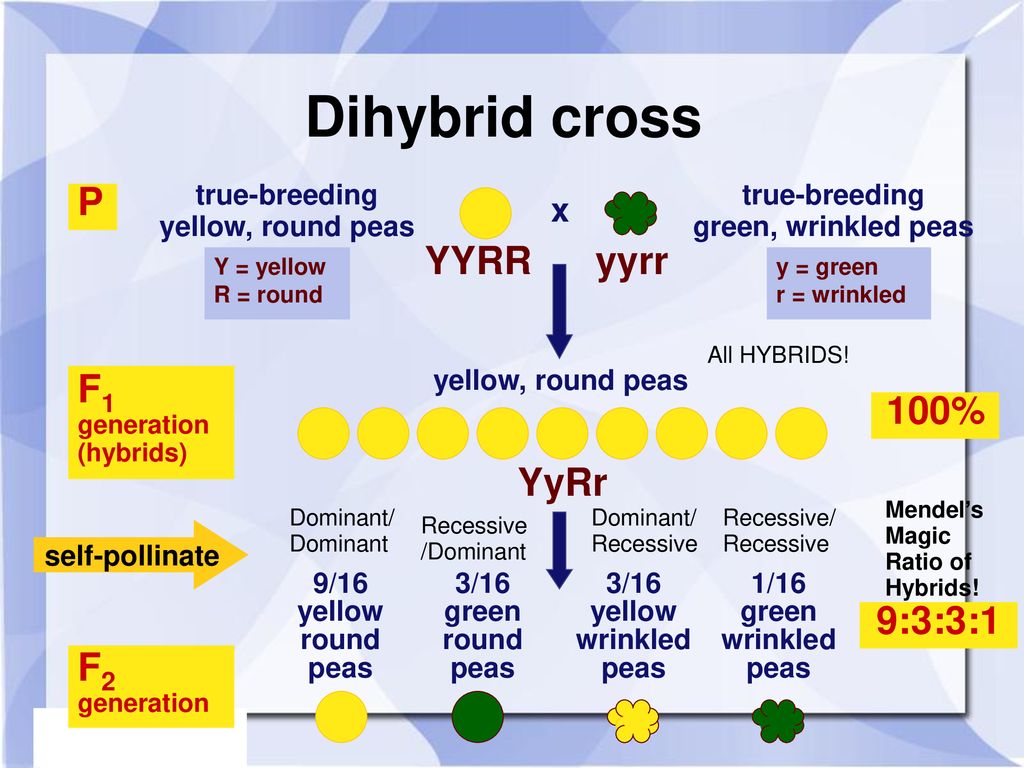
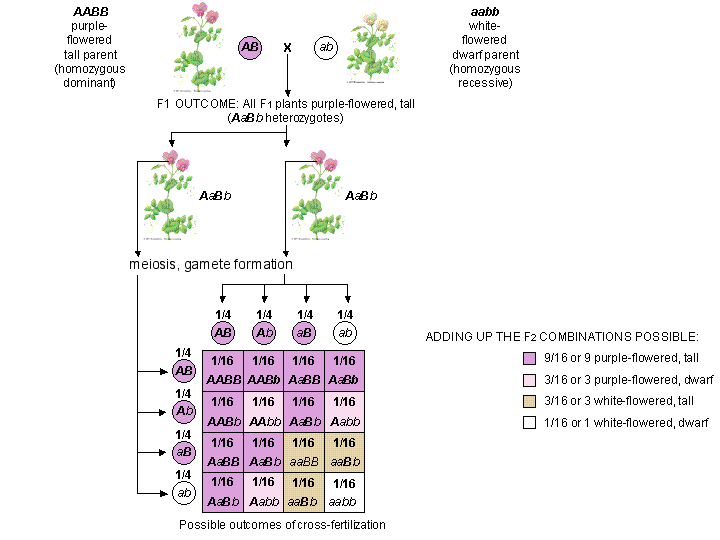
In the first generation f1 mendel carried out self pollination between pure lines of purple and white flowered plants and the new color of the new generation of flowers was completely purple. 916 tall plants with spherical seeds. Also a dihybrid cross is performed to describe the inheritance of two traits. The offsprings produced after the crosses in the f1 generation are all heterozygous for specific traits.
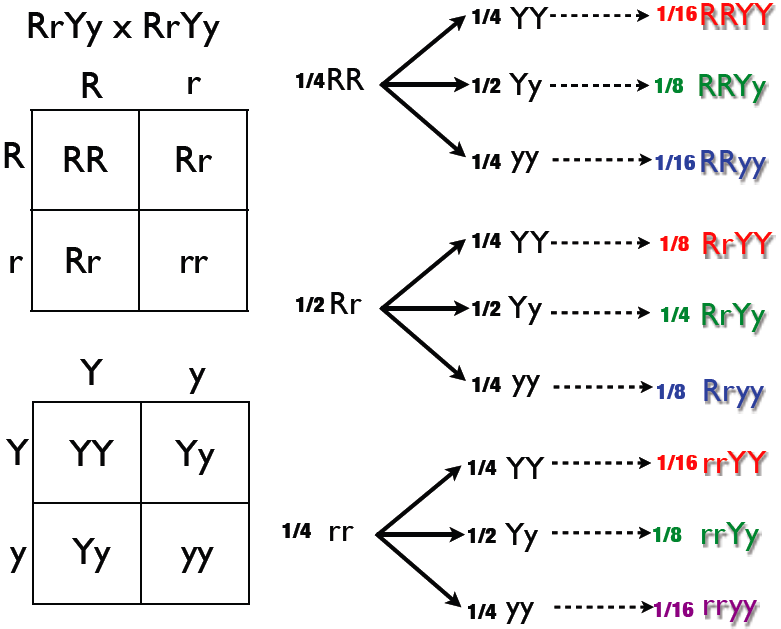
In f2 generation genotypic ratio will be 121. In the mendelian inheritance a dihybrid cross describes the second law or the law of independent assortment. If the two traits are unlinked and the f1 plants are self fertilized in the f2 generation plants we expect the 9331 ratio of offspring. All are heterozygous tall tt.
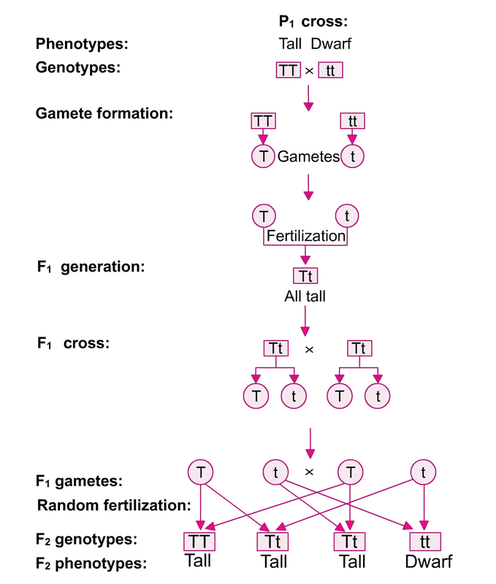
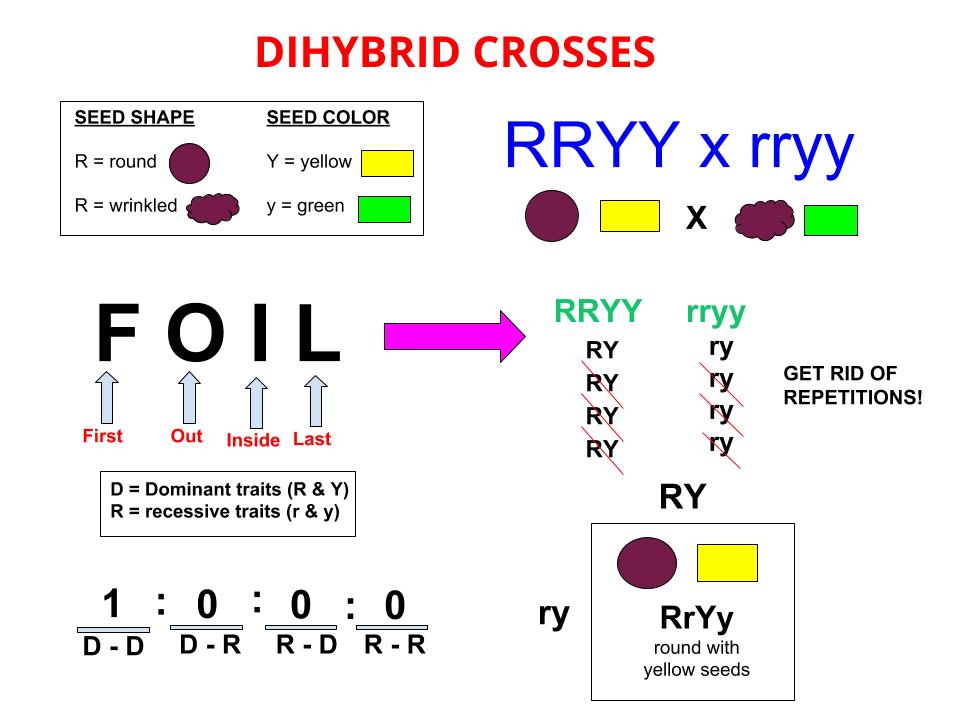
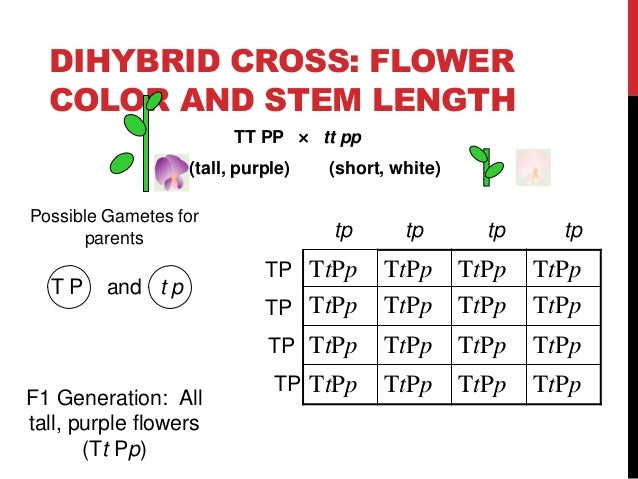
All f1 hybrids would be sstt. Let us take a cross between pure tall red plant and pure dwarf white pea plant. One parent carries homozygous dominant allele while the other one carries homozygous recessive allele. Given the principles revealed in a monohybrid cross mendel hypothesized that the result of two characters segregating simultaneously a dihybrid cross would be the product of their independent occurrence.
As in a dihybrid cross the f1 generation plants produced from a monohybrid cross are heterozygous and only the dominant phenotype is observed. The parents of the dihybrid cross are identically hybrid for two traits. In dihybrid cross two traits are considered together. About 34 exhibit the dominant phenotype and 14 exhibit the recessive phenotype.
Consider two characters seed color and seed shape.











































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dihybrid_cross_ratios-58ef9ddd5f9b582c4d02ceb2.jpg)

/dihybrid_cross_2-58ef84973df78cd3fc70a061.jpg)




/genetic-crosses-56e97ae13df78c5ba057ca68.jpg)